????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??? ??
Brown Solid
??
Herbicide used to control the spread of weedgrass.
??
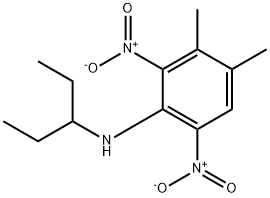
ChEBI: A member of the class of substituted anilines that is N-(pentan-3-yl)aniline bearing two additional nitro substituents at positions 2 and 6 as well as two methyl substituents at positions 3 and 4. A herbicide used to control most annual
rasses and many annual broad-leaved weeds.
?? ??
Orange-yellow crystals. Non corrosive. Used as an herbicide.
??? ?? ??
Insoluble in water.
?? ???
A dinitroaniline derivative.
???
Herbicide: Pendimethalin is a selective pre-emergence and
post-emergence herbicide used on various agricultural
and non-agricultural sites to control broadleaf weeds
and grassy weeds in crops such as apricot, carrot, cherry,
corn, cotton, fig, garbanzos, garlic, olive, onion, nectarine,
peach, pear, pecan, plum, rice and prune, and noncrop
areas. It is applied to soil preplant, pre-emergence, and
post-emergence with ground and aerial equipment.
???
AC 92553®; ACCOTAB®; BULLET® (pendimethalin
+ cyanazine); GO-GO-SAN®; HERBADOX®;
PAY-OFF®; PENOXALIN®; PENOXALINE®;
PROWL®; SIPAXOL®; SQUADRON® (with imazaquin);
STOMP®; TATA PANIDA®; VALOR®; WAY-UP®
??? ??
Pendimethalin is a selective preemergence
and postemergence 2,6-dinitroaniline herbicide
used on various agricultural and non-agricultural sites to
control broadleaf weeds and grassy weeds in crops such as
apricot, carrot, cherry, corn, cotton, fig, garbanzos, garlic,
olive, onion, nectarine, peach, pear, pecan, plum, rice and
prune, and noncrop areas. It is applied to soil preplant,
pre-emergence, and postemergence with ground and aerial
equipment.
?? ?? ??
Irradiation of pendimethalin in methanol yields, in
addition to the minor dealkylated product, the major
products 2-amino-6-nitro-N-(1-ethylpropyl)-3,4-xylidine
and 2-nitroso-6-nitro-3,4-xylidine. Pendimethalin
degrades rapidly through reductive cyclization of the
amino group and adjacent N-ethylpropyl to give a
cyclized benzimidazole product. The
photodecomposition of pendimethalin involves
oxidative dealkylation, nitro reduction, and cyclization.
By soil bacteria, pendimethalin degrades through
different pathways from the photodegradation reaction,
resulting in benzimidazole and hydroxylated products
of the N-alkyl and xylyl methyl groups. The major
metabolic routes of pendimethalin by rats involves
hydroxylation of the 4-methyl and the N-ethyl group,
oxidation of these alkyl groups to carboxylic acids, nitro reduction, cyclization, and conjugation in the
urine and the tissues. Products of cyclization reactions
giving methylbenzimidazole-carboxylic acids are
unique metabolites to the liver and kidney.
?? ??
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances,
solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous
hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
? ???
Reacts with oxidizers, acids and alkaline
materials. Contact with strong oxidizers may cause fire and
explosions.
??? ??
It is the responsibility of
chemical waste generators to determine if a discarded
chemical is classified as a hazardous waste. See 40 CFR
Parts 261.3 for United States Environmental Protection
Agency guidelines for the classification determination.
Additionally, in order to ensure complete and accurate
classification, waste generators must consult state and local
hazardous waste regulations. Organic pesticides, whether of
botanical or synthetic origin, can be destroyed by incineration
equipped with scrubbers to remove acid wastes.
????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??