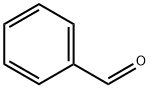
???????
|
|
??????? ??
- ???
- ?26 °C (lit.)
- ?? ?
- 178-179 °C (lit.)
- ??
- 1.044 g/cm3 at 20 °C (lit.)
- ?? ??
- 3.7 (vs air)
- ???
- 4 mm Hg ( 45 °C)
- ???
- n
20/D 1.545(lit.)
- FEMA
- 2127 | BENZALDEHYDE
- ???
- 145 °F
- ?? ??
- Store below +30°C.
- ???
- H2O: ???100mg/mL
- ?? ?? (pKa)
- 14.90(at 25℃)
- ??
- ?? ??
- pH ??
- 5.9
- ??????(pH)
- 5.9 (1g/l, H2O)
- ??
- ?????.
- ????
- 1.4-8.5%(V)
- ?? ??
- ?? ??
- ???
- 19.5 ºC?? <0.01g/100mL
- ???
- -56℃
- ??
- Air Sensitive
- Merck
- 14,1058
- JECFA Number
- 22
- BRN
- 471223
- Dielectric constant
- 17.8(20℃)
- ???
- ????. ?? ??. ????, ??, ???, ??? ???? ????. ??, ?, ??? ?????.
- InChIKey
- HUMNYLRZRPPJDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- LogP
- 1.4 at 25℃
- CAS ??????
- 100-52-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 22 | ||
| ????? | 24 | ||
| ????(UN No.) | UN 1990 9/PG 3 | ||
| WGK ?? | 1 | ||
| RTECS ?? | CU4375000 | ||
| F ?????? | 8 | ||
| ?? ?? ?? | 374 °F | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS ?? | 2912 21 00 | ||
| ?? ?? | 9 | ||
| ???? | III | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 100-52-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | LD50 in rats, guinea pigs (mg/kg): 1300, 1000 orally (Jenner) | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-02713 |
??????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
???? ??, ?? ??? ?? ???? ???, ???? ??? ?? ??? ???. ??? ??? ?? ???? ???????? ?? ???? ??? ? ??? ??? ?? ?? ??. ? ??????? ???? ???? ??????, ????? ?????? ??.??
???????(Benzaldehyde, C7H6O)? ?? ??? ??? ??????. ????? ?? ? ????.?? ??? ????? ?? ?? ??? ??? ??? ??? ?? ??? ????. ?? ??? ?? ???? ???? ??? ??? ???? ??, ??? ?? ???? ?? ???? ??.??
??? ?? ???? ??·??? ?? ???? ????, ?? ????? ????? ????.????
? (1) ?? : ? ??? ??? 1.041~1.046??? ??.
??(2) ??? : ? ??? ??? 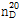 ? 1.544~1.547??? ??.
? 1.544~1.547??? ??.
??(3) ????? : ? ??? ????? ? ??????? ???? ?? ??? ?, ?? ????? ??.
????
? (1) ? ?? 1mL? ?????????? 3mL? ??? ??? ??? ? ???? ?????? ?? ?? ? 5mL? ??? ???.
??(2) ? ?? 3??? ?? 0.1g ? ?? 2mL? ??? ??? ??? ???? ?? ??? ?????. ? ? 2??? ??? ? 5mL? ??? ?????????? ????? ?? ?? ??? ????.
???
? ? ??? ? 0.8g? ??? ?? ????? ? ????? ? ????????? ??????? ?2?? ?? ????. ??, ????? 10??? ??.
0.5N ?? 1mL = 53.06mg C7H6O
??? ??
Benzaldehyde is a colorless to yellow, oily liquid with an odor of bitter almonds. Benzaldehyde is commercially available in two grades: (i) pure benzaldehyde and (ii) and double-distilled benzaldehyde. The latter has applications in the pharmaceutical, perfume, and fl avor industries. Benzaldehyde may contain trace amounts of chlorine, water, benzoic acid, benzyl chloride, benzyl alcohol, and/or nitrobenzene. Benzaldehyde is ignited relatively easily on contact with hot surfaces. This has been attributed to the property of very low auto-ignition temperature. Benzaldehyde also undergoes autoxidation in air and is liable to self-heat. It is used as a food flavoring and in the manufacture of dyes and antibiotics, and can be readily manufactured by the chlorination of methylbenzene and the subsequent hydrolysis of (dichloromethyl) benzene: C6H5CH3 + Cl2 →C6H5CHCl2C6H5CHCl2 + 2H2O →C6H5CH(OH)2+ 2HCl C6H5CH(OH)2 →C6H5CHO + H2O.??
Benzaldehyde exists in nature, occurring in combined and uncombined forms in many plants. It is also the main constituent of the essential oils obtained by pressing the kernels of peaches, cherries, apricots, and other fruits. Benzaldehyde is released into the environment in emissions from combustion processes, such as gasoline and diesel engines, incinerators, and wood burning. It is formed in the atmosphere through photochemical oxidation of toluene and other aromatic hydrocarbons.??
Benzaldehyde is a flavoring agent which is liquid and colorless, and has an almond-like odor. it has a hot (burning) taste. it is oxidized to benzoic acid when exposed to air and deteriorates under light. it is miscible in volatile oils, fixed oils, ether, and alcohol; it is spar- ingly soluble in water. it is obtained by chemical synthesis and by natural occurrence in oils of bitter almond, peach, and apricot kernel. it is also termed benzoic aldehyde.??
ChEBI: Benzaldehyde is an arenecarbaldehyde that consists of benzene bearing a single formyl substituent; the simplest aromatic aldehyde and parent of the class of benzaldehydes. It has a role as a flavouring agent, a fragrance, an odorant receptor agonist, a plant metabolite, an EC 3.5.5.1 (nitrilase) inhibitor and an EC 3.1.1.3 (triacylglycerol lipase) inhibitor.?? ??
Benzaldehyde is prepared by hydrolysis of benzal chloride, for example, in acidic media in the presence of a catalyst such as ferric chloride or in alkaline media with aqueous sodium carbonate. Part of the commercially available benzaldehyde originates from a technical process for phenol. In this process, benzaldehyde is a by-product in the oxidation, in air, of toluene to benzoic acid.?? ??
Benzaldehyde appears as a clear colorless to yellow liquid with a bitter almond odor. Flash point near 145 °F. More denser than water and insoluble in water. Hence sinks in water. Vapors are heavier than air. The primary hazard is to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit spread to the environment. Easily penetrates the soil to contaminate groundwater and nearby waterways. Used in flavoring and perfume making.??? ?? ??
Oxidizes in air to form benzoic acid, which is moderately toxic by ingestion. Insoluble in water.?? ???
A nontoxic, combustible liquid, reacts with oxidizing reagents. Benzaldehyde must be blanketed with an inert gas at all times since Benzaldehyde is oxidized readily by air to benzoic acid [Kirk-Othmer, 3rd ed., Vol. 3, 1978, p. 736]. In contact with strong acids or bases Benzaldehyde will undergo an exothermic condensation reaction [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 327]. A violent reaction was observed on contact with peroxyacids (peroxyformic acid) [DiAns, J. et al., Ber., 1915, 48, p. 1136]. An explosion occurred when pyrrolidine, Benzaldehyde, and propionic acid were heated to form porphyrins.???
Highly toxic.????
Benzaldehyde exhibited low to moderate toxicityin test animals, the poisoning effectdepending on dosage. Ingestion of 50–60 mLmay be fatal to humans. Oral intake of a largedose can cause tremor, gastrointestinal pain,and kidney damage. Animal experimentsindicated that ingestion of this compoundby guinea pigs caused tremor, bleeding fromsmall intestine, and an increase in urine volume;in rats, ingestion resulted in somnolenceand coma.LD50 value, oral (guinea pigs): 1000 mg/kg
LD50 value, oral (rats): 1300 mg/kg
A 500-mg amount for a 24-hour periodresulted in moderate skin irritation in rabbits.Because of its low toxicity, high boilingpoint, and low vapor pressure, the healthhazard to humans from exposure to benzaldehydeis very low.
????
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.?? ??
Reactivity with Water: No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: No reactions; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. An allergen. Acts as a feeble local anesthetic. Local contact may cause contact dermatitis. Causes central nervous system depression in small doses and convulsions in larger doses. A skin irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported. Combustible liquid. To fight fire, use water (may be used as a blanket), alcohol, foam, dry chemical. A strong reducing agent. Reacts violently with peroxyformic acid and other oxidizers. See also ALDEHYDES.??? ??
In manufacture of perfumes, dyes, and cinnamic acid; as solvent; in flavors.?? ??
Benzaldehyde was among 300 volatile constituents detected in the urine of ten adults . It is commonly converted to hippuric acid in vivo. In the rabbit and dog, hippuric acid appears to be the only metabolite there being practically no formation of benzoyl glucuronide. The conversion of benzaldehyde to benzoic acid in the rabbit follows first-order reaction kinetics??
Benzaldehyde should be kept stored in a tightly closed container and protected against physical damage. Storage of the chemical substance outside or in a detached area is preferred, whereas inside storage should be in a standard flammable liquids storage room or cabinet. Benzaldehyde should be kept separated from oxidizing materials. Also, storage and use areas should be no smoking areas. Containers of this material may be hazardous when empty since they retain product residues (vapors, liquid); observe all warnings and precautions listed for the product?? ??
UN1990 Benzaldehyde, Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9—Miscellaneous hazardous material.Purification Methods
To diminish its rate of oxidation, benzaldehyde usually contains additives such as hydroquinone or catechol. It can be purified via its bisulfite addition compound but usually distillation (under nitrogen at reduced pressure) is sufficient. Prior to distillation it is washed with NaOH or 10% Na2CO3 (until no more CO2 is evolved), then with saturated Na2SO3 and H2O, followed by drying with CaSO4, MgSO4 or CaCl2. [Beilstein 7 IV 505.]? ???
The substance reacts with air, forming explosive peroxides. Reacts violently with performic acid, oxidants, aluminum, iron, bases, and phenol, causing fire and explosion hazard. May self-ignite if absorbed in combustible material with large surface area, or otherwise dispersed over large areas. Reacts with rust, amines, alkalies, strong bases, reducing agents such as hydrideds and active metals.??? ??
Incineration; add combustible solvent and spray into incinerator with afterburner.?? ??
Workers should be careful when using benzaldehyde because there is a risk of spontaneous combustion. It may ignite spontaneously if it is absorbed onto rags, cleaning cloths, clothing, sawdust, diatomaceous earth (kieselguhr), activated charcoal, or other materials with large surface areas in workplaces. Workers should avoid handling the chemical substance and should not cut, puncture, or weld on or near the container. Exposure of benzaldehyde to air, light, heat, hot surfaces such as hot pipes, sparks, open flames, and other ignition sources should be avoided. Workers should wear proper personal protective clothing and equipment??????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?????(??)
????
?? ???
????
???
??(??)
???
???? ???
?? ??
??
?????
trans-Cinnamaldehyde
?? ????
??? ??
?????(??)
?? ??
DL-???
FLAVANONE
2-???-5-???-??????
Propafenone Hydrochloride
???-2-??-1-???????????
whitener WG for wool
?????,????-,?????
BENZYLHYDRAZINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE
?????????
Diaveridine
????? BLUE G-250
2,4,5-????????
L-Phenylglycine
3,4-????????
Magentagreencrystals
Reactive Blue BRF
4-????-3-?-2-?
????
1-???-4-??????????????
2-(Acetylamino)-3-phenyl-2-propenoic acid
??1H-??-2-???????
? ?? 9 (???? ?)
2-[2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl]-4-methyl-3-oxo-N-phenylpentanamide
N, N- ?????? ???? ? (????)
Bis(dibenzylideneacetone)palladium
ASTRAZON BRILLIANT RED 4G
??????104
NIFE??
Epalrestat
4-Hydroxybenzylideneacetone
2-PHENYL-1.3-DIOXOLANE-4-METHANOL
3,5-??????
2-((E)-2-Hydroxy-3-phenylacryloyl)benzoic acid ,97%
(R)-(+)-N-??-1-??????
N,N'-?????????
??? BT
L-Arginine hydrochloride
(E)-3-Benzylidene-3H-isochromene-1,4-dione ,97%
?? 2,3,5-???? ?????
??? (? ?? ?? ???) ? ???
??????? ?? ??
???( 1047)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubei Qianjia Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8618972721089 |
sales@meijiachem.com.cn | China | 2 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +8618949832763 |
info@tnjchem.com | China | 2986 | 55 |
| Wuhan Biet Co., Ltd. | +8617320528784 |
min@biet.com.cn | China | 41 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 |
abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8810 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615350571055 |
Sibel@weibangbio.com | China | 6086 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 |
1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12835 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8617732866630 |
bess@weibangbio.com | China | 18151 | 58 |
| Anhui Yiao New Material Technology Co., Ltd | +86-18033737140 +86-17354101231 |
sales1@hbganmiao.com | China | 227 | 58 |
| Hebei Kingfiner Technology Development Co.Ltd | +86-15532196582 +86-15373005021 |
lisa@kingfinertech.com | China | 3010 | 58 |