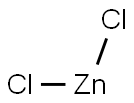?? ??
|
|
?? ?? ??
- ???
- 293 °C (lit.)
- ?? ?
- 732 °C (lit.)
- ??
- 1.01 g/mL at 20 °C
- ???
- 1 mm Hg ( 428 °C)
- ???
- 732°C
- ?? ??
- 2-8°C
- ???
- H2O: 4 M at 20 °C, ??, ??
- ?? ?? (pKa)
- pKa 6.06 (Uncertain)
- ??? ??
- ?? ??
- Specific Gravity
- 2.91
- ??
- ???
- ??????(pH)
- 5 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃)
- ??
- ?? ?? ??, ??
- ???
- 432g/100mL(25℃)
- ??
- Hygroscopic
- Merck
- 14,10132
- crystal system
- square
- Space group
- I42d
- Lattice constant
a/nm b/nm c/nm α/o β/o γ/o V/nm3 0.54 0.54 1.033 90 90 90 0.301
- ?? ??
- ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3; STEL 2 mg/m3
OSHA: TWA 1 mg/m3
NIOSH: IDLH 50 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3; STEL 2 mg/m3
- ???
- ???
- InChIKey
- JIAARYAFYJHUJI-UHFFFAOYSA-L
- CAS ??????
- 7646-85-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | Xi,N,C,F+,F,Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 36/37/38-50/53-34-22-51/53-67-66-19-12-11-40 | ||
| ????? | 26-36-61-60-45-36/37/39-16-36/37 | ||
| ????(UN No.) | UN 2924 3/PG 1 | ||
| OEB | C | ||
| OEL | TWA: 1 mg/m3, STEL: 2 mg/m3 | ||
| WGK ?? | 2 | ||
| RTECS ?? | TY2900000 | ||
| F ?????? | 3 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| ?? ?? | 3 | ||
| ???? | I | ||
| HS ?? | 28273600 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 7646-85-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | Inhalation of zinc chloride fumes can injure lungs and respiratory tract. Dusts or fumes also cause dermatitis, boils, conjunctivitis, and gastrointestinal tract upset (Lewis(Sr), R.J. 1996. Sax’s Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 9th ed. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold). LD50 oral (rat): 350mg/kg LCLO (inhalation): 1.960 g/m3/10 min |
||
| IDLA | 50 mg/m3 | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-35535 | ||
| ?????? ??? | 97-1-91 | ||
| ?? ? ???? | ????: ????; ???(??)????: ???? ?? ? ?? 25% ?? ??? ???. ??, ?? ??(Zinc carbonate) ? ?? ??(Zinc fulminate)? ?? |
?? ?? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
Zinc chloride is a white deliquescent salt. It forms acidic solutions in water and in polar organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, and ether. Anhydrous zinc chloride hydrolyzes with moisture to form hydrochloric acid. It also forms complex ions with water, ammonia, and some organic solvents. Zinc chloride reacts with sulphide to minimise release of H2S gas in waste treatment facilities. Zinc chloride 50% solution also serves as a high-quality mercerising agent for cotton. Zinc chloride is incompatible with strong oxidising agents, moisture, cyanides, sulphides, and potassium.??? ??
Zinc chloride is white/colorless crystalline granules.??? ??
White crystalline powder or granules; hygroscopic; density 2.907 g/cm3; melts at 290°C; vaporizes at 732°C; vapor pressure 1 torr at 428°C and 20 torrat 536°C; highly soluble in water, 432 g/100mL at 25°C; aqueous solution acidic in litmus test; also soluble in ethanol, glycerol, and acetone.??
Zinc chloride is used as a wood preservative and in fireproofing timber. Other uses are as a deodorant in disinfecting fluids; in dental cements; in electroplating; in etching metals and glass; as flux for soldering; as a mordant in printing and dyeing textiles; in making dry batteries; in denaturing alcohols; in vulcanizing rubber; in manufacturing parchment; in making artificial silk; in making activated carbon and cold-water glues; and in refining petroleum. Also, zinc chloride is used as a dehydrating and condensing agent in organic syntheses. In medicine it is used as an astringent and antiseptic.?? ??
Zinc chloride is prepared by the reaction of zinc oxide or zinc metal with dilute hydrochloric acid, followed by crystallization:ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
??
zinc chloride: A white crystalline compound, ZnCl2. The anhydrous salt, which is deliquescent, can be made by the action of hydrogen chloride gas on hot zinc; r.d. 2.9; m.p. 283°C; b.p. 732°C. It has a relatively low melting point and sublimes easily, indicating that it is a molecular compound rather than ionic. Various hydrates also exist. Zinc chloride is used as a catalyst, dehydrating agent, and Ûux for hard solder. It was once known as butter of zinc.?? ??
Zinc chloride is a colorless liquid. Zinc chloride is mildly corrosive to metals. Zinc chloride causes burns to eyes, skin and mucous membranes.??? ?? ??
When dissolved in water, Zinc chloride is a strong acid. [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 964]?? ???
Acidic salts, such as ZINC CHLORIDE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions.???
Inhalation of zinc chloride fumes can injure lungs and respiratory tract. Dusts or fumes also cause dermatitis, boils, conjunctivitis, and gastrointestinal tract upset (Lewis(Sr), R.J. 1996. Sax’s Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 9th ed. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold). LD50 oral (rat): 350mg/kg LCLO (inhalation): 1.960 g/m3/10 min.????
Exposures to zinc chloride cause adverse health effects and poisoning. On contact with the skin, zinc chloride causes skin burns and ulcerations, redness, eyes develop pain and blurred vision, and any splashes from solutions may cause eye damage. It is extremely destructive to the tissues of the mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. The symptoms of toxicity include, but are not limited to, burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea and vomiting, and irritation or corrosion to the gastrointestinal tract with abdominal pain. After repeated exposures of zinc chloride through skin contact, occupational workers develop varying degrees of skin problems, such as dermatitis and skin ulcerations. Repeated inhalation of zinc chloride causes occupational asthma among workers????
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by inhalation: pulm- onary changes. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes, Exposure to ZnCl2 fumes or dusts can cause dermatitis, boils, conjunctivitis, gastrointestinal tract upsets. The fumes are highly toxic. Incompatible with potassium. Mixtures of the powdered chloride and powdered zinc are flammable. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cland ZnO. See also ZINC COMPOUNDS and CHLORIDES.??? ??
Zinc chloride is used in iron galvanizing; as a wood preservative; for dry battery cells; as a soldering flux; in textile finishing; in vulcanized fiber; reclaiming rubber; in oil and gas well operations; oil refining; manufacturing of parchment paper; in dyes; activated carbon; in chemical synthesis; in adhesives; dentists’ cement; deodorants, disinfecting and embalming solutions; and taxidermy. It is also produced by military screeningsmoke.?? ??
UN2331 Zinc chloride, anhydrous, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1840 Zinc chloride, solution, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.Purification Methods
The anhydrous material can be sublimed under a stream of dry HCl, followed by heating to 400o in a stream of dry N2. It sublimes at high vacuum. Also purify it by refluxing (50g) in dioxane (400mL) with 5g zinc dust, filtering hot and cooling to precipitate ZnCl2. Crystallise it from dioxane and store it in a desiccator over P2O5. It has also been dried by refluxing in thionyl chloride. [Weberg et al. J Am Chem Soc 108 6242 1986.] Hygroscopic: minimal exposure to the atmosphere is necessary. [Wagenknecht & Juza Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1070 1965.]? ???
Aqueous solutions are strongly acidic. Incompatible with bases and potassium. Incompatible with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Corrosive to metals.??? ??
Dump in water; add soda ash and stir, then neutralize and flush to sewer with water. Alternatively, zinc chloride may be recovered from spent catalysts and used in acrylic fiber spinning solutions.?? ??
Exposures to zinc chloride are dangerous, corrosive, and cause burns to any area of contact. Harmful if swallowed or inhaled. Affects the cardiovascular system.?? ?? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??
2-Aminonicotinic acid
1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridine,3-methyl-(9CI)
2-Amino-3-cyanopyridine
4-?????????
?? ????
2-???-3-??-2-??-4H-??-g-???
4-????????
4, 4^<'^>-dimethylamino diphenyl ketone
polysulfone anion exchange membrane
Exifone
7-?????-3-?????
????(4-???)
??????
2-???-5-???-2'-????????
Anion exchange resin,strong basic styrene
2-(1-??????)??????
????
3-Amino-2-naphthoic acid
fluorescent whitening agent SWN
???151
?????
????????????
2-???-5-????????
4-N-DECYLANILINE
6-??-??-??-???
4-(?????)???????
o-Cresolphthalein
1,1-??????
1-??????
?????
??????G
styrene type polyethylene homogeneous anion exchange membrane
???(???)
4-(?????)-3,5-???????
5-???2-???
6-METHOXY-4-METHYLQUINOLINE
???-???????
2-(4-?????)??
2-???????
1H-PYRAZOLO[3,4-B]PYRIDINE
?? ?? ?? ??
???( 622)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qingdao Trust Agri Chemical Co.,Ltd | +8613573296305 |
aroma@qdtrustagri.com | China | 301 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34563 | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 |
sales@aladdinsci.com | United States | 52924 | 58 |
| Hengshui Haoye Co.,Ltd. | +86-2102300 +86-18632882519 |
hy@haoyecom.cn | China | 300 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 |
abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8810 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12835 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5889 | 58 |
| Hebei Kingfiner Technology Development Co.Ltd | +86-15532196582 +86-15373005021 |
lisa@kingfinertech.com | China | 3010 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21634 | 55 |
| Hangzhou FandaChem Co.,Ltd. | +8615858145714 |
FandaChem@Gmail.com | China | 9095 | 55 |