| Identification | More | [Name]
Bis(2-butoxyethyl)ether | [CAS]
112-73-2 | [Synonyms]
2,2′-Dibutoxyethylether
2-BUTOXYETHYL ETHER
BIS(2-BUTOXYETHYL) ETHER
BIS(2-N-BUTOXYETHYL) ETHER
BIS(BUTOXYETHYL)ETHER
BUTYL DIGLYME
DIBUTYL CARBITOL
DIBUTYL DIGLYCOL
DIETHYLENE GLYCOL DIBUTYL ETHER
DIETHYLENE GLYCOL DI-N-BUTYL ETHER
1,1’-(oxybis(2,1-ethanediyloxy))bis-butan
1,1’-[oxybis(2,1-ethanediyloxy)]bis-butan
1,1’-[oxybis(2,1-ethanediyloxy)]bis-Butane
1-[2-(2-Butoxyethoxy)ethoxy]butane
2-(2-Butoxyethoxy)-1-butoxyethane
5,8,11-Trioxapentadecane
Butane,1,1’-[oxybis(2,1-ethanediyloxy)]bis-
Dibutylether diethylenglykolu
dibutyletherdiethylenglykolu
Ether, bis(2-butoxyethyl) | [EINECS(EC#)]
204-001-9 | [Molecular Formula]
C12H26O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00009459 | [Molecular Weight]
218.33 | [MOL File]
112-73-2.mol |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Safety Statements ]
S23:Do not breathe gas/fumes/vapor/spray (appropriate wording to be specified by the manufacturer) .
S24/25:Avoid contact with skin and eyes . | [WGK Germany ]
1
| [RTECS ]
KN0350000
| [Autoignition Temperature]
268 °C | [TSCA ]
Yes | [HS Code ]
29091900 | [Safety Profile]
Moderately toxic by
ingestion. Mddly toxic by skin contact.
Experimental reproductive effects. A skin
and eye irritant. See also GLYCOL
ETHERS. Combustible when exposed to
heat or flame. To fight fire, use foam or
alcohol foam. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and
irritating fumes. | [Toxicity]
LD50 orally in Rabbit: 3900 mg/kg LD50 dermal Rabbit 3555 mg/kg |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
Colorless liquid. Floats on water. | [Reactivity Profile]
DIETHYLENE GLYCOL DIBUTYL ETHER(112-73-2) may react violently with strong oxidizing agents. Incompatible with nitric acid. May form salts with strong acids and addition complexes with Lewis acids. In other reactions, which typically involve the breaking of the carbon-oxygen bond, relatively inert. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Oxidizes readily in air to form unstable peroxides that may explode spontaneously [Bretherick, 1979 p.151-154, 164]. Insoluble in water. | [Health Hazard]
May be harmful by inhalation, ingestion and skin absorption. Causes eye and skin irritation. Material is irritating to mucous membrane and upper respiratory tract. | [Fire Hazard]
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Vapor may travel considerable distance to a source of ignition and flash back. | [Chemical Properties]
clear colorless to yellowish liquid | [Uses]
Butyl diglyme is used to extract gold from
hydrochloric acid solutions containing other metals. Treatment of the diglyme
extract with hydrogen or oxalic acid precipitates the ionic gold as gold powder. | [Uses]
Extraction of precious metalsDiethylene glycol dibutyl ether is used as a solvent in Grignard reactions. It is also used as solvents in gold refining, decorative inks for ceramics and digital inks. It finds application in electrochemistry, gas absorption, extractant and high boiling reaction medium. It is also used in fuel, lubricant, textile and medicine. | [Flammability and Explosibility]
Nonflammable | [Synthesis]
Into 120 g of 60% NaH and 500 ml of toluene were added dropweise 329 g of butyl bromide and 486 g of diethylene glycol butyl ether at 50 ℃. Diethylene glycol dibutyl ether was obtained by distillation (b.p.: 256 ℃. under normal pressure) from the reaction mixture.
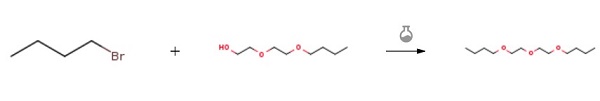 | [Purification Methods]
Dibutylcarbitol is freed from peroxides by slow passage through a column of activated alumina. The eluate is then shaken with Na2CO3 (to remove any remaining acidic impurities), washed with water, and stored with CaCl2 in a dark bottle [Tuck J Chem Soc 3202 1957]. [Beilstein 1 IV 2395.] |
|
|