| Identification | More | [Name]
Edrophonium chloride | [CAS]
116-38-1 | [Synonyms]
EDROPHONIUM CHLORIDE
ETHYL[M-HYDROXYPHENYL]-DIMETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE
antirex
dimethylethyl(m-hydroxyphenyl)-ammoniuchloride
ethyl(m-hydroxyphenyl)dimethyl-ammoniuchloride
n-ethyl-3-hydroxy-n,n-dimethyl-benzenaminiuchloride
tensilon
ethyl(3-hydroxyphenyl)dimethylammonium chloride
N-ethyl-3-hydroxy-N,N-dimethylanilinium chloride
Edrophonium
Benzenaminium, N-ethyl-3-hydroxy-N,N-dimethyl-, chloride
Enlon
Dimethylethyl(m-hydroxyphenyl)ammonium chloride | [EINECS(EC#)]
204-138-4 | [Molecular Formula]
C10H16ClNO | [MDL Number]
MFCD00055064 | [Molecular Weight]
201.69 | [MOL File]
116-38-1.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
White or almost white, crystalline powder | [Melting point ]
162-163 °C (decomp) | [density ]
1.0787 (rough estimate) | [refractive index ]
1.6000 (estimate) | [storage temp. ]
Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature | [solubility ]
Very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride. | [form ]
A crystalline solid | [color ]
White to light yellow | [InChIKey]
BXKDSDJJOVIHMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
116-38-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
BQ5870000
| [HS Code ]
2923900100 | [Toxicity]
mouse,LD50,intraperitoneal,30mg/kg (30mg/kg),Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal Vol. 10, Pg. 327, 1976. |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
White or almost white, crystalline powder | [Originator]
Tensilon,Roche,US,1951 | [Uses]
A reversible Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. | [Uses]
Edrophonium (chloride) is an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor that is known to prevent the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by binding specifically to its catalytic site. It has been shown to inhibit AChE activity in human red blood cells, purified calf forebrain, and purified octopus brain with Ki values of 0.2, 0.2, and 0.4 μM, respectively. Edrophonium is often used as part of a battery of pharmacological tests to confirm a diagnosis of the autoimmune neuromuscular junction disorder, myasthenia gravis. | [Uses]
Myasthenia Gravis test;Cholinergic | [Definition]
ChEBI: The chloride salt of edrophonium. A reversible inhibitor of cholinesterase with a rapid onset (30-60 seconds after injection) but a short duration of action (5-15 minutes), it is used in myasthenia gravis both diagnostically and to distinguish between unde
- or over-treatment with other anticholinesterases. It has also been used for the reversal of neuromuscular blockade in anaesthesia, and for the management of poisoning due to tetrodotoxin, a neuromuscular blocking toxin found in puffer fish and other mari
e animals. | [Manufacturing Process]
A solution made up of 10 grams of m-dimethylaminophenol, 50 cc of acetone
and 13 grams of ethyl iodide was heated at 50°C for five hours. On addition
of ether to the cooled solution, (3-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl dimethylammonium
iodide precipitated as an oil which soon crystallized. Upon recrystallization
from isopropanol the compound had a MP of 113° to 115°C.
A slight excess of a 10% sodium hydroxide solution was added to a solution of
23 grams of silver nitrate in 300 cc of water. The precipitated silver oxide was
washed free of silver ion with distilled water. To a suspension of the silver
oxide in 200 cc of water, a solution of 25 grams of (3-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl
dimethylammonium iodide in 300 cc of water was added. The precipitate of
silver iodide was removed by filtration and the filtrate concentrated to a
volume of about 100 cc in vacuo. The remainder of the water was removed by
lyophilization. (3-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl dimethylammonium hydroxide was
obtained as a hygroscopic, amorphous solid.
A solution of 5 grams of (3-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl dimethylammonium
hydroxide in about 200 cc of water was neutralized with dilute hydrochloric
acid. On concentration to dry ness in vacuo, (3-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl
dimethylammonium chloride crystallized. The compound was recrystallizedfrom isopropanol; MP 162° to 163°C (with decomposition). | [Brand name]
Enlon (Baxter Healthcare); Reversol (Organon); Tensilon (Valeant). | [Therapeutic Function]
Cholinergic (ophthalmic) | [General Description]
Edrophonium chloride,ethyl(m-hydroxyphenyl)dimethylammonium chloride(Tensilon), is a reversible anticholinesterase agent. It isbitter and very soluble in water and alcohol. Edrophoniumchloride injection has a pH of 5.2 to 5.5. On parenteral administration,edrophonium has a more rapid onset andshorter duration of action than neostigmine, pyridostigmine,or ambenonium. It is a specific anticurare agent andacts within 1 minute to alleviate overdose of d-tubocurarine,dimethyl d-tubocurarine, or gallamine triethiodide. | [Biological Activity]
edrophonium is a competitive inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (ache) [1]. ache is an extrinsic membrane-hound enzyme that functions in the central and peripheral nervous systems. ache rapidly terminates the ach receptor-mediated signal transmission by hydrolyzing ach. inhibition of ache results in accumulation of ach in the synaptic cleft and leads to impeded neurotransmission [2]. | [Clinical Use]
Edrophonium Chloride is also used to terminate the action of any one ofthese drugs when the physician so desires. It is of no value,however, in terminating the action of the depolarizing (i.e.,noncompetitive) blocking agents, such as decamethoniumand succinylcholine. In addition to inhibiting AChE, edrophoniumchloride has a direct cholinomimetic effect onskeletal muscle, which is greater than that of most otheranticholinesterase drugs. | [Synthesis]
Edrophonium, ethyl-(3-hydroxyphenyl)dimethylammonium chloride
(13.2.13), is made by reacting 3-dimethylaminophenol with ethylbromide, which forms
ethyl(3-hydroxyphenyl)dimethylammonium bromide (13.2.12), the bromine atom of
which is replaced with a chlorine atom by reacting it with silver chloride, giving edropho�nium (13.2.13) [45].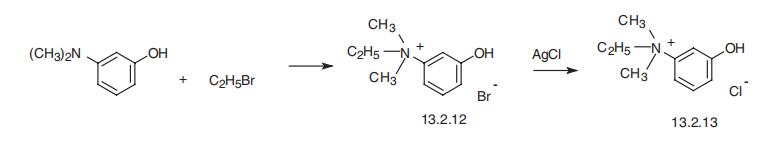
| [Veterinary Drugs and Treatments]
The primary use for edrophonium is in the diagnosis of myasthenia
gravis. It can also be used for the reversal of nondepolarizing
agents (e.g., vecuronium, pancuronium, metocurine, atracurium,
gallamine or tubocurarine). Because of its short duration of action,
its clinical usefulness for this indication is questionable as
longer acting drugs such as neostigmine or pyridostigmine may be
more useful. Edrophonium, in a controlled intensive
care-type setting,
may also be useful in the diagnosis and treatment of some
supraventricular arrhythmias, particularly when other more traditional
treatments are ineffective. | [in vitro]
edrophonium inhibited ache activity in human red blood cells, purified calf forebrain, and octopus brain with ki values of 0.2, 0.2, and 0.4 μm, respectively. the ic50s were 0.2, 0.05, and 0.5 μm, respectively [1]. | [in vivo]
in symptomatic patients without coronary artery disease, edrophonium (80 μg/kg, intravenous bolus) induced chest pain [3]. edrophonium increased esophageal amplitude and repetitive contractions. edrophonium was useful for provoking esophageal chest pain [3]. in infants and children during n2o-halothane anesthesia, the ed50 for edrophonium is 128 μg/kg for adults [4]. in patients anaesthetized with nitrous oxide and halothane undergoing kidney transplant nephrectomy or transplantation of a live related donor kidney, patients undergoing transplant nephrectomy showed a significant increase in elimination half-life and a significant decrease (67%) in serum clearance when compared with kidney transplant recipients or patients with normal renal function [5]. | [storage]
Store at -20°C, protect from light | [References]
[1] boyle n a j, talesa v, giovannini e, et al. synthesis and study of thiocarbonate derivatives of choline as potential inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase[j]. journal of medicinal chemistry, 1997, 40(19): 3009-3013.
[2] quinn d m. acetylcholinesterase: enzyme structure, reaction dynamics, and virtual transition states[j]. chemical reviews, 1987, 87(5): 955-979.
[3] cronnelly r, morris r b, miller r d. edrophonium: duration of action and atropine requirement in humans during halothane anesthesia[j]. anesthesiology, 1982, 57(4): 261-266.
[4] fisher d m, cronnelly r, sharma m, et al. clinical pharmacology of edrophonium in infants and children[j]. anesthesiology, 1984, 61(4): 428-433.
[5] morris r b, cronnelly r, miller r d, et al. pharmacokinetics of edrophonium in anephric and renal transplant patients[j]. british journal of anaesthesia, 1981, 53(12): 1311-1314. |
|
|