| Identification | More | [Name]
Bosutinib | [CAS]
380843-75-4 | [Synonyms]
SKI-606
BOSUTINIB
Bosutinib for research
4-[(2,4-Dichloro-5-methoxyphenyl)amino]-6-methoxy-7-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propoxy]-3-quinolinecarbonitrile | [EINECS(EC#)]
700-455-1 | [Molecular Formula]
C26H29Cl2N5O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD07367846 | [Molecular Weight]
530.45 | [MOL File]
380843-75-4.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
116-120 ºC | [Boiling point ]
649.7±55.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.36 | [vapor pressure ]
0-0Pa at 20℃ | [storage temp. ]
room temp | [solubility ]
DMSO: ≥15mg/mL | [form ]
powder | [pka]
7.63±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
off-white to light brown | [Stability:]
Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 1 month. | [InChIKey]
PICKMQXYAMDEPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [LogP]
3.3-4.3 at pH9.5 | [Surface tension]
72.4mN/m at 3.6mg/L and 20℃ | [CAS DataBase Reference]
380843-75-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Bosutinib, similar to dasatinib, was developed as a dual inhibitor of the SCR family of kinases and the ABL kinase, thus applicable for Ph+ leukemias. In September 2012, the US FDA approved bosutinib (also referred to as SKI-607) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory chronicmyeloid leukemia (CML) for patients with resistance or intolerance to prior therapy. | [Chemical Properties]
Pale Yellow Solid | [Originator]
Wyeth (United States) | [Uses]
A novel Src kinase inhibitor, suppresses migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells. | [Uses]
Bosutinib (380843-75-4) is a novel, dual Src/Abl inhibitor with IC50 of 1.2 nM and 1 nM, respectively. It is built around a chemical scaffold that is different from that of imatinib. peripheral vasolidator increases cerebral blood flow, potential therapeutic for Altzheimer’s disease, cognitive impairment and dementia. | [Definition]
ChEBI: An aminoquinoline that is 4-[(2,4-dichloro-5-methoxyphenyl)amino]-7-[3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)propoxy]quinoline bearing additional cyano and methoxy substituents at positions 3 and 6 respectively. | [Brand name]
Bosulif | [General Description]
Bosutinib is a safe oral medicine with good bioavailability. It is effective for treating chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). It is also a potent ATP-competitive inhibitor for Src tyrosine kinase. Bosutinib inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). It suppresses solid tumors associated with breast, pancreas and prostate. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Bosutinib (SKI-606) is an orally active; dual Src/Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potent antiproliferative activity. It does not appear to inhibit c-Kit and PDGRF, which are thought to be the cause of numerous side effects in anticancer treatment with some other tyrosine kinase inhibitors. | [Clinical Use]
Protein kinase inhibitor:
Treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive
chronic myelogenous leukaemia resistant or
intolerant to prior therapy | [Side effects]
Possible side effects of bosutinib include Nausea, vomiting, stomach/abdominal pain, loss of appetite, cough, joint pain, headache, or dizziness may occur. If any of these effects last or get worse, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly. Diarrhea is a common side effect.
www.webmd.com | [Drug interactions]
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Analgesics: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with methadone. Anti-arrhythmics: possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with amiodarone and disopyramide; concentration possibly increased by dronedarone - avoid or consider reducing dose of bosutinib. Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased by ciprofloxacin, clarithromycin, erythromycin and telithromycin - avoid or consider reducing dose of bosutinib; possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias with moxifloxacin; concentration reduced by rifampicin and possibly rifabutin - avoid. Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by St John’s wort - avoid. Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced by carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone - avoid. | [Metabolism]
Mainly hepatically metabolised. The major circulating
metabolites identified in plasma are oxydechlorinated
(M2) bosutinib (19% of parent exposure) and
N-desmethylated (M5) bosutinib (25% of parent
exposure), with bosutinib N-oxide (M6) as a minor
circulating metabolite. All the metabolites are inactive.
Excretion is mainly via the faeces. | [storage]
+4°C | [Mode of action]
Bosutinib is a synthetic quinolone derivative and dual kinase inhibitor that targets both Abl and Src kinases with potential antineoplastic activity. Unlike imatinib, bosutinib inhibits the autophosphorylation of both Abl and Src kinases, resulting in inhibition of cell growth and apoptosis. Because of the dual mechanism of action, this agent may have activity in resistant CML disease, other myeloid malignancies and solid tumors. Abl kinase is upregulated in the presence of the abnormal Bcr-abl fusion protein which is commonly associated with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Overexpression of specific Src kinases is also associated with the imatinib-resistant CML phenotype. | [References]
Golas et al. (2003), SKI-606, a 4-anilino-3-quinolinecarbonitrile dual inhibitor of Src and Abl kinases, is a potent antiproliferative agent against chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in culture and causes regression of K562 xenografts in nude mice; Cancer Res., 63 375
Remsing Rix et al. (2009), Global target profile of the kinase inhibitor bosutinib in primary chronic myeloid leukemia cells; Leukemia, 23 477
Redaelli et al. (2009), Activity of bosutinib, Dasatinib, and nilotinib against 18 imatinib-resistant BCR/ABL mutants; J. Clin. Oncol., 27 469
MacDonald et al. (2018), Src family kinase inhibitor bosutinib enhances retinoic acid-induced differentiation of HL-60 leukemia cells; Leuk. Lymphoma, 59 2941
Vultur et al. (2008), SKI-606 (bosutinib), a novel Src kinase inhibitor, suppresses migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells; Mol. Cancer Ther., 7 1185 |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Binding Mode]
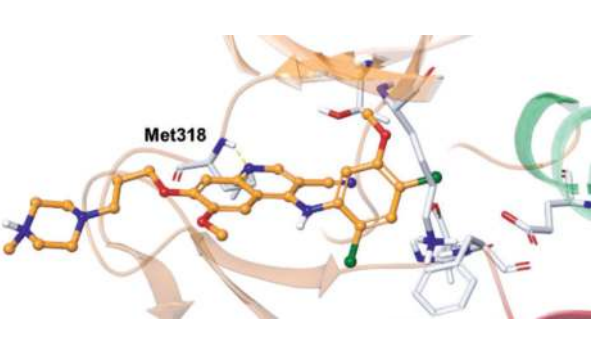
In the co-crystal structures of the two molecules of dasatinib (green and blue) in the asymmetric unit cell with ABL, it binds to an active DFG-information of ABL. The aminothiazole core, which is orthogonal to the 2-chloro-6-methylphenyl moiety, occupies the site that normally binds the adenine group of ATP. The pyrimidine NH and the thiazole nitrogen interact with the backbone amide carbonyl and NH of the hinge region Met318, and the carboxamide NH forms an H-bond with the side chain hydroxyl of Thr315. The terminal hydroxyethyl group interacts differently with each of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit cell: (1) via a hydrogen bond between the hydroxyethyl group and the backbone carbonyl of Tyr320? and (2) with the hydroxyethyl group pointing in the opposite direction and approaching the solvent front. By binding strongly to the active conformation of ABL within the ATP-binding site (vs. the inactive conformation for imatinib), dasatinib efficiently competes with ATP. Due to a different binding mode from that of imatinib, it maintains cellular activity against most imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutations (but not the T315I mutation due to the loss of a hydrogen bond with T315 and increased steric clash with the bulky isobutyl chain of 315I). Unfortunately, binding to the more highly conserved active conformation results in reduced selectivity relative to imatinib, and as a result, dasatinib inhibits many additional protein kinases at physiologically relevant concentrations.
|
|
|