| Identification | More | [Name]
4,4'-Isopropylidenedicyclohexanol | [CAS]
80-04-6 | [Synonyms]
2,2-BIS(4-HYDROXYCYCLOHEXYL)PROPANE
2,2-BIS(4-HYDROXYCYCLOHEXYL)PROPANONE
4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDICYCLOHEXANOL
BISPHENOL A HYDROGENATED
HYDROGENATED BISPHENOL A
PERHYDROBISPHENOL A
P,P'-DIHYDROXY-2,2-DICYCLOHEXYLPROPANE
4,4’-(1-methylethylidene)bis-cyclohexano
4,4’-(1-methylethylidene)bis-Cyclohexanol
4,4’-isopropylidenedicyclohexanol,mixtureo
2,2-Bis(hydroxycyclohexyl)propanone
4,4-Isopropylidenedicyclohexanol,mixture of isomers
H-BPA
4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDICYCLOHEXANOL, 90%,MIXTURE OF ISOMERS
HYDROGENATED BISPHENOL A, 4,4'-ISOPROPYLIDENEDICYCLOHEXANOL
4,4'-Isopropylidinedicyclohexanol
Cyclohexanol, 4,4-(1-methylethylidene)bis-
2,2-Bis(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)propane (mixture of isomers)
Maruzen H-BPA
4,4'-(Dimethylmethylene)bis(cyclohexane-1-ol) | [EINECS(EC#)]
201-244-2 | [Molecular Formula]
C15H28O2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00019334 | [Molecular Weight]
240.38 | [MOL File]
80-04-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
187 °C(Solv: benzene (71-43-2); ethanol (64-17-5)) | [Boiling point ]
230-234 °C14 mm Hg(lit.)
| [density ]
1.048±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [vapor pressure ]
0.001Pa at 25℃ | [Fp ]
>230 °F
| [solubility ]
Insoluble in water | [form ]
powder to lump | [pka]
15.01±0.40(Predicted) | [color ]
White to Almost white | [Water Solubility ]
192mg/L at 20℃ | [LogP]
2.5 at 25℃ | [CAS DataBase Reference]
80-04-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
80-04-6(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36:Irritating to the eyes. | [Safety Statements ]
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice . | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [HS Code ]
2906.19.5000 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
2,2-Bis(4-hydroxycyclohexyl)propane, also known as 4,4'-Isopropylidenedicyclohexanol, is a crystalline, colorless, and odorless compound. The conformation of the cyclohexane rings gives rise to cis-cis, cis-trans and trans-trans isomers. The industrial product is a mixture of these stereoisomers. The physical properties depend on the relative amounts of the isomers present. The trans-trans compound has the lowest energy and is formed from the other isomers at higher temperature. It has the lowest solubility in solvents such as methanol, butanol, and acetone and has the highest melting point of these isomers. | [Uses]
4,4'-isopropylidenedicyclohexanol is unsaturated polyester resin, epoxy resin raw materials, especially as glass, steel, artificial marble bathtub, plating tank and other components, and has a water resistance, chemical resistance, thermal stability and light stability. | [Production Methods]
4,4'-Isopropylidenedicyclohexanol is produced by hydrogenation of bisphenol A, 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane, an industrially important compound made from acetone and phenol (Phenol Derivatives). Bisphenol A is hydrogenated at about 10-30 MPa and at 150-250 ℃ on a nickel, cobalt, or ruthenium catalyst. | [Flammability and Explosibility]
Nonflammable | [Structure and conformation]
4,4' -Isopropylidenedicyclohexanol (HBPA), hydrogenated from bisphenol A (BPA), is a promising and revealing alicyclic candidate to offer diamine or dianhydride monomers. Due to the different spatial conformations of hydroxyls, HBPA has three isomers, including H' BPA, H''BPA, and H'''BPA, and their contents are 47%, 45%, and 8%, respectively. However, few reports about nonplanar HBPA-based polyimides were found, probably because of the difficulty separating HBPA isomers[1-2].
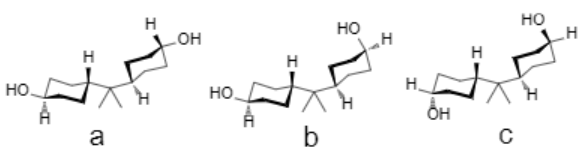 | [References]
[1] Z. Hou. “Soluble copolyimides containing 4,4′-isopropylidenedicyclohexanol (HBPA) isomer units: Synthesis, characterization, thermal, mechanical, and optical properties.” High Performance Polymers 32 1 (2019): 406–417.
[2] Zhiming Mi. “Transparent and soluble polyimide films containing 4,4′-isopropylidenedicyclohexanol (Cis-HBPA) units: Preparation, characterization, thermal, mechanical, and dielectric properties.” Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry 56 18 (2018): 2115–2128.
|
|
|