β,β-Carotin Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R44:Explosionsgefahr bei Erhitzen unter Einschluss.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R20/21/22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen,Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S7:Beh?lter dicht geschlossen halten.
S15:Vor Hitze schützen.
S18:Beh?lter mit Vorsicht ?ffnen und handhaben.
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Yellow to orange solid.beta-Carotene is insoluble in water, but is available in water-dispersible, oil-dispersible and oil-soluble forms. It has the activity of vitamin A.
Physikalische Eigenschaften
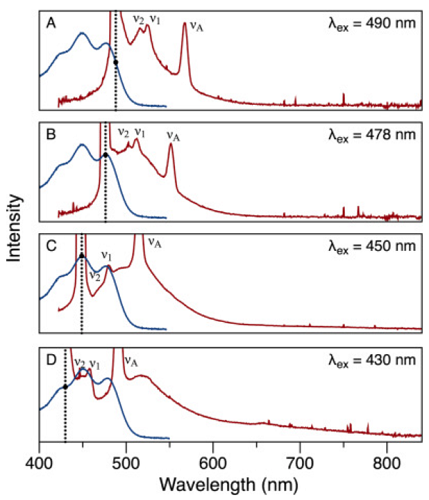
β-Carotene is a tetraterpene with 11 conjugated double bonds that give the molecule an orange color. It is a carotenoid compound that is present in large quantities in the human diet and subsequently is found in all human tissues, including blood. High temperature encourages the isomerization of the double bonds, which lightens the color. Absorption (blue) and fluorescence emission (red) spectra at four excitation wavelengths from β-carotene in hexane solvent at 23 °C are shown below.
Occurrence
Beta-carotene is available naturally in fruits and vegetables. Synthetically, it may be manufactured from fungi or algae.
Definition
ChEBI: A cyclic carotene obtained by dimerisation of all-trans-retinol. A strongly-coloured red-orange pigment abundant in plants and fruit and the most active and important provitamin A carotenoid.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
beta-Carotene is an antioxidant and is one of the most important carotenoids and a source of vitamin A. It is abundantly present in fruits and vegetables which is also used as a food supplement and a colorant.
Sicherheitsprofil
When heated to
decomposition it emits acrid smoke and
irritating fumes.
Source
The richest sources of β-Carotene are yellow, orange, and green leafy fruits and vegetables (such as carrots, spinach, lettuce, tomatoes, sweet potatoes, broccoli, cantaloupe, and winter squash). In general, the more intense the color of the fruit or vegetable, the more beta-carotene it has.

l?uterung methode
It forms purple prisms when crystallised from *C6H6/MeOH and red rhombs from pet ether. Its solubility in hexane is 0.1% at 0o. It is oxygen sensitive and should be stored under N2 at -20o in the dark. It gives a deep blue colour with λmax at 590nm when mixed with SbCl3 in CHCl3. UV: (*C6H6) 429infl, max at 454 and 484nm. The principal peak at 454nm has 1cm 1% 2000. [Synthesis: Surmatis & Ofner J Org Chem 26 1171 1961; Milas et al. J Am Chem Soc 72 4844 1950.] β-Carotene is also purified by column chromatography (Al2O3 activity I-II). It is dissolved in pet ether/*C6H6 (10:1), applied to the column and eluted with pet ether/EtOH; the desired fraction is evaporated and the residue is recrystallised from *C6H6/MeOH (violet-red plates). [UV: Inhoffen et al. Justus Liebigs Ann Chem 570 54, 68 1950; Review: Fleming Selected Organic Synthesis (J Wiley, Lond) pp. 70-74 1973.] Alternatively it can be purified by chromatography on a magnesia column, thin layer of Kieselguhr or magnesia. Crystallise it from CS2/MeOH, Et2O/pet ether, acetone/pet ether or toluene/MeOH. Store it in the dark, under an inert atmosphere, at -20o. Recrystallise it also from 1:1 EtOH/CHCl3. [Bobrowski & Das J Phys Chem 89 5079 1985, Johnston & Scaiano J Am Chem Soc 1 0 8 2349 1986, Strain J Biol Chem 105 523 1934, Meth Biochem Anal 4 1 1957, Beilstein 5 II 638, 5 III 2453, 5 IV 2617.]
β,β-Carotin Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

