627908-92-3
 627908-92-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
627908-92-3 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
受體酪氨酸激酶抑制劑(SU14813)
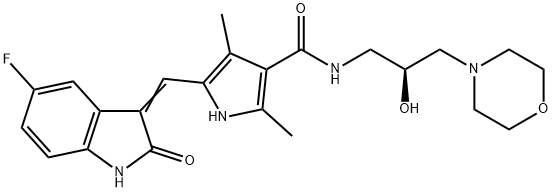
5-((5-氟-2-氧代吲哚-3-亞基)甲基)-N-(2-羥基-3-嗎啉代丙基)-2,4-二甲基-1H-吡咯-3-甲酰胺
5-[(5-氟-1,2-二氫-2-氧代-3H-吲哚-3-亞基)甲基]-N-[(2S)-2-羥基-3-(4-嗎啉基)丙基]-2,4-二甲基-1H-吡咯-3-甲酰胺
5-[(5-氟-1,2-二氫-2-氧代-3H-吲哚-3-亞烷基)甲基]-N-[(2S)-2-羥基-3-(4-嗎啉基)丙基]-2,4-二甲基-1H-吡咯-3-甲酰胺
CS-1149
SU-14813
SU 14813
SU14813(Random Configuration)
5-[(Z)-(5-Fluoro-2-oxo-1,2-dihydro-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-N- [ 2-hydroxy-3-(4-morpholinyl)propyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carb
5-[(5-Fluoro-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-N-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-morpholinyl)propyl]-2,4-dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxamide
1H-Pyrrole-3-carboxamide, 5-[(5-fluoro-1,2-dihydro-2-oxo-3H-indol-3-ylidene)methyl]-N-[(2S)-2-hydroxy-3-(4-morpholinyl)propyl]-2,4-dimethyl-
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
常見(jiàn)問(wèn)題列表
| Target | Value |
|
VEGFR1
(Cell-free assay) | 2 nM |
|
PDGFRβ
(Cell-free assay) | 4 nM |
|
KIT
(Cell-free assay) | 15 nM |
|
VEGFR2
(Cell-free assay) | 50 nM |
SU14813 inhibits ligand-dependent and ligand-independent proliferation, migration, and survival of endothelial cells and/or tumor cells expressing these targets. SU14813 inhibits cellular ligand-dependent phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 (transfected NIH 3T3 cells), PDGFR-β (transfected NIH 3T3 cells), KIT (Mo7e cells), and FLT3-internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD; MV4;11 cells) as well as FMS/CSF1R (transfected NIH 3T3 cells). SU14813 inhibits VEGFR-2, PDGFR-β, and KIT phosphorylation in porcine aorta endothelial cells overexpressing these targets, with cellular IC 50 values of 5.2, 9.9, and 11.2 nM, respectively. SU14813 inhibits the growth of U-118MG with an IC 50 of 50 to 100 nM.
SU14813 inhibits VEGFR-2, PDGFR-β, and FLT3 phosphorylation in xenograft tumors in a dose- and time-dependent fashion. The plasma concentration required for in vivo target inhibition is estimated to be 100 to 200 ng/mL. Used as monotherapy, SU14813 exhibits broad and potent antitumor activity resulting in regression, growth arrest, or substantially reduces growth of various established xenografts derived from human or rat tumor cell lines. Treatment in combination with docetaxel significantly enhances both the inhibition of primary tumor growth and the survival of the tumor-bearing mice compared with administration of either agent alone.