| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride | [CAS]
1256589-74-8 | [Synonyms]
CH-5428402
Alectinib HCl
CH5424802 HCl
CH-5428402 HCl
Alectinib HCl salt
AF-802 Hydrochloride
RG-7853 Hydrochloride
Alectinib Hydrochloride
CH5424802 Hydrochloride
CH-5424802 Hydrochloride
RO-5424802 Hydrochloride
CH 5424802,Alectinib(HCl)
Alectinib (CH5424802) HCl
Alectinib Hydrochloride (Alecensa)
Alectinib (CH5424802) hydrochloride
CH5424802 HCl (AF 802 HCl, Alectinib HCl)
CH5424802 HCl salt, Alectinib HCl salt, AF802 HCl salt
9-ethyl-6,6-dimethyl-8-(4-morpholin-4-ylpiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile,hydrochloride
9-ethyl-6,6-diMethyl-8-(4-Morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-5a,6,11,11a-tetrahydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
9-Ethyl-6,11-dihydro-6,6-dimethyl-8-[4-(4-morpholinyl)-1-piperidinyl]-11-oxo-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride (1:1)
5H-Benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile, 9-ethyl-6,11-dihydro-6,6-dimethyl-8-[4-(4-morpholinyl)-1-piperidinyl]-11-oxo-, hydrochloride (1:1)
9-ethyl-6,6-dimethyl-8-(4-morpholin-4-yl-piperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile monohydrochloride monohydrate | [Molecular Formula]
C30H37ClN4O2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD27987893 | [MOL File]
1256589-74-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
521.093 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [solubility ]
DMSO:3.5(Max Conc. mg/mL);6.74(Max Conc. mM) | [form ]
Solid | [color ]
White to Off-White | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Alectinib hydrochloride(1256589-74-8), developed by Chugai Pharmaceutical/
Hoffman-La Roche under the trade name Alecensa?, was approved
in Japan in April 2014 for the treatment of anaplastic lymphoma
kinase (ALK) fusion-gene positive, unresectable, advanced, or
recurrent non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The compound is
a highly selective second-generation ALK inhibitor, and while
alectinib currently remains a focus of further development in Europe
and the U.S., the compound has been granted orphan drug designation
in Japan after showing a 93.5% objective response rate in
phase II clinical trials. In addition to providing rapid treatment
response time in a majority of patients, trials showed a 76%
2-year progression-free survival rate. Since the initial approval
of crizotinib—the first ALK inhibitor indicated for treatment of ALKrearranged
NSCLC —patients treated with crizotinib have shown
remarkable improvement as compared to treatment with other
chemotherapeutic methods,21 although drug resistance has shown
to be a major side effect of this therapy. Preliminary preclinical
and clinical studies of alectinib have shown significant promise
for overcoming drug resistance developed with other ALK
inhibitors.
| [Uses]
Alectinib hydrochloride is a selective anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor leading to inhibition of tumor cell proliferation and induction of cell death. | [Definition]
ChEBI:Alectinib hydrochloride is a hydrochloride obtained by combining alectinib with one molar equivalent of hydrochloric acid. Used for the treatment of patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive, metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent and an EC 2.7.10.1 (receptor protein-tyrosine kinase) inhibitor. It contains an alectinib(1+). | [Synthesis]
The synthetic route to alectinib as reported by Chugai
begins with 7-methoxy-2-tetralone (1). Bis-methylation
with tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfide (TBAHS)/aq KOH/MeI
followed by bromination with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) provided
the bromo-tetralone 2 in 67% yield over the two steps. Further
reaction of 2 with 3-hydrazinobenzonitrile/trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) led to formation of the desired Fischer indole product,
albeit as a 1:1 mixture of regioisomers (3/4), which were carried
forward as a mixture to oxidation with 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-
1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ). It is important to note that although representative
procedures are published describing the conversion of
2 to alectinib (I), no yields were provided for these transformations.
Following oxidation, the desired product 5 could be isolated
as a single isomer via precipitation from the crude reaction mixture.
Installation of the 4-morpholino-piperidine moiety took place
in three transformations from 5, beginning with 1-dodecanethiol/
N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP)/NaOMe-facilitated methyl cleavage.
The corresponding phenol was then readily converted to the
triflate intermediate and displaced with 4-(piperidin-4-yl)morpholine
(6) at elevated temperature, providing intermediate 7. Crosscoupling
of the bromide 7 with ethynyl triisopropylsilane under
Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling conditions (Pd(CH3CN)2Cl2/2-dicyclohexylphosphino-
20,40,60-triisopropylbiphenyl (XPhos), reflux) followed
by cleavage of the resulting alkylsilane with
tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) yielded the ethynyl precursor
to alectinib. Hydrogenation of this unsaturated system under
standard conditions (H2, Pd/C) followed by HCl salt formation furnished
the final drug target alectinib hydrochloride (I).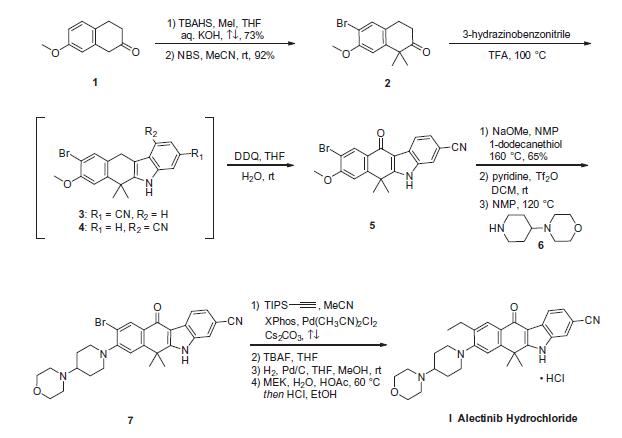
| [IC 50]
1.9 nM | [storage]
Store at -20°C |
|
|