?? ????
|
|
?? ???? ??
- ???
- 170-195 °C (decomp)
- ?? ?
- 0.100 °C
- ??
- 1.4 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- Tg
- 85
- ???
- n 1.54
- ???
- 736
- ?? ??
- 2-8°C
- ??? ??
- ??
- ??
- ???? ?????
- Specific Gravity
- 1.385
- Dielectric constant
- 3.4(Ambient)
- ???
- ????. ?? ??. ?? ???? ???? ????.
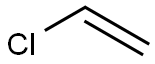
- InChI
- InChI=1S/C2H3Cl/c1-2-3/h2H,1H2
- InChIKey
- BZHJMEDXRYGGRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- SMILES
- C=CCl
- CAS ??????
- 9002-86-2(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 3 (Vol. 19, Sup 7) 1987
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 36/37/38 | ||
| ????? | 26-36/37-61 | ||
| WGK ?? | 3 | ||
| RTECS ?? | KV0350000 | ||
| TSCA | TSCA listed | ||
| HS ?? | 3904220000 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 9002-86-2(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-29063 |
| ????(GHS): |

|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ?: | Warning | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ??·?? ??: |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ??????: |
|
?? ???? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
PVC? ??? ?? ?????? ??? ????? ?????? ???? ??? ??? ??? ????? ????. ??? ??? ???? ?? ?? ?? ? ??? ??? ????? ????? ??? ?? ????. ?? ??? ???? ????? ??? ?? ????? ?????.??
???? ??? ???? ????? ??? ???, ?? ?? ??, ????? ????, ? ???? ???.??
?? ??·????·???·???·?????· ???? ????.??
Polyvinyl chloride, commonly abbreviated PVC, is the thirdmost widely produced plastic, after polyethylene and polypropylene. PVC is used in construction because it is more effective than traditional materials such as copper, iron or wood in pipe and profile applications. It can be made softer and more flexible by the addition of plasticizers, the most widely used being phthalates. In this form, it is also used in clothing and upholstery, electrical cable insulation, inflatable products and many applications in which it replaces rubber.
Pure polyvinyl chloride is a white, brittle solid. It is insoluble in alcohol, but slightly soluble in tetrahydrofuran.
??? ??
Peroxide- or thiadiazole-cured CPE exhibits good thermal stability up to 150°C and is much more oil resistant than nonpolar elastomers such as natural rubber or EPDFM.Commercial products are soft when the chlorine content is 28–38%. At more than 45% chlorine content, the material resembles polyvinyl chloride. Higher-molecular-weight polyethylene yields a chlorinated polyethylene that has both high viscosity and tensile strength.
??? ??
PVC is a thermoplastic polymer. Its properties for PVC are usually categorized based on rigid and flexible PVCs.Mechanical properties
PVC has high hardness and mechanical properties. The mechanical properties enhance with the molecular weight increasing, but decrease with the temperature increasing. The mechanical properties of rigid PVC (uPVC) is very good, the elastic modulus can reach to 1500-3,000 MPa. The soft PVC (Flexible PVC) elastic is 1.5- 15 MPa. However, elongation at break is up to 200% -450%. PVC friction is ordinary, the static friction factor is 0.4-0.5, the dynamic friction factor is 0.23.
Thermal properties
The heat stability of PVC is very poor, when the temperature reaches 140 °C PVC starts to decompose. Its melting temperature is 160 °C. The linear expansion coefficient of the PVC is small and has flame retardancy, the oxidation index is up to 45 or more. Therefore, the addition of a heat stabilizer during the process is necessary in order to ensure the product's properties.
Electrical properties
PVC is a polymer with good insulation properties but because of its higher polar nature the electrical insulating property is inferior to non polar polymers such as poly ethylene and poly propylene.
??
Polyvinyl Chloride could be useful for the removal epoxidation catalyst from epoxidized unsaturated oils.?? ??
In chlorinating polyethylene, chlorine atoms substitute for hydrogen atoms of the polyethylene chain in both crystalline and amorphous regions. The most common chlorination method is treating polyethylene powder in an aqueous suspension that contains hydrochloric acid and a free-radical initiator with chlorine gas. After the desired level of chlorination is obtained, the CPE is water washed and dried, and an antiblocking agent is then added.??
ChEBI: A polymer composed of repeating chloroethyl units.?? ??
Poly(vinyl chloride) [PVC] is a polymer which is mostly prepared from vinyl chloride monomer. In most cases PVC is mixed with heat stabilizers, lubricants, plasticizers, fillers, and other additives.???
Decomposes at 148C, evolving toxic fumes of hydrogen chloride. Pneumoconiosis, lower respi- ratory tract irritant, and pulmonary function effects. Questionable carcinogen.?? ??
Among the vinyl polymers and copolymers, the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) thermoplastics are the most commercially significant. With various plasticizers, fillers, stabilizers, lubricants, and impact modifiers, PVC is compounded to be flexible or rigid, opaque or transparent, to have high or low modulus, or to have any of a wide spectrum of properties or processing characteristics.PVC resin can also be chlorinated (CPVC) and it can be alloyed with other polymers such as ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), acrylic, polyurethane, and nitrile rubber to improve impact resistance, tear strength, resilience, heat-deflection temperature, or processibility.
PVC is a hard, flame-resistant, and chemicalresistant thermoplastic resin. The resin is available in the powder form, as a latex, or in the form of plastisol. PVC resin, pigments, and stabilizers are milled into plasticizers to form a viscous coating material (plastisol) that polymerizes into a tough elastic film when heated. Plastisols are used extensively for coating glass bottles and glass fabrics. The dispersion types of resins are used in flexible molding compounds. Such formulations consist of a vinyl paste resin, a suitable plasticizer such as dioctyl phthalate, and a stabilizer (usually a compound of lead). Flexible molds are widely applied to plaster casting and encapsulation of electronic circuits with epoxy resins.
Safety Profile
Chronic inhalation of dusts can cause pulmonary damage, blood effects, abnormal liver function. “Meat wrapper’s asthma” has resulted from the cutting of PVC films with a hot knife. Can cause allergic dermatitis. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Reacts violently with F2. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cland phosgene.?? ???? ?? ?? ? ???
???
DISPERSING AGENTS
????(???)
2,2' ???2,4-???-4-?????????
??(??)
????
METALLURGICAL COKE
???? ??? 1500
??
????
??
?????????
???
?? ??
Master-batches
polyacetylene (I)
conductive film
polymer electret
PVDF thermoelectric film
Polyvinyl chloride profiled material
????????
L-(-)-??
???? ?????
C.I. ?? ?? 13
2-Hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde
conductive polyvinyl chloride plastics
Polyvinyl chloride pipe material
polypyrrole composite film
polyethylene conductive plastics
????(Ⅰ)
?? ???? ?? ??
???( 327)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PT CHEM GROUP LIMITED | +86-85511178; +86-85511178; |
peter68@ptchemgroup.com | China | 35425 | 58 |
| Jinan Chengyuan Chemical Co. , Ltd. | +86-0531-88274992 +8615552568189 |
2408152070@qq.com | China | 10 | 58 |
| Auschemicals Pty Ltd | +61406202619 |
info@auschemicals.com | Australia | 426 | 58 |
| SHANGHAI KEAN TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. | +8613817748580 |
cooperation@kean-chem.com | China | 40066 | 58 |
| Wuxi High Mountain Hi-tech Development Co.,Ltd. | +86-86-0510-85881806 +8613357920996 |
wuxihighmountain@gmail.com | China | 30 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12835 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531190177 |
peter@yan-xi.com | China | 5857 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5889 | 58 |
| Hebei Dangtong Import and export Co LTD | +86-13910575315 +86-13910575315 |
admin@hbdangtong.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8617732866630 |
bess@weibangbio.com | China | 18151 | 58 |