Benzoylchlorid Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
RAUCHENDE FARBLOSE FLüSSIGKEIT MIT STECHENDEM GERUCH.
PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Die D?mpfe sind schwerer als Luft.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV: 0.5 ppm (als STEL, ceiling) Krebskategorie A4 (nicht klassifizierbar als krebserzeugend für den Menschen); (ACGIH 2008).
MAK: Krebserzeugend Kategorie 3B; (DFG 2008).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation und durch Verschlucken.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfung bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine gesundheitssch?dliche Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch schnell erreicht werden.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Tr?nenreizend. Die Substanz ver?tzt die Augen, die Haut und die Atemwege. ?tzend beim Verschlucken. Inhalation des Dampfes oder Aerosols kann zu Lungen?dem führen (s.Anm.).
Synthese
In einem 250 ml Rundkolben legt man 50 g trockene Benzoes?ure und 60 g (37 ml) frisch destilliertes Thionylchlorid vor und erhitzt die Mischung etwa für eine Stunde (bis die Gasentwicklung aufh?rt) unter Rühren auf einem siedenden Wasserbad (die Apparatur mit einem Trockenrohr gegen Luftfeuchtigkeit verschlie?en!). Nachdem die Reaktion beendet ist, l?sst man den Kolben abkühlen und destilliert dann das Reaktionsgemisch, wobei man den Kolben über einem Drahtnetz oder besser einem Luftbad, vorsichtig erhitzt (Trockenrohr!). Zuerst destilliert ein wenig nicht umgesetztes Thionylchlorid bei 70-80 °C über, dann steigt die Temperatur rapide an, und bei 194-198 °C geht das Produkt über. In dem Kolben bleibt meist nur ein geringer Rückstand, bestehend aus Benzoes?ureanhydrid (Sdp. 360 °C; Smp. 42 °C) zurück, welches sich aufgrund der dehydratisierenden Wirkung von Thionylchlorid gebildet hat (sowie einige braun-schwarze Zersetzungsprodukte). Man erh?lt ca. 60 g reines Benzoylchlorid, eine farblose, stark lichtbrechende Flüssigkeit, die an feuchter Luft raucht und zu Tr?nen reizt.

Synthese
In einem 250 ml Rundkolben legt man 50 g trockene Benzoes?ure und 60 g (37 ml) frisch destilliertes Thionylchlorid vor und erhitzt die Mischung etwa für eine Stunde (bis die Gasentwicklung aufh?rt) unter Rühren auf einem siedenden Wasserbad (die Apparatur mit einem Trockenrohr gegen Luftfeuchtigkeit verschlie?en!). Nachdem die Reaktion beendet ist, l?sst man den Kolben abkühlen und destilliert dann das Reaktionsgemisch, wobei man den Kolben über einem Drahtnetz oder besser einem Luftbad, vorsichtig erhitzt (Trockenrohr!). Zuerst destilliert ein wenig nicht umgesetztes Thionylchlorid bei 70-80 °C über, dann steigt die Temperatur rapide an, und bei 194-198 °C geht das Produkt über. In dem Kolben bleibt meist nur ein geringer Rückstand, bestehend aus Benzoes?ureanhydrid (Sdp. 360 °C; Smp. 42 °C) zurück, welches sich aufgrund der dehydratisierenden Wirkung von Thionylchlorid gebildet hat (sowie einige braun-schwarze Zersetzungsprodukte). Man erh?lt ca. 60 g reines Benzoylchlorid, eine farblose, stark lichtbrechende Flüssigkeit, die an feuchter Luft raucht und zu Tr?nen reizt.
LECKAGE
Ausgelaufene Flüssigkeit m?glichst in abdichtbaren Beh?ltern sammeln. Reste mit Sand oder inertem Absorptionsmittel aufnehmen und an einen sicheren Ort bringen. NICHT in die Kanalisation spülen. Chemikalienschutzanzug mit umgebungsluftunabh?ngigem Atemschutzger?t.
Quelle
Vogel, Arthur I. - A Text-Book of Practical Organic Chemistry, 3. Auflage, Longman, London 1974
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R34:Verursacht Ver?tzungen.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S36/37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung,Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
Aussehen Eigenschaften
C7H5ClO; Benzoesäurechlorid, alpha-Chlorbenzaldehyd, Chlorbenzoyl; farblose, an feuchter Luft schwach rauchende Flüssigkeit mit stechendem, zu Tränen reizendem, unangenehmem Geruch.
Gefahren für Mensch und Umwelt
Korrosiv gegenüber Metallen. Benzoylchlorid reagiert heftig mit Wasser unter Bildung von Salzsäure und Bezoesäure. Mit Alkali- und Erdalkalimetallen, sowie mit Aminen und Dimethylsulfoxid reagiert es sehr stürmisch. Mit Alkoholen entstehen neben HCl die Benzoesäureester. Bei Kontakt mit starken Oxidationsmitteln kann Entzündung eintreten.
Brennbar. Die Dämpfe sind schwerer als Luft. Im Brandfall können HCl und Chlor entstehen.
Benzoylchlorid ruft nach Einatmen starke Reizung der Atemwege hervor, die infolge der nur langsam ablaufenden Hydrolyse auch tiefere Bereiche betrifft und nach längerer Dauer zum Lungenödem führen kann.
Von der Flüssigkeit betroffene Haut bzw. Schleimhaut schmerzen sehr stark und bilden typische Ätzschorfe. Erblindungsgefahr!
Ein Verschlucken ist infolge der sehr starken Geruchswarnung kaum denkbar, kann jedoch zu Perforation von Speiseröhre und Magen führen.
Schutzma?nahmen und Verhaltensregeln
Im Abzug arbeiten.
Schutzhandschuhe aus Latex oder Neopren (nur als kurzzeitiger Spritzschutz).
Verhalten im Gefahrfall
Mit flüssigkeitsbindendem Material (z.B. Rench-Rapid) aufnehmen und als Sondermüll entsorgen.
CO
2, Schaum, Pulver.
Erste Hilfe
Nach Hautkontakt: Bei Berührung mit der Haut sofort mit viel Wasser und Seife abwaschen. Abtupfen mit Polyethylenglycol 400.
Nach Augenkontakt: Mindestens 15 Minuten bei geöffnetem Lidspalt mit viel Wasser spülen. Augenarzt konsultieren.
Nach Einatmen: Frischluft. Arzt hinzuziehen.
Nach Verschlucken: Viel Wasser trinken lassen, Erbrechen vermeiden (Perforationsgefahr!). Sofort Arzt hinzuziehen. Keine Neutralisationsversuche.
Nach Kleidungskontakt: Kontaminierte Kleidung sofort ausziehen.
Ersthelfer: siehe gesonderten Anschlag
Sachgerechte Entsorgung
Falls Recycling nicht möglich, darf die Substanz nicht mit Hausmüll entsorgt werden. Substanz darf nicht in die Kanalisation gelangen. Reste zur Sonderabfallverbrennung geben. Auskunft: Hr. Riepl, Tel.: 8884711 oder Hr. Uhl, Tel.: 2015557.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Benzoyl chloride is a colorless to slight brown liquid with a strong, penetrating odor; vapor causes tears. Soluble in ether and carbon disulfide; decomposes in water. Combustible. It is a liquid acyl chloride used as a benzoylating agent.
Vorbereitung Methode
Benzoyl chloride can be prepared from benzoic acid by reaction with PCl5 or SOCl2, from benzaldehyde by treatment with POCl3 or SO2 Cl2, from benzotrichloride by partial hydrolysis in the presence of H2SO4 or FeCl3, from benzal chloride by treatment with oxygen in a radical source, and from several other miscellaneous reactions. Benzoyl chloride can be reduced to benzaldehyde, oxidized to benzoyl peroxide, chlorinated to chlorobenzoyl chloride and sulfonated to m-sulfobenzoic acid. It will undergo various reactions with organic reagents. For example, it will add across an unsaturated (alkene or alkyne) bond in the presence of a catalyst to give the phenylchloroketone:
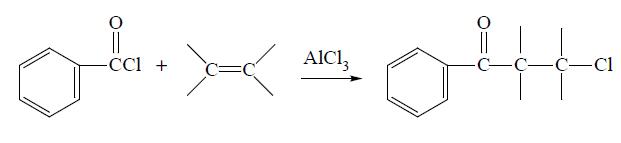
Definition
ChEBI: Benzoyl chloride is an acyl chloride consisting of benzene in which a hydrogen is replaced by an acyl chloride group. It is an important chemical intermediate for the manufacture of other chemicals, dyes, perfumes, herbicides and pharmaceuticals. It has a role as a carcinogenic agent. It is an acyl chloride and a member of benzenes. It is functionally related to a benzoic acid.?
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Benzoyl chloride appears as a colorless fuming liquid with a pungent odor. Flash point 162 °F. Lachrymator, irritating to skin and eyes. Corrosive to metals and tissue. Density 10.2 lb / gal. Used in medicine and in the manufacture of other chemicals.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
Benzoyl chloride reacts violently with protic solvents such as alcohols, with amines and amides (for example dimethylformamide [Bretherick 1979 p. 6] ) and with inorganic bases. Causes the violent decomposition of dimethyl sulfoxide [Chem. Eng. News 35(9): 87 1957]. May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291]. Friedel-Crafts acylation of naphthalene using Benzoyl chloride, catalyzed by AlCl3, must be conducted above the melting point of the mixture, or the reaction may be violent [Clar, E. et al., Tetrahedron, 1974, 30, 3296].
Hazard
Highly toxic. Strong irritant to skin, eyes,
and mucous membranes, and via ingestion, inhala-
tion. Upper respiratory tract irritant. Probable car-
cinogen.
Health Hazard
INHALATION: may irritate eyes, nose and throat. INGESTION: causes acute discomfort. SKIN: causes irritation and burning.
Chemische Reaktivit?t
Reactivity with Water Slow reaction with water to produce hydrochloric acid fumes. The reaction is more rapid with steam; Reactivity with Common Materials: Slow corrosion of metals but no immediate danger; Stability During Transport: Not pertinent; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Soda ash and water, lime; Polymerization: Does not occur; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Mechanism of action
Indicative of its high reactivity (relative to alkyl chlorides), benzyl chloride reacts with water in a hydrolysis reaction to form benzyl alcohol and hydrochloric acid. In contact with mucous membranes, hydrolysis produces hydrochloric acid. Thus, benzyl chloride is a lachrymator and has been used in chemical warfare. Theoretically, for every mole of benzyl chloride reacted, one mole of hydrochloric acid is released[1].
Toxikologie
Benzoyl chloride is of low acute oral toxicity in
rats (LD
50 2529 mg/kg). It is more toxic by
inhalation (LC
50 230 ppm, 4 h in male rats and
314 ppm, 4 h in female rats). The compound is
irritating to skin, mucous membranes, eyes, and
the respiratory tract.
When benzoyl chloride or solutions of benzoyl chloride in benzene were applied to the skin of
mice for up to 10 months irritation and keratinization resulted, and to some extent, ulceration
and necrosis of the skin occurred. A few tumors
(skin, lung) were observed in those mice.
There is no clear evidence that benzoyl chloride
is mutagenic.
For humans, benzoyl chloride is classified as a
lachrymator. It is irritating to the skin, eyes, and
mucous membranes. The available data are
inadequate to evaluate the carcinogenic potential
of benzoyl chloride to humans.
m?gliche Exposition
Benzoyl chloride is used as a chemical
intermediate; in organic synthesis; to produce other chemicals,
dyes, perfumes, herbicides, and medicines.
Versand/Shipping
UN 1736 Benzoylchloride, Hazard class: 8;
Labels: 8—Corrosive material.
l?uterung methode
A solution of benzoyl chloride (300mL) in *C6H6 (200mL) is washed with two 100mL portions of cold 5% NaHCO3 solution, separated, dried with CaCl2 and distilled [Oakwood & Weisgerber Org Synth III 113 1955]. Repeated fractional distillation at 4mm Hg through a glass helices-packed column (avoiding porous porcelain or silicon-carbide boiling chips, and hydrocarbon or silicon greases on the ground joints) gave benzoyl chloride that did not darken on addition of AlCl3. Further purification is achieved by adding 3 mole% each of AlCl3 and toluene, standing overnight, and distilling off the benzoyl chloride at 1-2mm [Brown & Jenzen J Am Chem Soc 80 2291 1958]. Refluxing for 2hours with an equal weight of thionyl chloride before distillation has also been used. [Beilstein 9 IV 721.] Strong IRRITANT. Use in a fume cupboard.
Inkompatibilit?ten
May form explosive mixture with air.
Contact with heat, hot surfaces, and flames causes decomposition,
forming phosgene and hydrogen chloride. Water
contact may be violent; forms hydrochloric acid. Reactions
with amines, alcohols, alkali metals, dimethyl sulfoxide,
strong oxidizers, and metal salts may be violent, causing
fire and explosions. Attacks metals in the presence of
moisture, forming explosive hydrogen gas. Attacks some
plastics, rubber or coatings.
Waste disposal
Pour into sodium bicarbonate
solution and flush to sewer.
Benzoylchlorid Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte
3-oxo-3-phenyl-propanamide
N,N-Dimethylpiperidin-4-amin
APLPHA-BROMO-M-BENZOYLOXYACETOPHENONE
2-(N,N-DIETHYLAMINOCARBONYL)PHENYLBORONIC ACID
2-Methyoxy-3-methyl-2-phenyl-4H-benzo-g-pyranone
[S-(R*,R*)]-2,3-Bis(benzoyloxy)bernsteinsure
Bentiamin
PHENOXYACETIC ACID
Benzoylcyanid
2,5-Dichlorbenzoylchlorid
7-HYDROXY-3-METHYLFLAVONE
1-Benzoylpiperidin
Proglumid
4-Chlorbenzophenon
2-Imidazol-4-ylethylamin
(3,4-Diaminophenyl)phenylmethanone
α-D-Glucopyranosid, β-D-Fructofuranosyl, Benzoat
m-Phenylendibenzoat
Chinolin-2-carbonitril
Benzoylnaphthalin
tert-Butylperbenzoat
4,4'-Dichlorbenzophenon
4'-Amino-2',5'-diethoxybenzanilid
dihydroxyethyl p-octadecyl phenylsulfonyl amino propyl ammoium propylsulfonate
3-Chlorbenzoylchlorid
2-Amino-5-nitrobenzophenon
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-benzo[b]pyran-4-on
N'-Benzoylbenzohydrazid
N-Hydroxy-N-phenylbenzamid
N,N-Dimethylbenzamid
Phenylbenzoat
Nitrazepam
Dibenzoyldisulfid
1-(PHENYLSULFONYL)-1H-INDOLE-2-CARBALDEHYDE
Oxybenzon
4-BROMOPHENYLTHIOUREA
1-BENZOYLPIPERAZINE HYROCHLORIDE 97
α-(Aminomethyl)benzylalkohol
Benzoylferrocen
4-Chlor-o-toluidin

