Diphenylcarbodiimid Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
synthetische
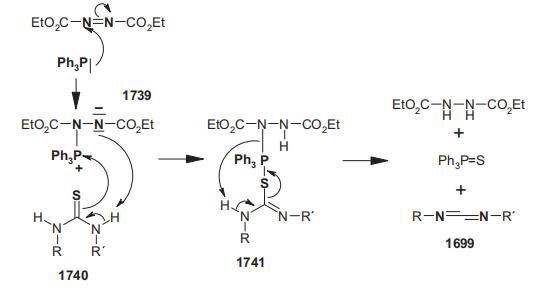
Triphenylphosphine (2.62 g, 0.01 mol) in THF (10 mL) was added dropwise to N,N'-diphenylthiourea (2.28 g, 0.01 mol) and diethyl azodicarboxylate (1.74 g, 0.01 mol) in THF (20 mL) at room temperature. After standing overnight, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure and the residue was extracted with light petroleum (bp 30–60 C°) to separate soluble material from the remainder. The light petroleum extract was concentrated and distilled to give diphenylcarbodiimide; bp 85–90 C°/ 0.2 mmHg, 1.27 g, 65%.
A further development of the method by immobilization of DEAD effects an easily separable (insoluble) and non-explosive reagent in Mitsunobu reactions. The methyl azodicarboxylate reagent immobilized on polystyrene 1742 functions well in Mitsunobu reactions and gives yields comparable to those obtained with soluble DEAD. Diphenylcarbodiimide was obtained in 41% yield.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 51, p. 2613, 1986
DOI: 10.1021/jo00363a046Synthetic Communications, 7, p. 387, 1977
DOI: 10.1080/00397917708050769
Diphenylcarbodiimid Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

