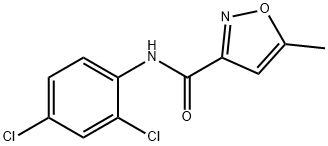
| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
3-Isoxazolecarboxamide, N-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl- | [CAS]
646530-37-2 | [Synonyms]
UTL-5g
UGL-5g
3-Isoxazolecarboxamide, N-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl- | [Molecular Formula]
C11H8Cl2N2O2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD08724989 | [MOL File]
646530-37-2.mol | [Molecular Weight]
271.1 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Boiling point ]
336.2±42.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.469±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
9.45±0.70(Predicted) | [color ]
White to off-white |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Biological Activity]
UTL-5g (GBL-5g) is an anti-inflammatory TNF-α inhibitor with chemoprotective and hepatic radioprotective effects. It reduces cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity and bone marrow toxicity by inhibiting factors such as TNF-α. | [in vitro]
RAW 264.7 macrophages are transfected with the respective reporter assay plasmids, pretreated with UTL-5g at 1, 10 or 50 μM for 60 min and then challenged with 100 ng/ml LPS. After a 16 h incubation, transcription factor activity is measured. Transcription factors that shows a UTL-5g dose-dependent decrease in activity in two experiments are categorized as being disrupted by UTL-5g. | [in vivo]
UTL-5g (GBL-5g) lowers levels of TGF-β and TNF-α elevated by lung irradiation.
UTL-5g (60 mg/kg; po; daily for 4 days) shows positive effects in increasing the survival rates and extending the survival times. | Animal Model: | C57BL/6, male mice (8-10 weeks) | | Dosage: | 15, 30, and 60 mg/kg | < /tr> | Administration: | Ip; before irradiation, daily x 5 | | Result: | Blood levels of TGF-β were lowered. | | Animal Model: | BDF1 female mice | | Dosage: | Po; daily for 4 days | | Administration: | 60 mg/kg (30 min before ip injection of Cisplatin at 10, 15, and 20 mg/kg respectively on Day 0) | | Result: | Increased the survival rate and delayed the time to death for mice treated with 150% of the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of Cisplatin (15 mg/kg). At 200% of the MTD of Cisplatin (20 mg/kg), treatment of UTL-5g increased the survival rate and delayed the time to death. | |
|
|