Benzotriazol (in atembarer Form) Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
ERSCHEINUNGSBILD
WEISSES BIS BRAUNES KRISTALLINES PULVER.
PHYSIKALISCHE GEFAHREN
Staubexplosion der pulverisierten oder granulierten Substanz in Gemischen mit Luft m?glich.
CHEMISCHE GEFAHREN
Zersetzung beim Erhitzen unter Bildung giftiger Rauche mit Aniline und Nitrobenzol. Schwache S?ure in w?ssriger L?sung. Kann bei Vakuumdestillation explodieren.
ARBEITSPLATZGRENZWERTE
TLV nicht festgelegt.
MAK: IIb (nicht festgelegt, aber Informationen vorhanden). (DFG 2008).
AUFNAHMEWEGE
Aufnahme in den K?rper durch Inhalation des Aerosols und durch Verschlucken.
INHALATIONSGEFAHREN
Verdampfen bei 20°C vernachl?ssigbar; eine bel?stigende Partikelkonzentration in der Luft kann jedoch schnell erreicht werden.
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION
WIRKUNGEN BEI KURZZEITEXPOSITION: Die Substanz reizt die Augen.
WIRKUNGEN NACH WIEDERHOLTER ODER LANGZEITEXPOSITION
Wiederholter oder andauernder Kontakt kann zu Hautsensibilisierung führen.
LECKAGE
Verschüttetes Material in Beh?ltern sammeln; falls erforderlich durch Anfeuchten Staubentwicklung verhindern. Reste sorgf?ltig sammeln. An sicheren Ort bringen. NICHT in die Umwelt gelangen lassen. Pers?nliche Schutzausrüstung: Atemschutzger?t, P1-Filter für inerte Partikel.
R-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
R20/22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen und Verschlucken.
R36:Reizt die Augen.
R52/53:Sch?dlich für Wasserorganismen, kann in Gew?ssern l?ngerfristig sch?dliche Wirkungen haben.
R5:Beim Erw?rmen explosionsf?hig.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
R20/21/22:Gesundheitssch?dlich beim Einatmen,Verschlucken und Berührung mit der Haut.
R11:Leichtentzündlich.
S-S?tze Betriebsanweisung:
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
S61:Freisetzung in die Umwelt vermeiden. Besondere Anweisungen einholen/Sicherheitsdatenblatt zu Rate ziehen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn m?glich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S36/37/39:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung,Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzbrille/Gesichtsschutz tragen.
Chemische Eigenschaften
yellow to beige solid or Colorless needle-like crystals. Slightly soluble in cold water, ethanol and ether.
Verwenden
1H-Benzotriazole is an anticorrosive agent, which is useful in aircraft deicing and antifreeze fluids. It is also employed in dishwasher detergents. Further, it is used as a restrainer in photographic emulsions and also useful as a reagent for the determination of silver in analytical chemistry. It also serves as a corrosion inhibitor in the atmosphere and underwater. Further, it is utilized in the synthesis of amines from glyoxal.
Definition
ChEBI: 1H-Benzotriazole is the simplest member of the class of benzotriazoles that consists of a benzene nucleus fused to a 1H-1,2,3-triazole ring. It has a role as an environmental contaminant and a xenobiotic.
synthetische
1H-Benzotriazole is prepared by the reaction of o-phenylenediamine with nitrous acid in dilute sulfuric acid. Damschrodner and Peterson were able to synthesize the 1H-benzotriazole in a high yield (80%) by nitrosation of o-phenylenediamine with sodium nitrite in glacial acetic acid and water.
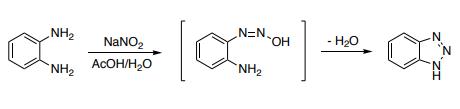
Synthesis of 1H-benzotriazole via diazotization of o-phenylenediamine
Reaction: Add o-phenylenediamine to 50°C water to dissolve, then add glacial acetic acid, cool down to 5°C, add sodium nitrite to stir the reaction. The reactant gradually turned dark green, the temperature rose to 70-80 ℃, the solution turned orange-red, placed at room temperature for 2 hours, cooled, filtered out the crystals, washed with ice water, dried to obtain the crude product, the crude product was distilled under reduced pressure, and collected 201 -204°C (2.0kPa) fraction, and then recrystallized with benzene to obtain 1H-Benzotriazole products with a melting point of 96-97°C, with a yield of about 80%.
Application
1H-Benzotriazole (BT) is a chemical used in a wide variety of industrial, commercial, and consumer products. It main used as an anticorrosive in metalworking, in art restoration, and as a tarnish remover and protective coating in the construction industry.
In the aircraft industry, 1H-benzotriazole and tolyl benzotriazole are found to be the primary agents in most types of aircraft deicing/antiicing fluid (ADAFs).
Benzotriazole is also used as a component of aircraft deicing fluid, pickling inhibitor in boiler scale removal, restrainer, developer and antifogging agent in photographic emulsions, corrosion inhibitor for copper, chemical intermediate for dyes, in pharmaceuticals, and as fungicide. (HSDB 1998).
Benzotriazole(BTA), ethylenediamine tetraaceticacid(EDTA), and potassium iodide(KI) were used for preparing the polishing slurries.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
White to light tan crystals or white powder. No odor.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Dust may form an explosive mixture in air. Slightly soluble in water.
Reaktivit?t anzeigen
The triazoles are a group of highly explosive materials that are sensitive to heat, friction, and impact. Sensitivity varies with the type substitution to the triazole ring. Metal chelated and halogen substitution of the triazol ring make for a particularly heat sensitive material. Azido and nitro derivatives have been employed as high explosives. No matter the derivative these materials should be treated as explosives.
Hazard
Highly toxic by ingestion. May explode under vacuum distillation.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition 1H-Benzotriazole emits toxic fumes. 1H-Benzotriazole can react violently during vacuum distillation.
Brandgefahr
Flash point data are not available for 1H-Benzotriazole. 1H-Benzotriazole is probably combustible.
Sicherheitsprofil
Poison by intravenous route.Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes.Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenicdata. Mutation data reported. May detonate at 220°C or during vacuum distillation. When heated to decompositionit
m?gliche Exposition
Because benzotriazoles are used in large quantities as a corrosion inhibitor, it is mainly through this type of use that benzotriazoles become an environmental contaminant. As a corrosion inhibitor and fire retardant, they are used in antifreeze in concentrations of 0.01-2.0% and in airplane deicing/antiicing fluids in unknown concentrations, up to 10% (Cancilla et al.,1997). Used antifreeze may leak or be poured down drains and thence enters the environment. Also, an estimated 80% of aircraft deicing/anti-icing fluids are deposited on the ground due to spray drift, jet blast, and wind shear during taxiing and takeoff, according to a recent study (Hartwell et al., 1995).
Carcinogenicity
Chronic (2-year) feeding studies
were conducted. Rats were given 0, 6700, or 12,000 ppm
in feed for 78 weeks and held for an additional 26 weeks.
Mice were given 0, 11,700, or 23,500 ppm in feed in
104 weeks. The authors concluded that under the conditions
shown in this study, there were no convincing
evidence that 1-H-benzotriazole was carcinogenic in rats
or mice.
l?uterung methode
1,2,3-Benzotriazole crystallises from toluene, CHCl3, Me2NCHO or a saturated aqueous solution, and is dried at room temperature or in a vacuum oven at 65o. Losses are less if the material is distilled in a vacuum. CAUTION: may EXPLODE during distillation; necessary precautions must be taken. [Damschroder & Peterson Org Synth Coll Vol III 106 1955, Beilstein 26 III/IV 93.]
Benzotriazol (in atembarer Form) Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

