| Identification | More | [Name]
Avobenzone | [CAS]
70356-09-1 | [Synonyms]
1-(4-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)phenyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-propanedione
1-(4-TERT-BUTYLPHENYL)-3-(4-METHOXYPHENYL) 1,3-PROPANEDIOL
1-(P-T-BUTYLPHENYL)-3-(P-METHOXYPHENYL)-1,3-PROPANEDIONE
4-T-BUTYL-4'-METHOXY-DIBENZOYLMETHANE
4-tert-butyl-4'-methoxy-dibenzoylmethane
AVOBENZONE
EUSOLEX(R) 9020
PARSOL 1789
1-[4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl]-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-propanedione
1-[4-(1,2-Dimethylethyl)phenyl]-3-(4-methoxyphenyl-1,3-propanedione
Butylmethoxydibenzoylmethane
1-[4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl]-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-dione
1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-Tert-Butylphenyl)Propan-1,3-Dione
EUSOLEX 9020 95-105%
1-(4-TERT-BUTYLPHENYL)-3-(4-METHOXYPHENYL)-PROPANE-1,3-DIONE [AVOBENZONE]
Avobenzone(USP)
Butyl-methoxydibenzoylmethane (B-MDM). Sunblock, Parsol1789
1-(4-TERT-BUTYLPHENYL)-3-(4-METHOXYPHENYL)-1,3-PROPANDIONE
4-TERT-BUTYLMETHOXYDIBENZOYLMETHANE
TERT-BUTYLMETHOXYDIBENZOYLMETHANE | [EINECS(EC#)]
274-581-6 | [Molecular Formula]
C20H22O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00210252 | [Molecular Weight]
310.39 | [MOL File]
70356-09-1.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
81-84 °C | [Boiling point ]
463.6±35.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.079 | [vapor pressure ]
0Pa at 25℃ | [storage temp. ]
Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature | [solubility ]
Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated) | [form ]
neat | [pka]
9.74±0.13(Predicted) | [color ]
White to Pale Yellow | [Water Solubility ]
27μg/L at 20℃ | [λmax]
356nm(EtOH)(lit.) | [Merck ]
14,888 | [InChIKey]
GTIRDWBOUTYFQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [LogP]
6.1 at 20℃ | [Uses]
Avobenzone provides strong absorption through a large portion of the UVA spectrum including the majority of the UVA I range with peak absorption at 360 nm. Photostability refers to the ability of a molecule to remain intact with irradiation. It is potentially a problem with all UV filters, but particularly with the use of avobenzone. This effect may degrade other sunscreens in a formulation including octyl methoxycinnamate. Octocrylene and some of the newer sunscreens including BEMT stabilized avobenzone. Non-UV filters such as diethylhexyl 2,6 naphthalate may also be used. These molecules function as triplet–triplet quenchers. Overall formulation with avobenzone is therefore particularly critical. | [CAS DataBase Reference]
70356-09-1(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
70356-09-1(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
N | [Risk Statements ]
R50/53:Very Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment . | [Safety Statements ]
S60:This material and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste .
S61:Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions safety data sheet . | [RIDADR ]
UN3077 9/PG 3 | [WGK Germany ]
2 | [HS Code ]
29145000 | [Hazardous Substances Data]
70356-09-1(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Overview]
Avobenzone is a sunscreen agent that protects against the full spectrum of UV light. Of all sunscreen agents, avobenzone has one of the largest absorbance spectrums, absorbing light between 320 – 400 nm (peak absorption ~ 360 nm). Exposure to UV rays is a leading cause of skin cancer, and so use of an effective sunscreen, like avobenzone or avobenzone in combination with other agents, helps to lower risk of developing skin cancer. Avobenzone is specifically the most effective sunscreen agent against UVA rays. Avobenzone is susceptible to photodegredation, and therefore it is important that avobenzone be combined with photostabilizers in the final sunscreen product. It's been considered a relatively safe chemical, but recent research suggests otherwise. Avobenzone degrades in the sun, resulting in the release of free radicals that may actually increase the risk for cancer.[1][2]
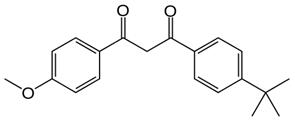
Figure 1 the chemical structure of Avobenzone
Ultraviolet (UV) light is harmful for skin cells since it can damage genetic material.[3–5] The ozone layer absorbs radiation below 290 nm and thus cosmetic sunscreens need to filter radiation in UV-A (320–380 nm) and UV-B (290–320 nm) bands. Although there are many available UV-B filters, proper UV-A filters are deficient. 1-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-3-(4-methoxyphenyl) propane-1, 3-dione (trade name avobenzone (AB)) is the most widely used UV-A absorber in cosmetic sunscreens.[6] Despite its importance as a UV-A absorber, the photodynamics of AB are not completely understood[7-9]. This is due to a fact that photoexcited AB transforms into several transient tautomeric forms the lifetimes of which range from ps to ms.[10-13] These tautomerizations together with photodegradation are responsible for a complete loss of UV-A protection under irradiation.; | [Application]
The Food and Drug Administration approved the use of avobenzone, a derivative of dibenzoylmethane, in commercial cosmetics for sunshine protection in 1988[14].
| [Properties]
Avobenzone belongs to a dibenzoyl methane derivative. It is oil soluble ingredient. Since it is very sensitive to light, photostablizers are added in the sunscreen product to increase its stability and duration of action. Avobenzone has an absorption maximum of 357 nm. Sunscreens containing avobenzone is indicated for providing protection from the sun. In addition to limiting the skin's exposure to the sun, using sunscreen agents may help reduce long-term sun damage such as premature aging of the skin and skin cancer. It is capable of blocking UVA I, UVA II and UVB wavelengths, thereby limiting the impact of UV rays on skin. Diminish the penetration of ultraviolet (UV) light through the epidermis by absorbing UV radiation within a specific wavelength range. The amount and wavelength of UV radiation absorbed are affected by the molecular structure of the sunscreen agent[15, 16].
| [Toxicity]
Although avobenzone itself has very low toxicity, when exposed to light in a chlorinated water solution, avobenzone can be broken down into a combination of aromatic acids, aldehydes, phenols and acetyl benzenes, several of which are highly toxic[14].
| [References]
- http://www.ewg.org/skindeep/ingredient/700596/AVOBENZONE/
- Karlsson I, Hillerström L, Stenfeldt AL, Mårtensson J, Börje A. "Photodegradation of dibenzoylmethanes: potential cause of photocontact allergy to sunscreens." Chemical Research in Toxicology. November 2009. doi: 10.1021/tx900284e.
- M.M.Petkovic?,M.R.Etinski,M.M.Ristic?,Hem.Ind.67(2013)203
- M.M.Ristic?,M.Petkovic?,M.Etinski,J.Serb.Chem.Soc.77(2012)1037
- G.P.Pfeifer,A.Besaratinia,Photochem.Photobiol.Sci.11(2012)90
- N.A.Shaath,Photochem.Photobiol.Sci.9(2010)464
- D. Veierov, T. Bercovici, E. Fischer, Y. Mazur, A. Yogev, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99 (1977) 2723
- H. Gonzenbach, T. J. Hill, T. G. Truscott, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 16 (1992) 377
- A.Cantrell,D.J.McGarvey,J.Photochem.Photobiol.,B64(2001)117
- M.Yamaji,M.Kida,J.Phys.Chem.,A117(2013)1946
- P.K.Verma,F.Koch,A.Steinbacher,P.Nuernberger,T.Brixner,J.Am.Chem.Soc.136 (2014) 14981
- A. D. Dunkelberger, R. D. Kieda, B. M. Marsh, F. F. Crim, J. Phys. Chem., A 119 (2015) 6155
- P. K. Verma, A. Steinbacher, F. Koch, P. Nuernberger, T. Brixner, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17 (2015) 8459
- https://www.upi.com/Science_News/2017/06/27/Sunscreen-chemical-breaks-down-into-toxic-compounds-when-exposed-to-sun-and-water/1241498577662/
- Zawadiak J, Mrzyczek M (October 2012). "Influence Of Substituent On UV Absorption And Keto–Enol Tautomerism Equilibrium Of Dibenzoylmethane Derivatives". Spectrochim Acta a Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 96: 815–819. Bibcode:2012 AcSpA..96..815Z. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2012.07.109. PMID 22925908.
- Vielhaber G, Grether-Beck S, Koch O, Johncock W, Krutmann J (March 2006). "Sunscreens with an absorption maximum of > or =360 nm provide optimal protection against UVA1-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1, interleukin-1, and interleukin-6 in human dermal fibroblasts". Photochem Photobiol Sci. 5 (3): 275&ndash, 282. doi:10.1039/b516702g. PMID 16520862.
|
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Avobenzone is a full-spectrum ultraviolet A (UVA) blocker.1 It inhibits UVA-induced increases in melanin levels and tyrosinase activity in B16/F10 melanoma cells (IC30s = 21.94 and 24.25 μM, respectively).2 Avobenzone (30 μM) also inhibits UVA-induced production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and 8-hydroxy-2''-deoxyguanosine (8-OH-dG; Item No. 89320), as well as inhibits UVA-induced depletion of glutathione (GSH; Item No. 10007461), in B16/F10 cells. It increases nuclear translocation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and upregulates the antioxidant response element (ARE) in UVA-irradiated B16/F10 cells when used at at a concentration of 30 μM. Formulations containing avobenzone have been used as a sun protectant in sunscreen products. | [Originator]
Avobenzone,AroKor Holdings
Inc. | [Definition]
ChEBI: Avobenzone is a member of dihydrochalcones. | [Manufacturing Process]
356.0 g (2 mol) of p-t-butylbenzoic acid, 243.0 g (7.6 mol) of methyl alcohol
and 35.0 g of sulfuric acid (96%) are added to a four-necked round flask
which is provided with a stirrer and a condenser. The mixture is held for 8 h at
reflux temperature with slight stirring. The condenser is then replaced by a
distillation column and the excess methyl alcohol is distilled off, towards the
end under a slight vacuum but without the temperature exceeding 100°C. The
mixture is cooled and poured on to ice. The phases are left to separate, the
organic phase is washed with ice-water, with a saturated sodium carbonate
solution in the presence of ice and finally with ice until neutral. The organic
phase is dried over sodium sulfate and there is thus obtained a precipitate. By
distillation on a Widmer column (120 mm) there are obtained 345.0 g (90%
yield) of the p-t-butylbenzoic acid methyl ester, boiling point 76°C/0.02
mmHg.
2 methods of producing of 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4'-methoxydibenzoylmethane from p-t-butylbenzoic acid methyl ester:
1). To a round flask which has been well dried and flushed with nitrogen are
added 85.0 g (1.1 mol) of sodium amide (50% suspension in toluene) and
180.0 g of isopropyl ether and there are now added dropwise thereto at a
temperature of 50°-60°C 150.2 g (1 mol) of acetylanisole in 180.0 g of
isopropyl ether. Reaction sets in immediately and a white paste-like mass
forms. After completion of the addition, the mixture is stirred for a further 0.5
h and then 192.3 g of p-t-butylbenzoic acid methyl ester are added rapidly at
25°-30°C. The mixture is stirred for 0.5 h at room temperature, then for 3 h
at 60°-70°C and left to stand for 12 h. 200.0 g of ice are then added and the
mixture is acidified with 128.0 g (1.1 mol) of technical hydrochloric acid and
200 ml of ice-water. The mixture is stirred until the sodium salt of the product
has dissolved. The phases are separated and the organic phase is washed with
ice-water until neutral. The organic phase is concentrated on a rotary
evaporator and there are thus recovered 290.0 g of isopropyl ether. The yield
of 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4'-methoxydibenzoylmethane, melting point 83.5°C is
199.8 g (64.5%) (recrystallisation from methanol).
2). 36.0 g (1.2 mol) of 80% sodium amide and 300.0 g of dry toluene are
added to a round flask which was flushed with nitrogen. The mixture is heated
to 50°C and 150.2 g (1 mol) of acetylanisole in 309.0 g of toluene are added
within 1.5 h. After completion of the addition, the mixture is held at 50°C for
15 min and there are then added thereto at this temperature within 1 h 50
min 192.3 g (1 mol) of p-t-butylbenzoic acid methyl ester. The mixture is
stirred for a further 1 h at 50°C and then heated at 100°C for 1 h, after which
time the product has separated out in the form of a solid precipitate. The
mixture is left to stand for 12 h and there are then added thereto 300 ml of
ice-water followed by a mixture of 100 ml of pure hydrochloric acid and 250
ml of ice-water. The phases are separated and the organic phase is washed
twice with water. The organic phase is dried over sodium sulfate and treated
simultaneously with 20.0 g of active carbon. After filtration, the filtrate is
concentrated until crystallisation begins. 50 ml of hexane are added, the
mixture is cooled and then filtered over a Buchner funnel. There is obtained a
total yield of 220.91 g (71.2%) of the desired 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4'-
methoxydibenzoylmethane, of melting point 83.5°C (recrystallisation from 600
ml of methanol). | [Brand name]
Parsol 1789 (Givaudan S.A.,
Switzerland). | [Therapeutic Function]
Sunscreen agent | [General Description]
Avobenzone is an UVA filter. It is used in sunscreen lotions and cosmetic formulations. It has maximum absorption at ca 340–350 nm, decreasing under UV irradiation resulting in loss of the UVA protecting effect. Its photostability is very sensitive as it is stable in polar protic solvent and is photolabile in nonpolar solvents. | [Flammability and Explosibility]
Nonflammable |
|
|