Hippursure Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Verschlucken.
R37/38:Reizt die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R41:Gefahr ernster Augensch?den.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S39:Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
S22:Staub nicht einatmen.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
C9H9NO3; N-Benzoylaminoessigsäure, Benzoylglycin, Benzoylglycocoll. Farblose Kristalle mit schwachem Eigengeruch. Kommt im Körper vor.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Brennbarer Feststoff.
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
nicht erforderlich.
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Trocken aufnehmen. Der Entsorgung zuführen. Reste mit viel Wasser wegspülen.
Kohlendioxid, Wasser, Pulver, Schaum.
Brennbar. Im Brandfall Entstehung gefährlicher Dämpfe (NO
x) möglich.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Mit Wasser abspülen.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mit Wasser mindestens 10 Minuten bei geöffnetem Lidspalt spülen.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft
Nach Verschlucken: Bei Verschlucken größerer Mengen und Unwohlsein Arzt konsultieren.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung entfernen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Laborchemikalienabfälle.
Chemische Eigenschaften
White crystalline powder
Verwenden
N-Benzoylglycine also known as Hippuric Acid is the glycine conjugate of benzoic acid commonly found in ruminant urine. It is synthesized in the liver and its production is greatly increased following consuption of benzoic acid. In itself it does not have a direct biological function, however p-hydroxy-hippurica acid can be used as an inhibitor of Ca2+ ATPase.
synthetische
Preparation of Hippuric acid from Glycine.
Principle: The hydroxy and amino functions can be easily benzoylated using Benzoyl chloride in aqueous alkaline conditions. This reaction is known as Schotten-Baumann reaction.
Reaction:
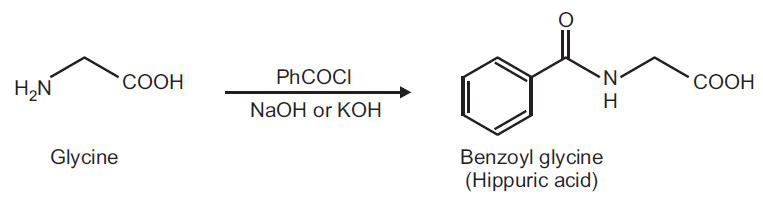
Procedure: Dissolve 0.5 g of glycine in 5 ml of 10% NaOH solution in a 25 ml conical flask. Add 0.9 ml of benzoyl chloride in five portions to the solution. Stopper the flask and shake vigorously after each addition until all the benzoyl chloride is reacted. Transfer the solution to a beaker and add few grams of ice and add conc. HCl slowly with stirring until the solution is acidic to litmus paper. Filter the crystalline precipitate of the product on a Buchner funnel, wash with cold water and drain well. Place the solid in a conical flask with 10 ml CCl4 and boil gently for 10 min. Allow the mixture to cool slightly, filter under gentle suction and wash with 10-20 ml CCl4. Record the practical yield and re-crystallize it.
Re-crystallization: Dissolve the crude product from boiling water (5 ml), with addition of decolorizing charcoal if necessary, filter the hot solution and cool the filtrate. The crystals of the product separate out. Filter, dry and record the melting point and TLC [using Butanal : acetic acid: water (4 : 1 : 1) as solvent or CHCl3:methanol (9 : 1) or toluene].
Definition
ChEBI: An N-acylglycine in which the acyl group is specified as benzoyl.
l?uterung methode
Crystallise the acid from boiling H2O. Dry it over P2O5. Also purify it by dissolving 135-140g in 2L of boiling H2O, filtering through a steam-heated funnel and allowing to crystallise at ~20o (yield 115-122g first crop, m 186-187o). [Ingersoll & Babcock Org Synth Coll Vol II 328 1943, Beilstein 9 225, I 100.]
Hippursure Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

