| Identification | More | [Name]
6-Dimethylaminopurine | [CAS]
938-55-6 | [Synonyms]
4DAMPY
4-DIMETHYLAMINOPYRIDINE
4-(N,N-DIMETHYLAMINO)-PYRIDINE
6-DIMETHYLAMINOPURINE
6 DMAP
DIMETHYLAMINO PYRIDINE
DIMETHYLAMINOPYRIDINE, 4-
DMAP
N4,N4-DIMETHYLPYRIDIN-4-AMINE
N-(4-PYRIDYL)DIMETHYLAMINE
N6,N6-DIMETHYLADENINE
N,N'-DIMETHYL-4-PYRIDINAMINE
N,N-DIMETHYL-N-(4-PYRIDINYL)AMINE
N,N-Dimethylpyridin-4-amine
TIMTEC-BB SBB008765
6-Dimethyladenine
6-Dimethylamino-9H-purine
Adenine, N,N-dimethyl-
Adenine, N6,N6-dimethyl-
Dimethyladenine | [EINECS(EC#)]
214-353-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C7H9N5 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00005573 | [Molecular Weight]
163.18 | [MOL File]
938-55-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white to light yellow crystal powder | [Melting point ]
259-262 °C(lit.)
| [Boiling point ]
162 °C (50 mmHg)
| [density ]
1.1407 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.6380 (estimate) | [Fp ]
110 °C
| [storage temp. ]
−20°C
| [solubility ]
methanol: 0.1 g/mL, clear
| [form ]
prilled
| [pka]
9.38±0.20(Predicted) | [color ]
off-white to yellow
| [biological source]
synthetic (organic) | [Water Solubility ]
water: 50mg/mL, clear to hazy, colorless to light yellow | [Usage]
A purine antagonist. In the benzodiazepine receptor (BZR) binding assay, it inhibits the binding of 1.5 nM [3H]diazepam at 100uM in rat brains | [BRN ]
7634 | [InChIKey]
BVIAOQMSVZHOJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
938-55-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
1H-Purin-6-amine, N,N-dimethyl-(938-55-6) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T+ | [Risk Statements ]
R25:Toxic if swallowed.
R27:Very Toxic in contact with skin.
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S28:After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of ... (to be specified by the manufacturer) .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show label where possible) .
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes .
S22:Do not breathe dust . | [RIDADR ]
UN 2811 6.1/PG 1
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
US9230000
| [F ]
10-23 | [HS Code ]
29335990 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
white to light yellow crystal powder | [Uses]
A purine antagonist. In the benzodiazepine receptor (BZR) binding assay, it inhibits the binding of 1.5 nM [3H]diazepam at 100uM in rat brains | [Application]
6-(Dimethylamino)purine has been used:
as a supplement in GR-1 aa medium (bovine medium) for parthenogenetic activation of bovine oocytes to study its potential for embryo development.
in the activation step during the production of nuclear transfer embryos.
as a supplement in HCR2aa medium to activate interspecies embryos derived from interspecies somatic cell nuclear transfer (iSCNT) technique.
A purine antagonist.
In the benzodiazepine receptor (BZR) binding assay, it inhibits the binding of 1.5 nM [3H]diazepam at 100uM in rat brains. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Adenine substituted at N-6 by geminal methyl groups. | [Preparation]
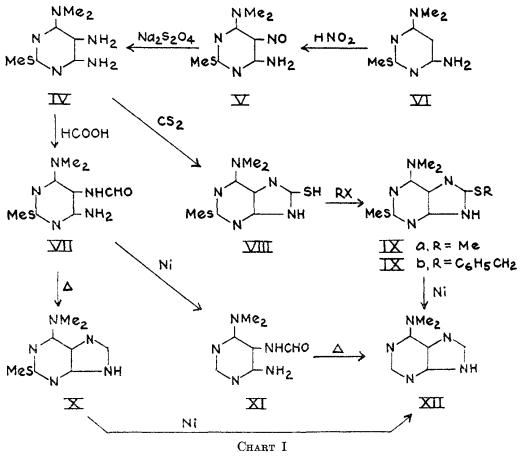
6-Dimethylaminopurine synthesis: 2-Methylmercapto-4-amino-6-dimethylaminopyrimidine (VI) was smoothly nitrosated in 10% acetic acid to the 5-nitrosopyrimidine (V) in 95% yield. Reduction of V with sodium hydrosulfite to the triamine (IV), followed by formylation gave the 5-formamidopyrimidine (VII) in 76% over-all yield for the two steps. Reductive formylation of V directly to VI1 with zinc and formic acid, although more rapid, was less efficient (50% yield). Ring closure of VII to 2-methyhercapto-6-dimethylaminopurine (X) was best done on a small scale by short fusion at 250°(99% yield), although boiling quinoline, formamide, or dilute alcoholic sodium hydroxide could also be employed. The latter reagent was most efficient on a large scale. Desulfurization of X with Raney nickel (7) in 1 N sodium hydroxide at 100° afforded the final product, 6-dimethylaminopurine (XII) in 43% yield.This compound was identical in all respects with the C7H9N5 moiety from puromycin (2).
 | [Origin]
6-Dimethylaminopurine is a puromycin analog that was first identified in the spores of Streptomyces alboniger (PMID: 5019066 ). It has subsequently been identified in several algae species (PMID: 4206669 ).
| [General Description]
6-(Dimethylamino)purine (6-DMAP) is a purine-based metabolite with two condensed heterocyclic rings and two methyl groups linked to the amino group of the purine unit of adenine. | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
6-(Dimethylamino)purine (6-DMAP) is a protein kinase and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. It acts as a secondary metabolite and mediates RNA modification. 6-DMAP is a potent cytokinetic inhibitor and is used in parthenogenesis and meiosis studies. It is also used to promote pronuclei formation in mammalian oocytes. 6-DMAP is a dual fluorescence molecule according to femtosecond fluorescence up-conversion spectroscopy studies. | [storage]
Store at -20°C | [Purification Methods]
It is purified by recrystallisation from H2O, EtOH (0.32g in 10mL) or CHCl3. [Albert & Brown J Chem Soc 2060 1954, UV: Mason J Chem Soc 2071 1954.] The monohydrochloride crystallises from EtOH/Et2O, m 2 5 3o(dec) [Elion et al. J Am Chem Soc 74 411 1952], the dihydrochloride has m 225o(dec) and the picrate has m 245o (235-236.5o) [Fryth et al. J Am Chem Soc 80 2736 1958]. [Beilstein 26 III/IV 3566.] |
|
|