| Identification | More | [Name]
D-Valine | [CAS]
640-68-6 | [Synonyms]
ALPHA-AMINO-ISOVALERIANIC ACID
D-2-AMINO-3-METHYLBUTANOIC ACID
D-2-AMINO-3-METHYLBUTYRIC ACID
D-2-AMINOISOVALERIC ACID
D-VAL
D-VALINE
H-D-VAL-OH
(R)-2-AMINO-3-METHYLBUTANOIC ACID
(R)-2-AMINO-4-METHYL-PENTANOIC ACID
(R)-ALPHA-AMINOISOVALERIC ACID
RARECHEM AB PP 3785
(R)-(-)-VALINE
VAL
Valine, D-
D-X-Amino-iso-valeric acid
D-Valine, (R)-alpha-Aminoisovaleric acid
D-VALINE, 98+% (99% EE/GLC)
D-VALINE CELL CULTURE TESTED
D-Valine, 98+%
(r)-(-)-2-amino-3-methylbutyric acid | [EINECS(EC#)]
211-368-9 | [Molecular Formula]
C5H11NO2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00064219 | [Molecular Weight]
117.15 | [MOL File]
640-68-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white to off-white crystalline powder | [Melting point ]
>295 °C (subl.)(lit.)
| [alpha ]
-27.5 º (c=5, 5N HCl) | [Boiling point ]
213.6±23.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.2000 (estimate) | [refractive index ]
-27 ° (C=8, 6mol/L HCl) | [storage temp. ]
Store at RT. | [solubility ]
56 g/L (20°C) | [form ]
Crystalline Powder | [pka]
2.37±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
White to off-white | [biological source]
synthetic (organic) | [optical activity]
[α]23/D 32.0 to 24.0°, c = 8 in 6 M HCl | [Water Solubility ]
56 g/L (20 ºC) | [Detection Methods]
NMR,Rotation | [BRN ]
1721135 | [InChIKey]
KZSNJWFQEVHDMF-SCSAIBSYSA-N | [LogP]
0.289 (est) | [CAS DataBase Reference]
640-68-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid(D)(640-68-6) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
640-68-6(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S22:Do not breathe dust .
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
YV9360000
| [TSCA ]
Yes | [HS Code ]
29224900 |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Description]
D-valine is the D-form of valine, being the non-proteinogenic isomer of valine. It can be supplemented into the cell culture for selectively inhibition of cell proliferation through inhibiting cells that are deficient in the enzyme D-amino acid oxidase. It has also been used to inhibit fibroblast growth while allowing the selective growth of epithelial cells.
| [Valine]
Valine is one kinds of the essential amino acids for human being with the requirement of adult males being 10mg/(kg ? d) (FAO/WHO1973). Being lack of this product can cause neurological disorders, reduction of developmental ability as well as anemia.
Valine is one of the 20 amino acids that form protein with its chemical name being 2-amino-3-methyl-butyric acid. It belongs to branched chain amino acids and is one of the eight kinds of essential amino acids and carbohydrate-producing amino acids of human body. It works together with the other two high-concentration amino acids (leucine and isoleucine) to promote the normal growth of body, tissue repair, regulate blood sugar, and provide the energy needed. When participating in intense physical activity, valine can provide extra energy to the muscles for producing glucose in order to prevent of muscle weakness. It also helps remove excess nitrogen (potentially toxic) from the liver, and transport nitrogen to all of the rest parts of the body.
Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that the human body itself cannot synthesize themselves so that it must be replenished through dietary sources. Its natural food sources include cereals, dairy products, mushrooms, mushrooms, peanuts, soy protein and meat. D-Valine is also found in some actinomyces (such as valeriana). While most people can get sufficient quantities of D-valine from the diet, however, there are still many cases about valine deficiency. Upon being lack of sufficient valine, rats get limb tremors due to disorder of the central nervous system as well as ataxia. Through dissecting slices of brain tissue, it was found about the phenomenon of the red nucleus cell degeneration. Owing to the liver function damage of patients with advanced cirrhosis of the liver, hyperinsulinemia is easy to occur, resulting in the reduction of branched chain amino acids in the blood. The ratio of branched-chain amino acids over aromatic amino acids decreases from 3.0-3.5 (normal body) to 1.0-1.5. It is common for using injection of branched chain amino acids such as valine in the treatment of liver failure, and the damage of alcoholism and drug abuse on these organs.
| [Uses]
1.D-valine can be used for the synthesis of newly efficient pesticide: pyrethroids permethrin and chlorofluorocarbons amyl because of its own biochemical characteristics.
2.D-valine is also widely used in biomedical research. For example, it can be used to inhibit the growth of fibroblasts, and be applied to the studies on its influence on the morphology and function of pulmonary artery endothelial cells.
3.D-Valine is an important organic chiral source which is mainly used in fields such as chiral pharmaceuticals, chiral additive, and chiral auxiliary and other areas. As an optically active organic acid, it plays an irreplaceable role in the asymmetric synthesis of certain chiral compounds. It is currently mainly used for the production of new broad-spectrum antibiotic, antineoplastic drugs, anti-diabetes and its complications drugs. | [Chemical Properties]
White crystal, m.p.> 295 °C (sublimation), [α] 25 = 27.35°; it is soluble in water and very slightly soluble in ethanol.
| [Production methods]
1. DL-Acetyl-methionine is used as the raw material. It undergoes acylase splitting, and further hydrochloric acid acidification to have D-valine crystals precipitated; refined product is finally obtained through recrystallization.
2. The preparation method is to use 2-isopropyl-acetyl ethyl to react with benzene diazonium to get corresponding hydrazine compound, and then further reduce it to valine in zinc-ethanol solution and finally go through chemical or biological split.
| [References]
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/v1255?lang=en®ion=US
Gilbert, S. F., and B. R. Migeon. "D-valine as a selective agent for normal human and rodent epithelial cells in culture." Cell 5.1(1975):11.
Hongpaisan, J. "Inhibition of proliferation of contaminating fibroblasts by D-valine in cultures of smooth muscle cells from human myometrium. " Cell Biology International 24.1(2000):1.
|
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Definition]
ChEBI: The D-enantiomer of valine. | [General Description]
L-Valine is an essential non-polar amino acid. D-Valine is the non-proteinogenic isomer of valine. | [reaction suitability]
reaction type: solution phase peptide synthesis | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
D-valine is used in cell culture as a selective inhibitor of cell proliferation, wherein it inhibits cells that lack the enzyme D-amino acid oxidase. Historically D-valine has been used to inhibit fibroblast growth while allowing selective growth of epithelial cells. | [Structure and conformation]
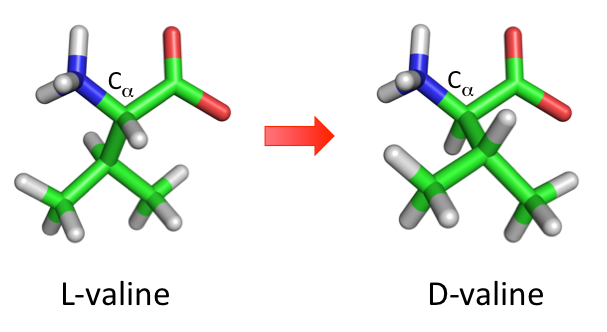
D-Valine is the non-proteinogenic isomer of valine. D-Valine is mirror image of L-Valine, where the chirality at carbon alpha has been inverted. They rarely occur naturally in organisms except for some bacteria. D-Valine is highly resistant to protease mediated degradation and have a low immunogenic response. This makes D-Valine interesting candidates for peptidomimetics drug design.
 |
|
|