|
|
| | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)peroxydicarbonate Basic information |
| Product Name: | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)peroxydicarbonate | | Synonyms: | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)peroxydicarbonate;bis(2-ethylhexyl) peroxydicarbonate;2-Ethylhexyl percarbonate;Peroxydicarbonic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester;Di-(2-ethylhexyl)-peroxydicarbonat;bis(ethylhexyl) peroxydicarbonate;Initiating agent EHP;peroxydicarbonic acid, di(2-ethylhexyl) ester | | CAS: | 16111-62-9 | | MF: | C18H34O6 | | MW: | 346.46 | | EINECS: | 240-282-4 | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 16111-62-9.mol | 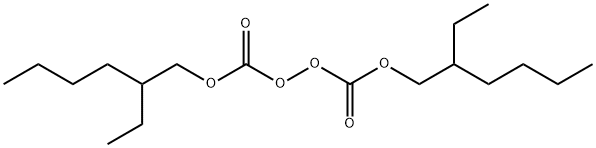 |
| | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)peroxydicarbonate Chemical Properties |
| Boiling point | 401.18°C (rough estimate) | | density | 1.0722 (rough estimate) | | vapor pressure | 0.001Pa at 25℃ | | refractive index | 1.4450 (estimate) | | Water Solubility | 880mg/L at 25℃ | | Stability: | Unstable if heated. Heating presents a potential risk of explosion. May be shock sensitive. Flammable. May react violently with organic materials. | | LogP | 2.73 | | EPA Substance Registry System | Peroxydicarbonic acid, bis(2-ethylhexyl) ester (16111-62-9) |
| RIDADR | 3117 | | HazardClass | 5.2 | | PackingGroup | II |
| | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)peroxydicarbonate Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | It is colorless liquid with unpleasant odor. Thermally unstable
with required continuous refrigeration below -10°C
(-14°F). Refer to the Code for the Storage of Organic
Peroxide Formulations. Storage incompatibility
includes strong acids, oxidizing agents, alkaline materials,
reducing agents, and amines. Also, it should be stored away
from excessive heat, sources of ignition, and reactive
materials (12b). | | General Description | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)peroxydicarbonate is particularly sensitive to temperature rises. Above a given "Control Temperature" they decompose violently. They are generally stored or transported in a solvent slurry. | | Reactivity Profile | DI-(2-ETHYLHEXYL) PEROXYDICARBONATE decomposes violently or explosively at temperatures 0-10° C. owing to self-accelerating exothermic decomposition; Several explosions were due to shock, heat or friction; amines and certain metals can cause accelerated decomposition [Bretherick, 1979 p. 156], Danger of explosion when dry | | Safety Profile | Moderately toxic by
ingestion. When heated to decomposition it
emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. See
also PEROXIDES, ORGANIC |
| | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)peroxydicarbonate Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|