| Identification | More | [Name]
Lithium chromate | [CAS]
14307-35-8 | [Synonyms]
chroman dilitny
LITHIUM CHROMATE
chromicacid(h2cro4),dilithiumsalt
Chromicacid,dilithiumsalt
chromiumlithiumoxide
chromiumlithiumoxide(crli2o4)
dilithiumchromate
dilithiumchromate(li2cro4)
lithiumchromate(li2cro4)
lithiumchromate(vi)
lithiumchromiumoxide(li2cro4)
Lithium chromate anhydrous
Lithiumchromate,min.95%
Lithiumchromat
lithium chromium oxide
Lithium chromate
Lithium chromate, min. 95%
Lithiumchromateminyellowxtl | [EINECS(EC#)]
238-244-7 | [Molecular Formula]
CrLi2O4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00016175 | [Molecular Weight]
129.88 | [MOL File]
14307-35-8.mol |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T,N | [Risk Statements ]
R8:Contact with combustible material may cause fire.
R43:May cause sensitization by skin contact.
R49:May cause cancer by inhalation.
R50/53:Very Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment . | [Safety Statements ]
S17:Keep away from combustible material .
S36/37/39:Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection .
S53:Avoid exposure-obtain special instruction before use .
S60:This material and/or its container must be disposed of as hazardous waste . | [RIDADR ]
1479 | [HazardClass ]
6.1(b) | [PackingGroup ]
III | [Hazardous Substances Data]
14307-35-8(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
A yellow crystalline solid. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. LITHIUM CHROMATE(14307-35-8) is used as a corrosion inhibitor and in the manufacture of other chemicals. | [Reactivity Profile]
LITHIUM CHROMATE is an oxidizing agent. Can oxidize combustibles [USCG, 1999]. Combining the chromate with zirconium can be explosive given the right proportions of reactants, [Z. Anorg., 1930, 191, 113]. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Deliquescent. Water soluble | [Health Hazard]
INHALATION: Corrosive to skin and mucous membranes causing dermatitis and slow healing ulcers. EYES: Conjunctivitis and lacrimation. INGESTION: Violent gastroenteritis, peripheral vascular collapse, vertigo, muscle cramps, coma, hemorrhagic diathesis, fever, liver damage and renal failure. | [Potential Exposure]
Used as a corrosion inhibitor, heat
transfer agent; and oxidizing agent in leather and metal finishing. Also used in photography, wood preservatives; batteries, safety matches, and cement | [First aid]
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any
contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least
15 minutes, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek
medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the
skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately
with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately.
If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,
begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if
heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical
facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce
vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. | [Shipping]
UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard
Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical
Name Required.
| [Incompatibilities]
Aqueous solution is caustic. A strong
oxidizer; strong reaction with reducing agents, combustibles, organic material, hydrazine, chromic acid; sulfur,
acids. Attacks plastics and aluminum | [Description]
Lithium chromate is a yellow crystalline powder. Molecular weight = 165.92; 129.87 (lithium chromate(VI)); 131.90 (dilithium chromate); Melting point =75℃.Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 2, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Soluble inwater. | [Chemical Properties]
Lithium chromate is a yellow crystalline powder. | [Uses]
Lithium Chromate is used in preparation method method of permeable crystalline cement-based waterproof coating by using maifanstone composite high water-absorbing resin and its application in building. | [Preparation]
According to the following equations, Li2CrO4 is formed on boiling a solution of (NH4)2Cr2O7 with LiOH.
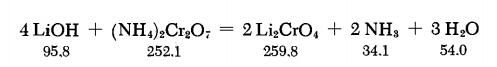 | [storage]
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. A regulated, marked area should be establishedwhere this chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045. Store in tightlyclosed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from acids, hydrazine, chromic acid, combustible materials, sulfur, aluminum, plastics, and reducing agents. | [References]
[1] YINGCHUN LYU. Atomic insight into electrochemical inactivity of lithium chromate (LiCrO2): Irreversible migration of chromium into lithium layers in surface regions[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 273 1: 1218-1225. DOI:10.1016/J.JPOWSOUR.2014.09.082.
[2] N.K. SHUKLA. Thermochemistry of lithium chromate Li2CrO4(cr) and lithium molybdate Li2MoO4(cr)[J]. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 1992, 24 9: Pages 897-903. DOI:10.1016/S0021-9614(05)80001-1. |
|
|