|
|
| | IsoMaculosidine Basic information |
| Product Name: | IsoMaculosidine | | Synonyms: | IsoMaculosidine;Furo[2,3-b]quinolin-4(9H)-one, 6,8-dimethoxy-9-methyl-;6,8-dimethoxy-9-methylfuro[2,3-b]quinolin-4-one;6,8-Dimethoxy-9-methylfuro[2,3-b]quinolin-4(9H)-one | | CAS: | 518-96-7 | | MF: | C14H13NO4 | | MW: | 259.26 | | EINECS: | | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 518-96-7.mol | 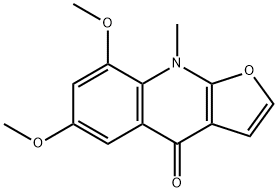 |
| | IsoMaculosidine Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 168-170℃ | | Boiling point | 434.3±45.0 °C(Predicted) | | density | 1.268±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | | pka | 1.65±0.20(Predicted) | | form | Solid | | color | Off-white to light yellow |
| | IsoMaculosidine Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | This alkaloid is very hygroscopic and difficult to obtain crystalline. It occurs in
the roots of Dictamnus albus and is somewhat unstable, turning red on exposure
to light. Isolation under mild conditions show it to be a true alkaloid and not an
artifact. | | Uses | Isomaculosidine is an alkaloid that can be isolated from D. dasycarpus. Isomaculosidine can inhibit nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated BV2 microglial cells[1]. | | References | Gellert et al., Herba Hung., 10, 123 (1971)
Storer, Young., Tetrahedron, 29, 1217 (1973) |
| | IsoMaculosidine Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|