| Identification | More | [Name]
Isosorbide dinitrate | [CAS]
87-33-2 | [Synonyms]
1,4:3,6-dianhydro-d-glucitol dinitrate
dilatrate-sr
ISDN
ISOSORBIDE DINITRATE
1,4:3,6-dianhydro-,dinitrate,d-glucito
1,4:3,6-dianhydro-d-glucitodinitrate
1,4:3,6-dianhydrosorbitol2,5-dinitrate
cardis
carvanil
carvasin
cedocard
claodical
corosorbide
dianhydrosorbitol2,5-dinitrate
dinitrosorbide
flindix
frandol
harrical
iso-bid
isochron | [EINECS(EC#)]
201-740-9 | [Molecular Formula]
C6H8N2O8 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00868238 | [Molecular Weight]
236.14 | [MOL File]
87-33-2.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
white to light yellow crystal powde | [Melting point ]
700C | [alpha ]
D20 +135° (alc) | [Boiling point ]
378.59°C (rough estimate) | [density ]
1.7503 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.5010 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
-20°C Freezer | [solubility ]
Undiluted isosorbide dinitrate is very slightly soluble in water, very soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent). The solubility of the diluted product depends on the diluent and its concentration. | [form ]
neat | [color ]
White to Off-White | [Water Solubility ]
549.7mg/L(25 ºC) | [Usage]
Coronary vasodilator | [BCS Class]
3 | [InChIKey]
MOYKHGMNXAOIAT-JGWLITMVSA-N | [LogP]
1.31 at 25℃ | [CAS DataBase Reference]
87-33-2(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
87-33-2(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R5:Heating may cause an explosion.
R22:Harmful if swallowed. | [Safety Statements ]
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing . | [RIDADR ]
UN 2907 | [HazardClass ]
4.1 | [PackingGroup ]
II | [HS Code ]
2932999000 | [Safety Profile]
Moderately toxic by
ingestion, intraperitoneal, intramuscular, and
subcutaneous routes. Experimental
reproductive effects. Mutation data
reported. A flammable solid. When heated
to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of
NOx. A coronary vasodilator. See also
NITRATES. | [Hazardous Substances Data]
87-33-2(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 oral in rat: 747mg/kg |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
A crystalline solid. May be toxic by ingestion. Used to make pharmaceuticals. Used as a heart drug. | [Reactivity Profile]
Nitroalkanes, such as ISOSORBIDE DINITRATE MIXTURE(87-33-2), range from slight to strong oxidizing agents. If mixed with reducing agents, including hydrides, sulfides and nitrides, they may begin a vigorous reaction that culminates in a detonation. Nitroalkanes are milder oxidizing agents, but still react violently with reducing agents at higher temperature and pressures. Nitroalkanes react with inorganic bases to form explosive salts. The presence of metal oxides increases the thermal sensitivity of nitroalkanes. Nitroalkanes with more than one nitro group are generally explosive. Nitroalkanes are insoluble in water. This heart drug is detonable when dry, but non-explosive with 30% of water. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water. | [Health Hazard]
Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution. | [Fire Hazard]
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by friction, heat, sparks or flames. Some may burn rapidly with flare burning effect. Powders, dusts, shavings, borings, turnings or cuttings may explode or burn with explosive violence. Substance may be transported in a molten form at a temperature that may be above its flash point. May re-ignite after fire is extinguished. | [Chemical Properties]
white to light yellow crystal powde | [Originator]
Isordil,Ives,US,1959 | [Uses]
Antianginal;Nitric oxide (NO) donor | [Uses]
Coronary vasodilator | [Uses]
Isosorbide dinitrate is also used in chronic cardiac insufficiency for preventing angina pectoris
attacks. It is a long-lasting drug. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Isosorbide dinitrate is a nitrate ester and a glucitol derivative. It has a role as a vasodilator agent and a nitric oxide donor. | [Manufacturing Process]
An aqueous syrup of 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-D-glucitol is slowly added to a cooled
mixture of HNO3 and H2SO4. After standing a few minutes the mixture is
poured into cold water and the precipitated product is collected and
recrystallized from ethanol. | [Brand name]
Dilatrate (Schwarz Pharma); Isordil (Biovail);
Isordil (Wyeth); Sorbitrate (AstraZeneca). | [Therapeutic Function]
Coronary vasodilator | [Clinical Use]
Vasodilator:
Prophylaxis and treatment of angina
Left ventricular failure | [Synthesis]
Isosorbiddinitrate, 1,4:3,6-dianhydrosorbate-2,5-dinitrate (19.1.4), is
synthesized by intermolecular dehydration of D-sorbite into isosorbide (19.1.3) using paratoluenesulfonic
acid and subsequent nitration of the two hydroxyl groups by nitric acid.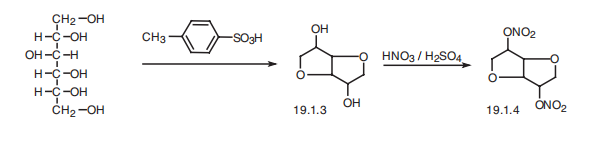
| [Veterinary Drugs and Treatments]
Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN) and dinitrate (ISDN) are organic
nitrates potentially useful as preload reducing agents in treating
heart failure in small animals, however, research and clinical experience
demonstrating clinical efficacy are lacking in dogs or cats.
Limited research indicates that dogs may require much higher dosages
of isosorbide dinitrate to achieve therapeutic effects than do
humans.
In humans, isosorbide nitrates are used for treating or preventing
angina, treating esophageal spasm, and as an adjunctive treatment
in CHF. | [Drug interactions]
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Avanfil, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil: hypotensive
effect significantly enhanced - avoid concomitant
use.
Riociguat: avoid concomitant use due to risk of
hypotension. | [Metabolism]
Isosorbide dinitrate undergoes extensive first-pass
metabolism in the liver. It is taken up by smooth muscle
cells of blood vessels and the nitrate group is cleaved
to inorganic nitrite and then to nitric oxide. It is also
rapidly metabolised in the liver to the major active
metabolites isosorbide 2-mononitrate and isosorbide
5-mononitrate. Isosorbide mononitrate is metabolised to
inactive metabolites, including isosorbide and isosorbide
glucuronide. Only about 2% of isosorbide mononitrate is
excreted unchanged in the urin | [storage]
4°C, protect from light |
|
|