| Identification | More | [Name]
Benzil | [CAS]
134-81-6 | [Synonyms]
1,2-DIPHENYL-1,2 ETHANEDIONE
1,2-DIPHENYLETHANEDIONE
AURORA 14062
BENZIL
BIBENZOYL
DIBENZOYL
DIPHENYL-A B-DIKETONE
DIPHENYL DIKETONE
DIPHENYLETHANEDIONE
DIPHENYLGLYOXAL
'LGC' (2403)
'LGC' (2604)
1,2-Diphenylethane-1,2-dione
Benzil (1,2-diphenylethan-dion)
Diphenyl-alpha,beta-diketone
diphenyl-ethanedion
diphenyl-glyoxa
Ethanedione,diphenyl-
Glyoxal, diphenyl-
Wy 20910 | [EINECS(EC#)]
205-157-0 | [Molecular Formula]
C14H10O2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00003080 | [Molecular Weight]
210.23 | [MOL File]
134-81-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
yellow crystals or powder | [Melting point ]
94-95 °C(lit.)
| [Boiling point ]
346 °C | [density ]
1,521 g/cm3 | [vapor pressure ]
1 mm Hg ( 128.4 °C)
| [refractive index ]
1.5681 (estimate) | [Fp ]
346-348°C | [storage temp. ]
Store below +30°C. | [solubility ]
<0.5g/l | [form ]
Crystalline Powder | [color ]
White | [Stability:]
Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. | [Water Solubility ]
0.5 g/L (20 ºC) | [Detection Methods]
HPLC | [Merck ]
14,1078 | [BRN ]
608047 | [Dielectric constant]
13.0(94℃) | [InChIKey]
WURBFLDFSFBTLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [Uses]
Organic synthesis; insecticide. | [CAS DataBase Reference]
134-81-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
Ethanedione, diphenyl-(134-81-6) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
134-81-6(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S37/39:Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection . | [WGK Germany ]
2
| [RTECS ]
DD1925000
| [F ]
10 | [Hazard Note ]
Irritant | [TSCA ]
Yes | [HS Code ]
29143900 | [Toxicity]
LD50 orally in Rabbit: 2710 mg/kg |
| Raw materials And Preparation Products | Back Directory | [Raw materials]
Sodium cyanide-->Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate-->Copper (II) acetate monohydrate-->Benzoin | [Preparation Products]
(1R,2R)-(+)-1,2-Diphenylethylenediamine-->(1S,2S)-(-)-1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethanediamine-->Benzilic acid-->2,4,5-Triphenylimidazole-->DIPHENYLGLYOXIME-->Phenytoin sodium-->BENZIL DIHYDRAZONE-->Dipyrazino[2,3-f:2',3'-h]quinoxaline-->2-dihydroxyphosphinoyloxyacrylic acid-->3-(2-PYRIDYL)-5,6-DIPHENYL-1,2,4-TRIAZINE-->2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-4,5-diphenylimidazole |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Description]
Benzil (134-81-6) also known as 1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-dione is an organic compound with the molecular formula (C6H5CO)2. The compound belongs to the group of organic compounds known as stilbenes which contains a 1,2-diphenylethylene moiety. Benzyl is yellow in color and is one of the most common diketones.
| [Structure]
The most noticeable feature in Benzil’s structure is the long carbon-carbon bond of 1.54 Å, which shows there is no pi-bonding between the two carbonyl centers. Although the par of benzoyl groups are twisted with respect to the other with a dihedral angler of 117o, the PhCO are planar.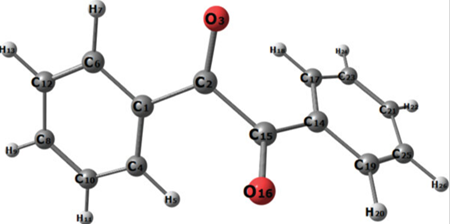 | [Preparation]
Benzyl is synthesized from benzoin, for instance with copper (II) acetate.
PhC(O)CH(OH)Ph + 2 Cu2+ → PhC(O)C(O)Ph + 2 H+ + 2 Cu+
| [Applications]
Benzil is utilized as an intermediate in pharmaceuticals and UV curing resin photosensitizer. Benzyl is mostly used in the free-radical curing of polymer networks. Benzyl is decomposed by ultraviolet radiation that generates free-radical species within the material, leading to the formation of cross-links. It is normally employed as a photoinitiator in polymer chemistry. In addition, Benzil is a potent inhibitor of human carboxylesterases, which are enzymes involved in the hydrolysis of many drugs used clinically as well as carboxylesters. It is also used in the synthesis of diketimines by reaction with amines. Benzyl is also used as an intermediate in the famous benil-benzilic acid arrangement. Further, it reacts with 1,3-diphenylacetone to get tetraphenylcyclopentadienone.
|
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
yellow crystals or powder | [Definition]
A reaction in which benzil (1,2- diphenylethan-1,2-dione) is treated with hydroxide and then with acid to give benzilic acid (2-hydroxy-2,2-diphenylethanoic acid):
C6H5.CO.CO.C6H5→
(C6H5)2C(OH).COOH
The reaction, which involves migration of a phenyl group (C6H5-) from one carbon atom to another, was the first rearrangement reaction to be described (by Justus von Liebig in 1828). | [Definition]
ChEBI: An alpha-diketone that is ethane-1,2-dione substituted by phenyl groups at positions 1 and 2 respectively. | [Reactions]
A reaction in which benzil (1,2- diphenylethan-1,2-dione) is treated with hydroxide and then with acid to give benzilic acid (2-hydroxy-2,2-diphenylethanoic acid):
C6H5.CO.CO.C6H5→
(C6H5)2C(OH).COOH
The reaction, which involves migration of a phenyl group (C6H5-) from one carbon atom to another, was the first rearrangement reaction to be described (by Justus von Liebig in 1828). | [benefits]
Benzil has potential applications in biological metabolism and clinical medicine. Benzil derivates exhibit radical scavenging and antibacterial and hypertensive, antiprotozoal, antiproliferative, and antimitotic activities. Benzil derivatives have versatile applications in the pharmaceutical industry, and various heterocyclic compounds such as triazine, quinoxaline, and imidazole can be synthesized from 1,2-diketones. It is also used as a nanocatalyst in the application of imidazole derivatives. Recently, it is reported that benzil derivatives acted as photosensitive agents and photoinitiators due to its antitumor activity[1].
| [Synthesis Reference(s)]
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 105, p. 7755, 1983 DOI: 10.1021/ja00364a054
Tetrahedron Letters, 30, p. 6267, 1989 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)93869-9 | [Safety]
Potential Acute Health Effects: Very hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant). Hazardous in case of ingestion, of inhalation.
The substance is toxic to lungs, mucous membranes. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Eye Contact: Check for and remove any contact lenses.
Fine dust dispersed in air may ignite. Dust can form an explosive mixture in air. Thermal decomposition can lead to release of irritating gases and vapors. Keep product and empty container away from heat and sources of ignition. | [Safety Profile]
Low toxicity by ingestion. An eyeirritant. Combustible. When heated to decomposition itemits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. | [Solubility in organics]
Soluble in ethanol (50 mg/ml), chloroform, ether, and ethyl acetate. Insoluble in water.
| [Purification Methods]
Crystallise benzil from *benzene after washing with alkali. (Crystallisation from EtOH did not free benzil from material reacting with alkali.) [Hine & Howarth J Am Chem Soc 80 2274 1958.] It has also been crystallised from CCl4, diethyl ether or EtOH [Inoue et al. J Chem Soc, Faraday Trans 1 82 523 1986]. [Beilstein 7 IV 2502.] | [References]
[1] N. Kanagathara. “Structural and Vibrational Investigation of Benzil-(1,2-Diphenylethane-1,2-Dione): Experimental and Theoretical Studies.” New Journal of Chemistry 3 1 (2022).
|
|
|