| | ERGONOVINE Basic information |
| Product Name: | ERGONOVINE | | Synonyms: | ergoatetrine;ergoklinine;ergoline-8beta-carboxamide,9,10-didehydro-n-((s)-2-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-6-me;ergometrin;ergonovine;ergostetrine;ergotocine;ermetrine | | CAS: | 60-79-7 | | MF: | C19H23N3O2 | | MW: | 325.4 | | EINECS: | 200-485-0 | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 60-79-7.mol | 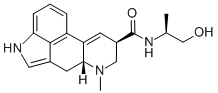 |
| | ERGONOVINE Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 162° | | alpha | D20 +90° (in water) | | Boiling point | 463.59°C (rough estimate) | | density | 1.1611 (rough estimate) | | refractive index | 1.5900 (estimate) | | solubility | Water soluble | | pka | 6.8(at 25℃) | | optical activity | +9020 (H2O)-1620 (c 1, pyridine) | | Water Solubility | >394g/L(25 ºC) | | Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| | ERGONOVINE Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | solid | | Originator | Ergotrate,Lilly | | Uses | Oxytocic. | | Uses | Ergonovine is a water-soluble lysergic acidderivative that occurs in ergot. It is used as anoxytocic agent. Its maleate derivative is usedin the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage. | | Definition | ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide that is lysergamide in which one of the hydrogens attached to the amide nitrogen is substituted by a 1-hydroxypropan-2-yl group (S-configuration). An ergot alkaloid that has a particularly powerful action on th
uterus, its maleate (and formerly tartrate) salt is used in the active management of the third stage of labour, and to prevent or treat postpartum of postabortal haemorrhage caused by uterine atony: by maintaining uterine contraction and tone, blood vesse
s in the uterine wall are compressed and blood flow reduced. | | Manufacturing Process | A solution of the mixed anhydride of lysergic acid and trifluoroacetic acid is
prepared from 530 mg of d-lysergic acid and 930 mg of trifluoroacetic
anhydride in 30 ml of acetonitrile at -20°C. The mixture is allowed to stand at
-20°C for about 1.5 hours during which time the suspended material
dissolves, and the d-lyserginic acid is converted to the mixed anhydride of
liserginic and trifluoroacetic acids. The mixed anhydride can be separated as
an oil by evaporating the solvent in vacuo at a temperature about 0°C. The
solution containing the mixed anhydride is added to a solution of 300 mg of L-
(+)-2-aminopropan-1-ol, and 640 mg of triethylamine in 15 ml of acetonitrile,
the triethylamine being employed to displace any L-(+)-2-aminopropan-1-ol
from adducts with acid components of the reaction mixture. After 15 minutes
of standing at room temperature, the reaction mixture is filtered, and the
crystalline material thus obtained is washed with acetonitrile and dried in air.
This material is substantially pure d-lysergic acid. The filtrate which contains
the desired reaction product is evaporated to dryness in vacuo. The residue is
treated with chloroform and water. The chloroform layer is separated, and the
aqueous layer is extracted with 4x50 ml portions of chloroform. The combined
chloroform extracts washed 4x50 ml portions of cold water in order to remove
the residual amounts of amine salts, dried over sodium sulfate and the
chloroform is evaporated yielding a crystalline material, which separates when
the volume of residual solution is decreased to about 2 ml. The solution is
chilled, thereby, causing further crystalline material to separate from solution.
The crystalline material is substantially pure ergonovine. The crystalline
ergonovine is removed from the solution by filtration, is washed with cold
chloroform and dried. MP: 155°-156°C. Paper chromatography shows that this
compound is identical with authentic ergonovine produced from crude ergot.
The mother liquors and chloroform washes from the above crystallization of
ergonovine are combined, and the solvents are evaporated in vacuo. The
residue containing ergonovinine (the "iso" form of ergonovine) is dissolved in
2 ml of ethyl acetate. From this solution crystalline ergonovinine precipitates
almost immediately. The crystals are separated by filtration and dried. A
sample melts at about 188-190°C. The ergonovinine can be isomerized to
ergonovine with alkali for example by employing the method of Stoll and
Hofmann, Helvetica Chimica Acta 26, 944 (1943).
The ethyl acetate mother liquor from the preceding isolation of ergonovinine is
evaporated to dryness in vacuo and the residue (the mixture of 1-
aminopropan-2-ol esters of d-lysergic acid and of d-iso-lysergic acid) is
dissolved in 2 ml of ethanol. 0.4 ml of 4 N potassium hydroxide solution in
50% aqueous ethanol are then added, and the resulting mixture is allowed to
stand at room temperature in the dark for about two hours. This treatment of
the aminopropanol esters of d-lysergic acid and d-isolysergic acid with base
rearranges them to the propanol amides of d-lysergic acid and d-iso-lysergic
acid, which are ergonovine and ergonovinine, respectively. Solid carbon
dioxide is added to the reaction mixture in order to neutralize the potassium
hydroxide. The solvents are then removed in vacuo and the residue of
ergonovine and ergonovinine is separated into its components by a
chromatogrophy on the basic alumina. Two blue fluorescing zone appear on
the alumina column and could light isolate. The mixture (3:1) of benzene and
chloroform is used as eluent. | | Brand name | Ergotrate Maleate (Lilly). | | Therapeutic Function | Oxytocic, Abortifacient | | Hazard | Extremely toxic; vaso-constrictor; central nervous system stimulant; adrenergic blocking
compound. | | Health Hazard | The toxicity of ergonovine is low to moderate.The toxic symptoms include excitability,respiratory depression, cyanosis, and convulsions.The intravenous LD50 value in mice is144 mg/kg. |
| | ERGONOVINE Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|