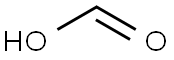
???
|
|
??? ??
- ???
- 8.2-8.4 °C (lit.)
- ?? ?
- 100-101 °C (lit.)
- ??
- 1.22 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- ?? ??
- 1.03 (vs air)
- ???
- 52 mm Hg ( 37 °C)
- ???
- n
20/D 1.377
- FEMA
- 2487 | FORMIC ACID
- ???
- 133 °F
- ?? ??
- 2-8°C
- ???
- H2O: ??? 1g/10mL, ??, ??
- ?? ?? (pKa)
- 3.75(at 20℃)
- ??? ??
- ??
- Specific Gravity
- 1.216 (20℃/20℃)
- ??
- APHA: ≤15
- ??????(pH)
- 3.47(1 mM solution);2.91(10 mM solution);2.38(100 mM solution);
- ??
- ?? 0.10%. ?? ?? ???
- ?? ??
- ??
- ????
- 12-38%(V)
- ???
- ?? ??
- ??
- Hygroscopic
- ?? ??(λmax)
- λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.03
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01
- Merck
- 14,4241
- JECFA Number
- 79
- BRN
- 1209246
- Henry's Law Constant
- At 25 °C: 95.2, 75.1, 39.3, 10.7, and 3.17 at pH values of 1.35, 3.09, 4.05, 4.99, and 6.21, respectively (Hakuta et al., 1977)
- Dielectric constant
- 58.0(16℃)
- ?? ??
- TLV-TWA 5 ppm (~9 mg/m3) (ACGIH, MSHA, OSHA, and NIOSH); IDLH 100 ppm (180 mg/m3) (NIOSH).
- ???
- ????. ??? ? ???? ???, ????, ?? ??, ???? ??? ?? ????. ?? ??. ???. ??? ?? ??? ??? ?? ? ???? ?? ????? ?? ????? ????? ???.
- InChIKey
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- LogP
- -0.540
- CAS ??????
- 64-18-6(CAS DataBase Reference)
- NIST
- Formic acid(64-18-6)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | T,C,Xi | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 23/24/25-34-40-43-35-36/38-10 | ||
| ????? | 36/37-45-26-23-36/37/39 | ||
| OEB | B | ||
| OEL | TWA: 5 ppm (9 mg/m3) | ||
| ????(UN No.) | UN 1198 3/PG 3 | ||
| WGK ?? | 2 | ||
| RTECS ?? | LP8925000 | ||
| F ?????? | 10 | ||
| ?? ?? ?? | 1004 °F | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| ?? ?? | 8 | ||
| ???? | II | ||
| HS ?? | 29151100 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 64-18-6(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | LD50 in mice (mg/kg): 1100 orally; 145 i.v. (Malorny) | ||
| IDLA | 30 ppm | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-17233 | ||
| ???? ?? ??? | 3 |
??? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
?? ??? ????? ???? ??? ?? ???. ????? ??? ?? ? ??? ????? ??. ?? ??? ?? ? ????? ?? ??? ???? ???. ??? ???? ?? ??? ???? ???? ????. ?? ?? ???? ???? ????? ??.????
? (1) ?? : ? ?? 1mL(? 1.2g? ???? ?)? ?? ??? 100mL? ?? ? ? 50mL? ??? 250mL ??????? ?? ??? ?????? 5g? ???. ?????? ??? ?? 2?? ?? ?? ???? ??? ?? ? ???? ???? ? 25mL? ?? ?? ?? ??? ??? ????????? ????? ?? 0.02N ?????????? ??? ?, ? ???? 2.0mL ????? ??.
??(2) ???? : ? ?? 1??? ? 3??? ????? ?, 1?? ?? ?????? ?? ??.
??(3) ??? : ? ?? 2.4g? ????? ? 10mg? ?? ?? ????? ?????? ???? ??? ??????? ?? ??? ?, ? ?? 0.01N ?? 0.2mL? ???? ? ????? ??.
??(4) ? : ? ?? 5.0g? ??? ??????? ?? ?????????????? ?? ??? ?, ? ?? 2.0ppm ????? ??.
????
? ? ?? 5mL? ???????? 2mL? ??? ???? ??? ????????? ???.
???
? ? 15mL? ???? ??? ?? ??????? ??? ? ?? ? ?? 1.5mL? ??? ?? ??? ??. ? ?? ?? ?? 50mL? ?? 1N ?????????? ????(??? : ????????).
1N ???????? 1mL = 46.03mg CH2O2
??
?? ? ??? ??? ??????? ??? ??? ??? ???? ???? ???? ??? ??? ?? ??? ??? ????? ???? ????. ??? ??? ?????? ???? ??? ? ?? ???? ????.??
Formic acid is a clear, colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Formic acid was first isolated from certain ants and was named after the Latin formica, meaning ant. It is made by the action of sulfuric acid on sodium formate, which is produced from carbon monoxide and sodium hydroxide. It is also produced as a by-product in the manufacture of other chemicals such as acetic acid.It can be anticipated that use of formic acid will continuously increase as it replaces inorganic acids and has a potential role in new energy technology. Formic acid toxicity is of a special interest as the acid is the toxic metabolite of methanol.
??? ??
Formic acid, or methanoic acid, is the first member of the homologous series identified as fatty acids with the general formula RCOOH. Formic acid was obtained first from the red ant; itscommon name is derived from the family name for ants, Formicidae. This substance also occurs naturally in bees and wasps, and is presumed to be responsible for the "sting" of these insects. Formic acid has a pungent, penetrating odor. It may be synthesized from anhydrous sodium formate and concentrated H2S04 at low temperature followed by distillation.??? ??
Clear, colorless, fuming liquid with a pungent, penetrating odor. Odor threshold concentration is 49 ppm (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983). it is miscible in water, alcohol, ether, and glycerin, and is obtained by chemical synthesis or oxidation of methanol or formaldehyde.??
Widespread in a large variety of plants; reported identifed in Cistus labdanum and the oil of Artemisia trans- iliensis; also found among the constituents of petit grain lemon and bitter orange essential oil; reported found in strawberry aroma Reported found in apple, sweet cherry, papaya, pear, raspberry, strawberry, peas, cheeses, breads, yogurt, milk, cream, buttermilk, raw fsh, cognac, rum, whiskey, cider, white wine, tea, coffee and roasted chicory root??
Formic acid is taken from the Latin word forant, formica. Naturalists had observed the acrid vapor from ant hills for hundreds of years. One of the earliest descriptions of formic acid was reported in an extract of a letter written from John Wray (1627–1705) to the publisher of Philosophical Transactions published in 1670. Wray’s letter reported on “uncommon Observations and Experiments made with an Acid Juyce to be Found in Ants” and noted the acid was previously obtained by Samuel Fisher from the dry distillation of wood ants. Formic acid is found in stinging insects, plants, unripe fruit, foods, and muscle tissue. J?ns Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848) characterized formic acid in the early 19th century, and it wasfirst synthesized from hydrocyanic acid by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac (1778–1850) at about the same time. A number of synthetic preparations of formic acid were found in the first half of the 19th century. Marcellin Berthelot (1827–1907) discovered a popular synthesis using oxalic acid and glycerin in 1856; he and several other chemists from his period found syntheses of formic acid by heating carbon monoxide in alkaline solutions.?? ??
Formic acid is manufactured as a by-product of the liquidphase oxidation of hydrocarbons to acetic acid. It is also produced by (a) treating sodium formate and sodium acid formate with sulfuric acid at low temperatures followed by distillation or (b) direct synthesis from water and CO2 under pressure and in the presence of catalysts.??
ChEBI: Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid, containing a single carbon. Occurs naturally in various sources including the venom of bee and ant stings, and is a useful organic synthetic reagent. Principally used as a preservative and antibacterial agent in livestock feed. Induces severe metabolic acidosis and ocular injury in human subjects. It has a role as an antibacterial agent, a protic solvent, a metabolite, a solvent and an astringent. It is a conjugate acid of a formate.?? ??
Formic acid solution reacts as follows: (1) with hydroxides, oxides, carbonates, to form formates, e.g., sodium formate, calcium formate, and with alcohols to form esters; (2) with silver of ammonio-silver nitrate to form metallic silver; (3) with ferric formate solution, upon heating, to form red precipitate of basic ferric formate; (4) with mercuric chloride solution to form mercurous chloride, white precipitate; and (5) with permanganate (in the presence of dilute H2SO4) to form CO2 and manganous salt solution. Formic acid causes painful wounds when it comes in contact with the skin. At 160 °C, formic acid yields CO2 plus H2. When sodium formate is heated in vacuum at 300 °C, H2 and sodium oxalate are formed. With concentrated H2SO4 heated, sodium formate, or other formate, or formic acid, yields carbon monoxide gas plus water. Sodium formate is made by heating NaOH and carbon monoxide under pressure at 210 °C.?? ??
Formic acid is the simplest carboxylic acid. Crystal structure study by single-crystal X-ray diffraction technique at -50°C has shown that it has an orthorhombic structure with space group Pna. The photodegradation of formic acid has been investigated using ab intio calculations and time-resolved Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Its utility as a fuel in direct fuel cells has been studied. The momentum distribution for its monomer have been evaluated by electron momentum spectroscopy (EMS).??? ?? ??
Fumes in air. Soluble in water with release of heat.?? ???
Formic acid reacts exothmerically with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Reacts with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Reacts with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Reacts with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides to generate flammable or toxic gases. Reacts with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates to generate carbon dioxide but still heat. Can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. May initiate polymerization reactions or catalyze other chemical reactions. A mixture with furfuryl alcohol exploded [Chem. Eng. News 18:72(1940)].???
Corrosive to skin and tissue.????
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic vapor generated in firesSafety Profile
Poison by inhalation, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mutation data reported. Corrosive. A skin and severe eye irritant. A substance migrating to food from packaging materials. Combustible liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Explosive reaction with furfuryl alcohol, H202, T1(NO3)3*3H2O nitromethane, P2O5. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical, alcohol foam. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.??? ??
Formic acid is a strong reducing agent and is used as a decalcifier. It is used in pharmaceuticals; in dyeing textiles and finishing color-fast wool; electroplat ing, coagulating latex rubber; regeneration old rubber, and dehairing, plumping, and tanning leather. It is also used in the manufacture of acetic acid, airplane dope; allyl alcohol; cellulose formate; phenolic resins; and oxalate; and it is used in the laundry, textile, insecticide, refrigeration, and paper industries; as well as in drug manufacture.?? ??
UN1779 Formic acid, with>85% acid by mass, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material, 3-Flammable liquidPurification Methods
Anhydrous formic acid can be obtained by direct fractional distillation under reduced pressure, the receiver being cooled in ice-water. The use of P2O5 or CaCl2 as dehydrating agents is unsatisfactory. Reagent grade 88% formic acid can be satisfactorily dried by refluxing with phthalic anhydride for 6hours and then distilling it. Alternatively, if it is left in contact with freshly prepared anhydrous CuSO4 for several days about one half of the water is removed from 88% formic acid; distillation then removes the remainder. Boric anhydride (prepared by melting boric acid in an oven at a high temperature, cooling in a desiccator, and powdering) is a suitable dehydrating agent for 98% formic acid; after prolonged stirring with the anhydride the formic acid is distilled under vacuum. Formic acid can be further purified by fractional crystallisation using partial freezing. [Beilstein 2 IV 3.]? ???
Vapors may form explosive mixture with air. A medium strong acid and a strong reducing agent. Violent reaction with oxidizers, furfuryl alcohol; hydrogen peroxide; nitromethane. Incompatible with strong acids; bases, ammonia, aliphatic amines; alkanolamines, isocya nates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin. Decomposes on heating and on contact with strong acids forming carbon monoxide. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrideds and active metals. Contact with active metals or nitrides form flammable gaseous hydrogen. Incompatible with strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides. Attacks metals: aluminum, cast iron and steel; many plastics, rubber and coatings.??? ??
Incineration with added solvent. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥ kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transpor tation, treatment, and waste disposal.??? ?? ?? ? ???
???
Methanol solution
?????(??)
dilute sulphuric acid
??
Ethylamine water solution
??????
METALLURGICAL COKE
????
??? ???
??????
????
??????
?????
??
????(??)
?? ??
5,7-????????[5,4-d]????
C.I. ?? ?? 83
2-OXO-2,3-DIHYDRO-BENZOOXAZOLE-5-?????
3-FLUORO-N-METHYLANILINE
5-AMINO-6-CHLORO-PYRIMIDIN-4-OL
METHYL PENT-4-YN-2-YLCARBAMATE
??2,4-??????
7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline
2-?????-4-??-????
2-Hydroxy-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-11H-benzo[a]carbazole-3-carboxamide
[4-???-2-(????????)????-5-?]???
4-???-2-(????????)????-5-??????
Sulfur Yellow GC
dimethyl dodecyl thioic propylene betaine
4,4'-?????(N,N-???)????
5-Ethyl-2-pyridineethanol
8-BROMO-3-METHYL-3,7-DIHYDRO-PURINE-2,6-DIONE
Sulfur Red Brown B3R
3-?????-2-?????
??????22
CINNAMYL FORMATE
???
1-Methylpiperidine-4-carboxylic acid hydrochloride
1H-?????-5-?????
(1H-INDAZOL-3-YL)-????
??????
1-???-4-??????
?? ??, ?????
GUANINE SULFATE
?????????
1,3,5-TRIMETHYL-1,3,5-TRIPHENYLCYCLOTRISILOXANE
4-????????
1-(2-??????)-4-??????
2-AMINO-4,4'-DICHLORODIPHENYL ETHER
5-Methyl-2-(methylsulfonyl)pyrimidine ,97%
2-????? ?
3,4-DIHYDROISOQUINOLINE
??????????
Diethoxymethyl acetate
1-????????-1-???? ?
??? ?? ??
???( 1165)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 |
sales@aladdinsci.com | United States | 52924 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 |
1026@dideu.com | China | 8670 | 58 |
| PT CHEM GROUP LIMITED | +86-85511178; +86-85511178; |
peter68@ptchemgroup.com | China | 35425 | 58 |
| Wuhan Quanjinci New Material Co.,Ltd. | +86-15271838296; +8615271838296 |
kyra@quanjinci.com | China | 1512 | 58 |
| Qingdao Minzhi Yijie new material Co., LTD | +86-13589435123 +86-13589435123 |
qdmzyj@126.com | China | 240 | 58 |
| Yujiang Chemical (Shandong) Co.,Ltd. | +86-17736087130 +86-18633844644 |
catherine@yjchem.com.cn | China | 990 | 58 |
| Runte International Trade Limited | 19565631292 19565631292 |
lucky@sdruntechem.com | China | 270 | 58 |
| Wuxi High Mountain Hi-tech Development Co.,Ltd. | +86-86-0510-85881806 +8613357920996 |
wuxihighmountain@gmail.com | China | 30 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 |
abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8810 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12835 | 58 |