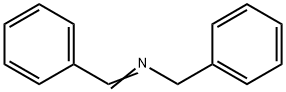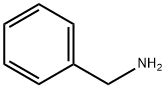
Benzylamine synthesis
- Product Name:Benzylamine
- CAS Number:100-46-9
- Molecular formula:C7H9N
- Molecular Weight:107.15
Benzyl chloride, 84.3g
49% Aqueous NaOH, 52.3g
Diethyl Ether, 200g
A three-necked flask was equipped with a reflux condenser dropping funnel and an agitator. All of the aqueous ammonium hydroxide solution was poured into the flask, then the benzyl chloride was introduced drop by drop; over a period of two hours with constant stirring of the mixture. The exothermic heat of reaction kept the temperature between 30-34°C during this period. When it is desired to introduce the benzyl chloride at a faster rate, conventional cooling means can be employed to control the temperature. A large excess of ammonia was employed as the molar ratio of reactants was 20:1. An additional two hours was allowed to insure completion of the following reaction:

Then the equimolecular quantity of caustic soda solution was added. When quiescent, the mixture split into an aqueous layer and an oily layer. After separating these two layers by use of a separatory funnel, the aqueous phase was made available for further repeated use by merely adding sufficient ammonium hydroxide to bring the total quantity of ammonia up to the original figure. The oily layer was steam distilled until no further oily constituent was visible in the condensed distillate as it dripped down the condenser tube. This distillate was saturated with sodium chloride and successively extracted with an initial 80 and three 40 gram batches of ethyl ether. Upon evaporation of the ether from the extract, 52g of crude benzylamine remain which was distilled at atmospheric pressure. 41g grams of substantially pure benzylamine distilled over in the boiling range 185-192°C, while the residue was found to contain an additional 2.3g of benzylamine and 8.7g of other matter which was believed to consist entirely of dibenzyl amine. Thus the total yield of benzylamine was 43.3g or 60.7% based on the weight of benzyl chloride.
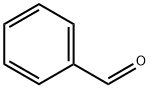
100-52-7
963 suppliers
$20.37/250g

100-46-9
487 suppliers
$5.00/5G
Yield:100-46-9 99.7%
Reaction Conditions:
with ammonia;hydrogen in methanol at 90; under 15001.5 Torr; for 4 h;Autoclave;Solvent;Temperature;Pressure;
Steps:
1-5; 33 A method for catalyzing the reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones to prepare primary amines includes the following steps:
1) Mix 0.05 mol of nickel nitrate hexahydrate, 0.05 mol of citric acid and 8 mL of ethanol, then heat and stir at 70°C until it is gelatinous, then dry the gelatinous material at 100°C for 24h, and then place it in a nitrogen atmosphere Roasted at 700°C for 3h, cooled, and then added the roasted product to a sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 1mol/L, pickled at 80°C until no bubbles were generated and the acid solution was clear, and then washed with water until neutral and dry, to obtain a graphene-coated nickel catalyst ( NiC), and then place the graphene-coated nickel catalyst in an oxygen-nitrogen mixed atmosphere with an oxygen volume fraction of 2% for 2 hours at 200°C to obtain a graphene-coated nickel-nickel oxide catalyst (Ni-NiOC), namely Reductive amination reaction catalyst; 2) Mix 0.5mmol of benzaldehyde, 5mL of methanol solution of 2mol/L ammonia and 10mg of graphene-coated nickel-nickel oxide catalyst into the autoclave, and then add hydrogen, control the system hydrogen pressure to 2MPa, stir The reaction rate was 400 rpm, and the reaction was conducted at 90° C. for 4 hours to obtain benzylamine (yield 99.7%).
References:
CN111116375,2020,A Location in patent:Paragraph 0027-0042; 0056-0059
1576-37-0
145 suppliers
$5.00/50mg

100-46-9
487 suppliers
$5.00/5G
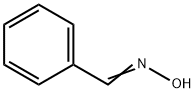
932-90-1
139 suppliers
$17.67/1gm:

100-46-9
487 suppliers
$5.00/5G
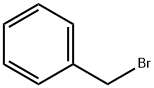
100-39-0
435 suppliers
$10.00/10g

100-46-9
487 suppliers
$5.00/5G