| Identification | More | [Name]
Cadmium sulfide | [CAS]
1306-23-6 | [Synonyms]
CADMIUM SULFIDE
aurorayellow
c.p.goldenyellow55
cadmiumgolden366
cadmiumlemonyellow527
cadmiummonosulfide
cadmiumorange
cadmiumprimrose819
cadmiumsulfide(cds)
cadmiumsulfideyellow
cadmiumsulphide
Cadmiumyellow
cadmiumyellow000
cadmiumyellow10gconc
cadmiumyellow892
cadmiumyellowconc.deep
cadmiumyellowconc.golden
cadmiumyellowconc.lemon
cadmiumyellowconc.primrose
cadmiumyellowconcdeep | [EINECS(EC#)]
215-147-8 | [Molecular Formula]
CdS | [MDL Number]
MFCD00010922 | [Molecular Weight]
144.48 | [MOL File]
1306-23-6.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Definition]
A native cadmium sulfide containing 77.7% cadmium. Ore of cadmium | [Appearance]
Cadmium sulfide is an odorless, crystalline,
lemon yellow to orange solid. | [Melting point ]
980°C (subl.) | [Boiling point ]
980°C (estimate) | [density ]
4.82 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
| [Fp ]
4℃ | [storage temp. ]
2-8°C | [solubility ]
Soluble in acid, very slightly soluble in ammonium hydroxide. | [form ]
powder
| [color ]
Yellow to orange | [Specific Gravity]
4.82 | [Water Solubility ]
Insoluble | [Crystal Structure]
Cubic, Sphalerite Structure - Space Group F(-4)3m | [λmax]
370-390 nm | [crystal system]
Cube | [Merck ]
14,1628 | [Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)]
pKsp: 26.1 | [Space group]
F43m | [Lattice constant]
| a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/o | β/o | γ/o | V/nm3 | | 0.58304 | 0.58304 | 0.58304 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 0.1982 |
| [Exposure limits]
ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3; TWA 0.002 mg/m3
NIOSH: IDLH 9 mg/m3 | [Uses]
cadmium sulfide is used as a colorant for paints and rubber; cadmium acetate is used in the production of craftware. | [CAS DataBase Reference]
1306-23-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
1306-23-6(EPA Substance) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
T,N | [Risk Statements ]
R45:May cause cancer.
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R48/23/25:Toxic: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation and if swallowed .
R53:May cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.
R62:Possible risk of impaired fertility.
R63:Possible risk of harm to the unborn child.
R68:Possible risk of irreversible effects. | [Safety Statements ]
S53:Avoid exposure-obtain special instruction before use .
S45:In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show label where possible) .
S61:Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions safety data sheet . | [RIDADR ]
UN 3077 9/PG 3
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
EV3150000
| [TSCA ]
Yes | [HazardClass ]
6.1 | [PackingGroup ]
III | [Safety Profile]
Confirmed human
carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic
and tumorigenic data. Moderately toxic by
ingestion and inhalation. Human mutation
data reported. When heated to
decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of
Cd and SOx. See also CADMIUM
COMPOUNDS and SULFIDES | [Hazardous Substances Data]
1306-23-6(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Hazard]
A confirmed carcinogen, highly toxic. See
cadmium.
| [Potential Exposure]
Used in pigments; as an active ingredient in dandruff shampoos; making photoconductors, solar
cells, and other electronic components. | [First aid]
Move victim to fresh air. Call 911 or emergency
medical service. Give artificial respiration if victim is not
breathing. Do not use mouth-to-mouth method if victim
ingested or inhaled the substance; give artificial respiration with the aid of a pocket mask equipped with a one-way
valve or other proper respiratory medical device.
Administer oxygen if breathing is difficult. Remove and
isolate contaminated clothing and shoes. In case of contact
with substance, immediately flush skin or eyes with running water for at least 20 minutes. For minor skin contact,
avoid spreading material on unaffected skin. Keep victim
warm and quiet. Effects of exposure (inhalation, ingestion,
or skin contact) to substance may be delayed. Ensure that
medical personnel are aware of the material(s) involved
and take precautions to protect themselves. Medicalobservation is recommended for 24 to 48 hours after
breathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may be
delayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor or
authorized paramedic may consider administering a drug or
other inhalation therapy. | [Shipping]
UN2570 Cadmium compounds, Hazard Class:
6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name
Required. | [Incompatibilities]
Contact with water or moisture releases
poisonous hydrogen sulfide gas. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause | [Description]
Cadmium sulfide is an odorless, crystalline,lemon yellow to orange solid. Molecular weight=144.48;Specific gravity (H2O:1)=4.8; Sublimation point=978℃.Insoluble in water. | [Chemical Properties]
Cadmium sulfide is an odorless, crystalline,
lemon yellow to orange solid. | [Chemical Properties]
yellow to orange crystalline powder | [Waste Disposal]
Use a licensed professional
waste disposal service to dispose of this material. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be
observed. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies
for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators
of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must
conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposa | [Physical properties]
Yellow to orange crystal; occurs as two polymorphs, hexagonal alpha form and cubic beta form; exhibits stable wurtzite structure at lower temperature, and zinc blende type structure at higher temperatures; the beta form converts to alpha form when heated at 750°C in sulfur atmosphere; sublimes at 980°C; practically insoluble in water (1.3 mg/L at 20°C); Ksp 3.6x10-29; dissolves in dilute mineral acids on heating or concentrated acids at ordinary temperatures (decomposes with liberation of H2S). | [Occurrence]
Cadmium sulfide occurs in nature as the mineral greenoktite. The compound is widely used in pigments for paints, baking enamels, ceramics and plastics. It imparts bright yellow to maroon, with strong retention of color and resistance to alkalis. It also is used in inks, phosphors, and fluorescent screens. Other applications of this compound are in photovoltaic and solar cells (for converting solar energy to electrical energy), photoconductors (in xerography), thin film transistors and diodes, rectifiers, scintillation counters, pyrotechnics, and smoke detectors. | [Preparation]
Cadmium sulfide may be prepared by precipitation from an aqueous solution of its soluble salts such as cadmium chloride or cadmium nitrate by passing hydrogen sulfide. The reactions may be carried out in acidic, neutral or alkaline solutions using various cadmium salts to obtain different crystal modifications as shown in the table below.
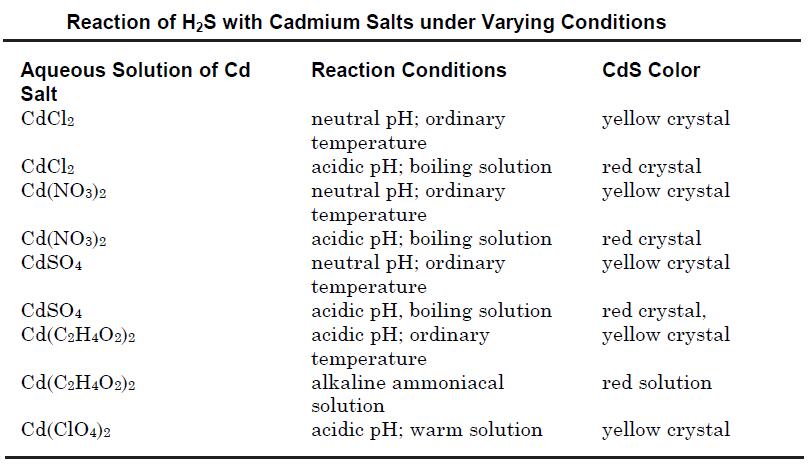
Cadmium sulfide also may be obtained by treatment of sodium or other alkali metal sulfide solution with that of a soluble cadmium salt. The compound also may be prepared by heating a mixture of cadmium or its oxide with sulfur at 800°C; or by the reaction of H2S with cadmium vapor at 800°C.
| [Production Methods]
Cadmium sulfide may be prepared by the reaction between
hydrogen sulfide and cadmiumvapor at 800 Cor by heating a
mixture of cadmium or cadmium oxide with sulfur. | [General Description]
Natural occurrence: hawleyite (structural type of sphalerite) and greenockite (structural type of wurtzite) | [reaction suitability]
reagent type: catalyst
core: cadmium | [Solubility in water]
Cadmium sulfide is soluble in water, with a solubility of 13×10-5 g/100 ml H2O (18℃). CdS is soluble in acid.
| [storage]
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard: Store in asecure poison location. Prior to working with Cadmium sulfide, you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. A regulated, marked area should be established wherethis chemical is handled, used, or stored in compliance withOSHA Standard 1910.1045. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, dark, well-ventilated area away from oxidizersand metals, strong acids, water or moisture, and otherincompatible materials listed above. | [Structure and conformation]
Cadmium sulfide takes two types of structure, zinc blend and wurtzite structures.
Cubic system that has a zinc-blend structure, with a lattice constant of a=0.582 nm and Cd– S=0.252 nm.
Hexagonal system that has a wurtzite structure with lattice constants of a=0.4136 nm, c=0.6713 nm and c/a=1.624, Cd–S=0.252 nm.
|
|
|