??????
|
|
?????? ??
- ???
- 150-152 °C(lit.)
- ??
- 52.75 º (c=10, H2O, NH4OH 25 ºC)
- ?? ?
- 232.96°C (rough estimate)
- ??
- 1.5440
- ?? ??
- 630kg/m3
- ???
- 53 ° (C=10, H2O)
- ?? ??
- room temp
- ???
- H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, ??, ??
- ?? ?? (pKa)
- pKa 12.43(H2O,t = 18,)(Approximate)
- ??? ??
- ??? ??
- ??
- ???
- ??????(pH)
- 5.0-7.0 (25℃, 1M in H2O)
- ??
- ?? ??
- pH ??
- 5.9
- optical activity
- [α]25/D +52.5 to +53.0°(lit.)
- ???? ??
- wheat
- ???
- ??
- ?? ??(λmax)
- λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.03
λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.02
- Merck
- 14,4459
- BRN
- 1281608
- ???
- ????. ??? ? ???? ?? ???? ?????. ?? ??.
- InChIKey
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-DVKNGEFBSA-N
- LogP
- -2.490 (est)
- CAS ??????
- 50-99-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
- NIST
- Glucose(50-99-7)
??
- ?? ? ?? ??
- ?? ? ???? ?? (GHS)
| ??? ?? | Xi,Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ?? ???? ?? | 36/37/38-63-62-46-36/38-21 | ||
| ????? | 26-36/37-24/25-53-25 | ||
| WGK ?? | 1 | ||
| RTECS ?? | LZ6600000 | ||
| F ?????? | 3 | ||
| ?? ?? ?? | 500 °C | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| HS ?? | 17023051 | ||
| ?? ?? ??? | 50-99-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| ?? | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 25800 mg/kg | ||
| ???? ?? | KE-17727 |
?????? C??? ??, ??, ??
??
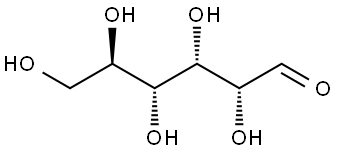
D(+)-Glucose is one of the most important biological compounds found in nature. It is a main product in photosynthesis and is oxidized in cellular respiration. D(+)-Glucose polymerizes to form several important classes of biomolecules including cellulose, starch, and glycogen. It also combines with other compounds to produce common sugars such as sucrose and lactose. The form of D(+)-Glucose displayed above is D-D(+)-Glucose. The “D” designation indicates the configuration of the molecule. The “D” configuration specifies that the hydroxyl group on the number 5 carbon is on the right side of the molecule. The mirror image of D-D(+)-Glucose produces another form of D(+)-Glucose called L-D(+)-Glucose.D(+)-Glucose is the most common form of a large class of molecules called carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the predominant type of organic compounds found in organisms and include sugar, starches, and fats. Carbohydrates, as the name implies, derive their name from D(+)-Glucose,C6H12O6, which was considered a hydrate of carbon with the general formula of Cn(H2O)n, where n is a positive integer. Although the idea of water bonded to carbon to form a hydrate of carbon was wrong, the term carbohydrate persisted. Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, with the carbon atoms generally forming long unbranched chains. Carbohydrates are also known as saccharides derived from the Latin word for sugar, saccharon.??? ??
White or almost white, crystalline powder.??
D(+)-Glucose is the most important and predominant monosaccharide found in nature. It was isolated from raisins by Andreas Sigismund Marggraf (1709–1782) in 1747, and in 1838, Jean-Baptiste-André Dumas (1800–1884) adopted the name glucose from the Greek word glycos meaning sweet. Emil Fischer (1852–1919) determined the structure of glucose in the late 19th century. Glucose also goes by the names dextrose (from its ability to rotate polarized light to the right), grape sugar, and blood sugar. The term blood sugar indicates that glucose is the primary sugar dissolved in blood. Glucose’s abundant hydroxyl groups enable extensive hydrogen bonding, and so glucose is highly soluble in water.??
D(+)-Glucose anhydrous for biochemistry Reag. Ph Eur. CAS 50-99-7, molar mass 180.16?g/mol.??
ChEBI: The open chain form of D-glucose.?? ??
Watery odorless colorless liquid. Denser than water and soluble in water. Hence sinks in and mixes with water.??? ?? ??
Water soluble.?? ???
A weak reducing agent.????
No toxicitySafety Profile
Mildly toxic by ingest ion. An experimental teratogen. Experi mental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported. Potentially explosive reaction with potassium nitrate + sodium peroxide when heated in a sealed container. Uxtures with alkali release carbon monoxide when heated. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.Purification Methods
Crystallise -D-glucose from hot glacial acetic acid or pyridine. Traces of solvent are removed by drying in a vacuum oven at 75o for >3hours. [Gottfried Adv Carbohydr Chem 5 127 1950, Kjaer & Lindberg Acta Chem Scand 1 3 1713 1959, Whistler & Miller Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry I 1301962, Academic Press, Beilstein 1 IV 4306.] [For equilibrium forms see Angyal Adv Carbohydr Chem 42 15 1984, Angyal & Pickles Aust J Chem 25 1711 1972.]?????? ?? ?? ? ???
???
?? ??
?????
???
PALATINOSE
Tobacco essence
???? B1
High Fructose Syrups
FERROUS GLUCONATE DIHYDRATE
??? ?
????????
Glucosyl licorice
Doxycycline hydrochloride
???
???? G ??
alkyl polyglucoside
?????
5′-????????
5'-????
Cytidine triphosphate
??????
4-NITROPHENYL-ALPHA-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE
AZOXYBENZENE
L-(-) ????
Vat Yellow 33
O-3-???-3-???-??-D-???????-(1→6)-O-[2,6-????-2,3,6-?????-??-D-??????-(1→4)]-2-???-D-
????????
Flour improver
????????
???????
Basic chromic sulfate
COPPER (II) GLUCONATE, MIN. 98
CALCIUM GLUCONATE MONOHYDRATE
Thienamycin
??????????
???? ??-????? ??
???????
????
????????
POLYOXIN A
?????
γ-????????
?????? ?? ??
???( 1139)?? ??
| ??? | ?? | ??? | ?? | ?? ? | ?? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEAP CHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 |
market18@leapchem.com | China | 24727 | 58 |
| Jiangsu Guotai Guomian Trading Co. Ltd. | +86-512-58916079 +86-13601562190 |
pharmachem@gtgmt.com | China | 148 | 58 |
| Hebei Saisier Technology Co., LTD | +86-18400010335 +86-18034520335 |
admin@hbsaisier.cn | China | 1015 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86-15531157085 +86-15531157085 |
abby@chuanghaibio.com | China | 8809 | 58 |
| Hebei Yime New Material Technology Co., Ltd. | +86-66697723 +86-17703311139 |
admin@china-yime.com | China | 563 | 58 |
| Wuhan Fortuna Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-027-59207850 |
info@fortunachem.com | China | 5966 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 |
sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5876 | 58 |
| Hebei Kingfiner Technology Development Co.Ltd | +86-15532196582 +86-15373005021 |
lisa@kingfinertech.com | China | 3007 | 58 |
| Hebei Jingbo New Material Technology Co., Ltd | +8619931165850 |
hbjbtech@163.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618092446649 |
sarah@tnjone.com | China | 1143 | 58 |