- Nicaraven
-

- $29.00 / 25mg
-
2025-05-16
- CAS:79455-30-4
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.77%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Nicaraven
-

- $1.00 / 1ASSAYS
-
2019-09-06
- CAS:79455-30-4
- Min. Order: 1ASSAYS
- Purity: 95%~99%
- Supply Ability: per week:100kg
|
| | Nicaraven Basic information |
| Product Name: | Nicaraven | | Synonyms: | n,n'-propylenedinicotinamide;NICARAVEN;1,2-bis(nicotinamido)propane;AVS;N,N'-(1-Methylethylene)bis(pyridine-3-carboxamide);N,N'-(1-Methylethylene)bisnicotinamide;N,N'-Propylenebis(nicotinamide);N,N'-Propylenebisnicotinamide | | CAS: | 79455-30-4 | | MF: | C15H16N4O2 | | MW: | 284.31 | | EINECS: | 1806241-263-5 | | Product Categories: | Inhibitors | | Mol File: | 79455-30-4.mol | 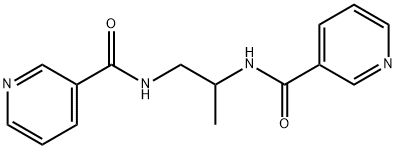 |
| | Nicaraven Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 156-157° | | Boiling point | 635.9±40.0 °C(Predicted) | | density | 1.213±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | | storage temp. | under inert gas (nitrogen or Argon) at 2-8°C | | solubility | DMF: 5 mg/ml; DMSO: 10 mg/ml; Ethanol: 2 mg/ml; PBS (pH 7.2): 2 mg/ml | | form | A crystalline solid | | pka | 12.93±0.46(Predicted) | | color | White to off-white |
| | Nicaraven Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Nicaraven is an antioxidant that exhibits hydroxyl radical scavenging activity in vitro. Nicaraven (1-3 mg/kg per min, i.v.) reduces occurrence of chronic cerebral vasospasms in a dose-dependent manner in a canine model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. In a canine model of warm hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury, nicaraven (2 mg/kg per min, i.v.) reduces liver enzyme release and inhibits lipid peroxidation and neutrophil infiltration in the liver. Nicaraven (100 mg/kg per day, i.p.) also decreases plasma levels of the inflammatory cytokines Il-6 and Tnf-α and the urinary levels of 8-oxo-2''-deoxyguanosine, a marker of DNA oxidation, in a mouse model of radiation-induced injury. | | Uses | Nicaraven is a novel chemically synthesized hydroxyl radical-specific scavenger. | | in vivo | Nicaraven inhibits lipid peroxidation in the liver, improves hepatic and systemic hemodynamics and energy metabolism, and suppresses liver enzyme release, endothelin-1 elevation in hepatic venous blood, histologic damage, and neutrophil infiltration into the liver[1]. Nicaraven increases the number of c-kit(+) stem/progenitor cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood, with a recovery rate around 60-90% of age-matched non-irradiated healthy mice. The potency of colony forming from hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells as indicator of function is completely protected with nicaraven treatment[2]. Administration of nicaraven significantly increases the number, improves the colony-forming capacity, and decreases the DNA damage of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. The urinary levels of 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine, a marker of DNA oxidation, are significantly lower in mice that are given nicaraven compared with those that receive a placebo. The administration of nicaraven significantly decreases the levels of the inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α in the plasma of mice[3]. | | References | [1] Komiya T, et al. A novel free radical scavenger, nicaraven, inhibits human platelet aggregation in vitro. Clin Neuropharmacol. 1999 Jan-Feb;22(1):11-4. DOI:10.1097/00002826-199901000-00003
[2] Yokota R, et al. A novel hydroxyl radical scavenger, nicaraven, protects the liver from warm ischemia and reperfusion injury. Surgery. 2000 Jun;127(6):661-9. DOI:10.1067/msy.2000.105864
[3] Ali H, et al. The potential benefits of nicaraven to protect against radiation-induced injury in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells with relative low dose exposures. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.112
[4] Nicaraven attenuates radiation-induced injury in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60023. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0060023 |
| | Nicaraven Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|