| Identification | More | [Name]
Floxuridine | [CAS]
50-91-9 | [Synonyms]
1-(2-DEOXY-BETA-D-RIBOFURANOSYL)-5-FLUOROURACIL
2'-DEOXY-5-FLUOROURIDINE
2-DEOXY-5'-FLUOROURIDINE
5-FDU
5-FLOXURIDINE
5-FLUORO-1-((2R,4S,5R)-4-HYDROXY-5-HYDROXYMETHYL-TETRAHYDRO-FURAN-2-YL)-1H-PYRIMIDINE-2,4-DIONE
5-FLUORO-2'-DEOXY-BETA-URIDINE
(+)-5-FLUORO-2'-DEOXYURIDINE
5-FLUORO-2'-DEOXYURIDINE
5-FLUORO-2-DEOXYURIDINE
(+)-5-FLUORODEOXYURIDINE
5-FLUORODEOXYURIDINE
FDURD
FLOXURIDINE
fluorodeoxyuridine
fluoruridine deoxyribose
FUDR
1-beta-d-2’-deoxyribofuranosyl-5-flurouracil
1beta-D-2'-Deoxyribofuranosyl-5-fluorouracil
2’-deoxy-5-fluoro-uridin | [EINECS(EC#)]
200-072-5 | [Molecular Formula]
C9H11FN2O5 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00006530 | [Molecular Weight]
246.19 | [MOL File]
50-91-9.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
White Solid | [Melting point ]
148 °C(lit.)
| [alpha ]
35.9 º (c=1, water) | [Boiling point ]
150 °C | [density ]
1.3751 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
Soluble to 100 mM in water and to 100 mM in DMSO | [form ]
Powder | [pka]
pKa 7.44 (Uncertain) | [color ]
White to almost white | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. | [biological source]
synthetic (organic) | [Water Solubility ]
soluble | [Usage]
Antiviral; antineoplastic. | [Merck ]
14,4112 | [BRN ]
2645818 | [InChIKey]
ODKNJVUHOIMIIZ-GFCOJPQKSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
50-91-9(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
Uridine, 2'-deoxy-5-fluoro-(50-91-9) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
50-91-9(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn,T,Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R68:Possible risk of irreversible effects.
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin .
R40:Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect.
R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . | [Safety Statements ]
S22:Do not breathe dust .
S36:Wear suitable protective clothing .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice . | [RIDADR ]
UN 2811 6.1/PG 3
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
YU7525000
| [F ]
10-23 | [Hazard Note ]
Toxic | [HazardClass ]
6.1 | [PackingGroup ]
III | [HS Code ]
29349990 | [Safety Profile]
Poison by ingestion.
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route.
An experimental teratogen. Other
experimental reproductive effects. Human
systemic effects: hypermotitity, diarrhea,
nausea, vomiting and other gastrointestinal
effects, allergic dermatitis, and bone marrow
changes. Human mutation data reported.
When heated to decomposition it emits very
toxic fumes of Fand NOx. | [Hazardous Substances Data]
50-91-9(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 oral in rat: 215mg/kg |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
Inhibits DNA synthesis. | [Health Hazard]
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: This material is highly toxic by ingestion. | [Fire Hazard]
Flash point data for this chemical are not available, but 5-FLUORODEOXYURIDINE is probably combustible. | [Description]
Floxuridine is a nucleoside analog that inhibits the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase, which is involved in the synthesis of DNA. Floxuridine has been shown to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis in vivo. Floxuridine has also been shown to inhibit tumor growth in animal models by inhibiting the production of reactive oxygen species and upregulating tumor suppressor genes, such as p53. This drug also has inhibitory effects on enzymes that are involved in cell proliferation, such as protein kinase C and tyrosine kinases. | [Chemical Properties]
White Solid | [Originator]
FUDR,Roche,US ,1971 | [Uses]
Antiviral; antineoplastic. | [Uses]
Floxuridine USP is used in Palliative treatment of gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma with liver metastases. | [Uses]
renal function diagnosis | [Definition]
ChEBI: A pyrimidine 2'-deoxyribonucleoside compound having 5-fluorouracil as the nucleobase; used to treat hepatic metastases of gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas and for palliation in malignant neoplasms of the liver and gastrointestinal tract. | [Manufacturing Process]
Cells of Streptococcus fecalis (ATCC-8043) were grown in the AOAC folic acid
assay medium [Lepper, Official and Tentative Methods of the Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, Washington, D.C., 7th edition, 784 (1950)],
supplemented with 2 mg per liter of thymine; following the teachings of
Prusoff, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. & Med. 85, 564 (1954). After 20 hours of
incubation at 37°C, the cells were harvested by centrifugation. The collected
cells were washed three times with four volumes of potassium phosphate
buffer solution (M/15 aqueous KH2PO4 solution, adjusted to pH 8.0 by addition
of 2 N aqueous KOH) and the wet cells were weighed. The cells were finally
suspended in the above potassium phosphate buffer solution and ground in a
glass tissue homogenizer.
An amount of enzyme preparation equivalent to 900 mg of wet cells was
made up to 25 ml with the above potassium phosphate buffer solution. 150
mg (1.15 mmol) of 5-fluorouracil and 1.0 gram of thymidine (4.12 mmol)
were dissolved in 15 ml of the above potassium phosphate buffer solution.
The mixture was incubated at 37°C for 18 hours. After this time, enzyme
action was stopped by the addition of four volumes of acetone and one
volume of peroxide-free diethyl ether. The precipitated solids were removed by
filtration, and the filtrate was evaporated under nitrogen at reduced pressure
until substantially all volatile organic solvent had been removed. About 20 ml
of aqueous solution, essentially free of organic solvent, remained. This
solution was diluted to 100 ml with distilled water.
Ten microliters of this solution were submitted to descending chromatography
on a paper buffered with 0.2 N KH2PO4 (pH 7.8), using a solvent mixture of
tertiary amyl alcohol:water:n-butyl ether (80:13:7 by volume). A spot visible
under ultraviolet light and having Rf = 0.55 was leached with 0.1 N HCl and
assayed for deoxyribose by the method of Stumpf, J. Biol. Chem. 169, 367
(1947). This analysis indicated the presence of a minimum of 85.5 mg (0.35
mmol) of 2'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine in the protein-free reaction mixture
according to US Patent 2,885,396. An alternate route from 5-fluorouracil via
the mercury derivative, through toluoyl deoxyuridines and then toluoyl
removal to give floxuridine is described in US Patent 3,041,335.
| [Brand name]
Fudr (Mayne). | [Therapeutic Function]
Antiviral, Cancer chemotherapy | [Biochem/physiol Actions]
Antineoplastic drug that acts as a potent inhibitor of thymidylate synthetase Resistance to FUdR can develop in cancer cell cultures, among other means, by low-level Mycoplasma infection. | [Synthesis]
Fluoxuridine, 5-fluoro-1-(2-deoxyribofuranosyl)-pyrimidin-2,4-(1H,3H)-
dione (30.1.3.5), is a pyrimidine nucleotide made by reacting fluorouracil (30.1.3.3) with
2-deoxyribofuranosylbromide in the presence of silver or mercury salts.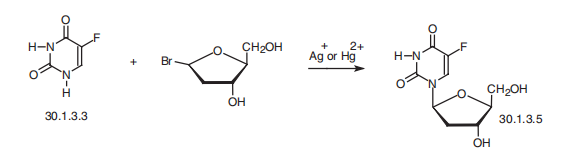
| [storage]
Store at -20°C |
|
|