6170-42-9
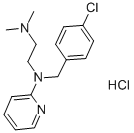 6170-42-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
6170-42-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
鹽酸氯吡胺
N-(4-氯芐基)-N,N’-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基-1,2-乙二胺
氯吡胺
氯吡胺鹽酸鹽
CHLOROPYRAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
CHLOROPYRAMINE MONOHYDROCHLORIDE
N-P-CHLOROBENZYL-N,N-DIMETHYL-N-(2-PYRIDYL)ETHYLENEDIAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
N-P-CHLOROBENZYL-N',N'-DIMETHYL-N-[2-PYRIDYL]ETHYLENEDIAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
N-P-CHLOROBENZYL-N',N'-DIMETHYL-N-[2-PYRIDYL]LETHYLENEDIAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Chloropyramine HCI
N-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-N’,N’-dimethyl-N-2-pyridinyl-1,2-ethanediamine
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報價日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號 | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號 | 包裝 | 價格 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-B1305 | 鹽酸氯吡胺 Chloropyramine hydrochloride | 6170-42-9 | 25 mg | 429元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-B1305 | 鹽酸氯吡胺 Chloropyramine hydrochloride | 6170-42-9 | 10mM * 1mLin DMSO | 471元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-B1305 | 鹽酸氯吡胺 Chloropyramine hydrochloride | 6170-42-9 | 50mg | 600元 |
常見問題列表
|
VEGFR-3
|
BT474 cells are highly sensitive to Chloropyramine hydrochloride (compound 1) treatment, whereby 1 μM concentrations cause a 40% reduction of viability after 48 h of treatment. It is found that at 1 μM concentrations of Chloropyramine hydrochloride, viability of control MCF7-pcDNA3 cells is significantly higher than the viability of MCF7-VEGFR-3 cells (P<0.01) and at 10 μM concentration this difference reaches twofold (P<0.001). In the BT474 cells treatment with Chloropyramine hydrochloride also leads to a concentration-dependent decrease of cell proliferation. When treatment with Chloropyramine hydrochloride is continued for 48 h, the breast cancer cells that overexpressed VEGFR-3 undergo apoptosis. This effect is dose-dependent, with 10 μM Chloropyramine hydrochloride inducing apoptosis in more than 60% of BT474 cells. In our model cell lines MCF7-pcDNA3 and MCF7-VEGFR-3, treatment with 10 μM Chloropyramine hydrochloride for 48 h leads to a 4-fold increase in apoptotic cell death in the cell line that overexpressed VEGFR-3 (18% versus 76 % respectively).
Chloropyramine hydrochloride causes a dramatic reduction of tumor growth in both model systems whereby the tumor size in the treated groups is approximately 20% of the tumor size in vehicle control groups. Doxorubicin administered at 3 mg/kg causes approximately 60% reduction of tumor growth, but has no effect on tumor growth at 0, 3 mg/kg. In contrast, there is a modest effect of Chloropyramine hydrochloride alone (50% reduction of tumor growth). The low-dose combination of Chloropyramine hydrochloride and doxorubicin has a prolonged anti-tumor effect (85% reduction of tumor growth) that is greater than either drug alone.
