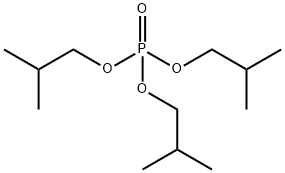
Triisobutyl phosphate C??? ??, ??, ??
??
Triisobutyl phosphate (TIBP) is a very strong polar solvent, sometimes known as Phosphoric acid triisobutyl ester. It is primarily used as an admixture for liquefying concrete, paper coating systems, and textile auxiliaries. It is mainly used as an antifoaming agent in various aqueous systems, where it can destroy foam and act as a foam inhibitor. TiBP is also used to introduce solutions for synthetic resins and natural rubber. In both ellulose-based plastics and synthetic resins, it is used as a flame-retarding plasticizer. TiBP is employed as a pasting agent for pigment pastes. Due to the limited influence of temperature on the viscosity of TiBP, it also serves as an important component in the manufacture of hydraulic fluids for aircraft. As a very strong wetting agent, TiBP is used in the textile industry and the field of adhesives.
??
Phosphoric Acid Tris(2-?methylpropyl) Ester is found in the groundwater downgradient of a landfill (Grindsted, Denmark). It is also a flame retardant and plasticizer.
????
Routes and pathways relevant physicochemical properties
(e.g., solubility, Pow, Henry constant.)consumer and industrial items and play an important role in
safeguarding life and property. A large and diverse group of
anthropogenic compounds constitute flame retardants, which
are added to combustible materials to render them more
resistant to ignition. They are designed to minimize the risk of
a fire in the event of contact with a small heat source such as
a cigarette. A wide range of different flame retardants is
produced, because many materials and products that are to be
rendered fire safe are very different in nature and composition.
Therefore, having variety in flame retardant products is necessary
so as to retain key material functionality. For example,
plastics have a wide range of mechanical and chemical properties
and differ in combustion behavior. These materials in
particular are the main focus of phosphate ester flame
retardants.
Phosphate esters are derivatives of tri protic acid, phosphoric
acid, with a general formula of RxH3°xPO4. Flame retardants are
composed of a group of chemicals with similar properties but
slightly different structures. They are typically liquids and some
are solids at room temperature. Some examples of the phosphate
ester flame retardants include: tris(2-chloroethyl)phosphate
(TCEP), tributyl phosphate (TnBP), tris(2-butoxyethyl)
phosphate (TBEP), tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate
(TDCP), triphenyl phosphate (TPP), tris(2-chloro-isopropyl)
phosphate (TCPP), and triisobutyl phosphate (TiBP). These
compounds are trisubstituted and categorized as alkyl (TnBP,
TiBP), alkyl ether (TBEP), chloroalkyl (TCEP, TCPP, TDCP),
and aryl (TPP) phosphate esters.
Purification Methods
Purify it by repeated crystallisation, from hexane, of its addition compound with uranyl nitrate. (see tributyl phosphate.) [Siddall J Am Chem Soc 81 4176 1959; see Cherbuliez in Organo Phosphorus Compounds (Kosolapoff & Maier eds) Wiley Vol 6 pp 211-577 1973.]
Triisobutyl phosphate ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??