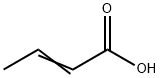
???? C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
Crotonic acid is a white or colorless, crystalline solid with a pungent odor. May be transported as a molten liquid.
??
Crotonic acid is used in the synthesis of resins, polymers,
plasticizers, and drugs. It is also used as a softening
agent for synthetic rubber and in medicinal chemicals.
??
Exists in cis and trans isomeric forms, the latter being
the stable isomer used commercially. The cis form
melts at 15C and is sometimes called isocrotonic
acid.
?? ??
A white crystalline solid. Shipped as either a solid or liquid. Melting point 59°F. Soluble in water and less dense than water. Flash point 190°F. Corrosive to metals and tissue.
??? ?? ??
Soluble in water.
???
Strong irritant to tissue.
????
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
????
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Safety Profile
Poison by
intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by
ingestion, skin contact, and subcutaneous
routes. A powerful corrosive and irritant.
Flammable when exposed to heat or flame;
can react with oxidizing materials. To fight
fire, use alcohol foam, CO2, dry chemical.
When heated to decomposition it emits
acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
??? ??
Used to make plastics, resins, plasticizers, lacquers, and medicines; other chemicals as a chemical intermediate.
?? ??
UN2823 Crotonic acid, solid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
? ???
May form explosive mixture with air. A strong reducing agent. The aqueous solution is a weak acid. Violent reaction with oxidizers, combustibles, strong bases; peroxides. Moisture or strong sunlight (UV) may cause explosive polymerization. May accumulate static electrical charges, and may cause ignition of its vapors. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water, and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds 938 Crotonic Acid (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, sulfides (releasing heat, toxic, and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates, and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur).
???? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??