(-)-Huperzine A Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R26/27/28:Sehr giftig beim Einatmen, Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36/37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung,Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
Beschreibung
Huperzine A is obtained from Huperzia serrata, which is the perennial fern. It
shows activities in antipyretic, hemostasis, and dehumidification and is used for the
treatment in folk of pneumonia, lung abscess, hematemesis, hematochezia, traumatic injury, etc.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Pale Brown Solid
Physikalische Eigenschaften
Appearance: white crystalline powder. Bitter with hygroscopicity. Solubility: easily
soluble in chloroform, soluble in methanol and ethanol, and slightly soluble in
water. Melting point: 211–216?°C.
Verwenden
Huperzine A is a potential therapeutic agent for Alzheimer disease that reversible alkaloid inhibitor of AChE which crosses the blood-brain barrier. It reduces cell death induced by glutamate in primary cultures derived from forebrain, hippocampus, cortex and cere.
In China, it is approved for use in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Huperzine A was classified as a dietary supplement by the FDA in 1997. As a nutraceutical, it is available in American health food stores or via the Internet, labeled as a memory aid.
Indications
Huperzine A is purified from Chinese club moss and has been traditionally used in China for the treatment of swelling, fever, inflammation, blood disorders, and schizophrenia. It was mainly applied to age-related memory dysfunction and Alzheimer and has a good effect on improving memory function. It can be used to treat various types of Alzheimer's disease and also myasthenia gravis.
synthetische
(-)-Huperzine A, a Lyco-podium alkaloid isolated in 1986 from the club moss Huperzia serrata, has drawn considerable attention after it was revealed to be a potent, selective, and reversible AChE inhibitor.
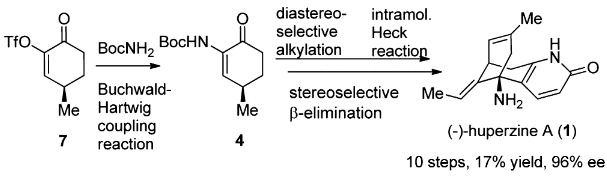
The total synthesis of Lycopodium alkaloid (-)-huperzine A has been accomplished in 10 steps with 17% overall yield from commercially abundant (R)-pulegone. The synthetic route features an efficient synthesis of 4 via a Buchwald–Hartwig coupling reaction, a dianion-mediated highly stereoselective alkylation of 4, and a rare example of an intramolecular Heck reaction of an enamine-type substrate. The stereoselective β-elimination and the accompanying Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement are of particular interest.
[1] RUI DING Guo Q L Bing Feng Sun*. An Efficient Total Synthesis of (-)-Huperzine A [J]. Organic Letters, 2012, 14 17: 4446-4449. DOI:
10.1021/ol301951r.
[2] RUI DING. Divergent Total Synthesis of the Lycopodium Alkaloids Huperzine A, Huperzine B, and Huperzine U[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2013, 79 1: 240-250. DOI:
10.1021/jo402419h.
[3] TUN M K M, WüSTMANN D J, HERZON S B. A robust and scalable synthesis of the potent neuroprotective agent (-)-huperzine A [J]. Chemical Science, 2011, 11: 2251-2253. DOI:
10.1039/C1SC00455G.
Definition
ChEBI: Huperzine A is a sesquiterpene alkaloid isolated from a club moss Huperzia serrata that has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective activity. It is also an effective inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and has attracted interest as a therapeutic candidate for Alzheimer's disease. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, a neuroprotective agent, a plant metabolite and a nootropic agent. It is a sesquiterpene alkaloid, a pyridone, a primary amino compound and an organic heterotricyclic compound. It is a conjugate base of a huperzine A(1+).
Pharmakologie
Huperzine A has the ability to enhance learning and memory, improve spatial memory, and can be used for age-related dementia, vascular dementia, and other neurodegenerative diseases. Compared with the current anti-AD drugs, huperzine A can go through the blood-brain barrier, with a high oral bioavailability and longer time
inhibition on AChE.
As a highly selective AChE reversible inhibitor, huperzine A can inhibit AChE,
reduce acetylcholine hydrolysis, and improve the level of acetylcholine in the synaptic gap. This inhibition is reversible, lasts for a long time, shows no drug dependence if repeated administration, and does not induce significant liver toxicity.
X-ray diffraction results show that the direct binding of huperzine A to AChE active
sites inhibits the binding of AChE to its substrate.
In addition to the potent inhibition on AChE, huperzine A only shows a weak
inhibitory effect on the butyrylcholinesterase; also protects neurons by inhibiting
oxidative stress, reducing somatostatin, reducing the content of glutamate, decreasing the increased intracellular calcium, and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis; further
improves AD-related cognitive function and reduces the symptoms of AD patients.
Clinical Use
Since 1994, huperzine A has been approved for clinical use in improving memory
and cognitive impairment in old patients with memory loss and dementia. A large
number of domestic clinical studies have found that huperzine A shows therapeutic
effect on learning and cognitive dysfunction of vascular dementia, mental retardation, and schizophrenia patients with mild adverse reactions.
(-)-Huperzine A Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

