| Identification | More | [Name]
Acetonylacetone | [CAS]
110-13-4 | [Synonyms]
1,2-DIACETYLETHANE
2,5-HEXANDIONE
2,5-HEXANEDIONE
ACETONYLACETONE
AKOS BBS-00004255
2,5-Diketohexane
2,5-Hexadione
Acetone, acetonyl-
Acetonyl acetone 2,5-hexanedione
acetonyl-aceton
alpha,beta-Diacetylethane
Diacetonyl
hexane-2,5-
Hexane-2,5-dione
Hexanedione-(2,5)
Hexan-2,5-Dion
ACETONYLACETONE, 98+%
2,5-Hexanedione, Wacker Quaility
2,5-Hexanedione, Standard f GC
α,β-Diacetylethane | [EINECS(EC#)]
203-738-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C6H10O2 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00008792 | [Molecular Weight]
114.14 | [MOL File]
110-13-4.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
colourless to pale yellow liquid | [Melting point ]
-6--5 °C (lit.) | [Boiling point ]
191 °C (lit.) | [density ]
0.973 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
| [vapor pressure ]
0.43 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
| [refractive index ]
n20/D 1.425(lit.)
| [Fp ]
174 °F
| [storage temp. ]
Store below +30°C. | [solubility ]
alcohol: miscible | [form ]
Liquid | [color ]
Clear yellow to brown | [Odor]
Pleasant, sweet-ethereal odor. | [PH]
6.1 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) | [Stability:]
Stable. Incompatible with strong bases, strong reducing agents, strong oxidizing agents. Flammable. | [explosive limit]
1.5%(V) | [Water Solubility ]
miscible | [Merck ]
14,71 | [BRN ]
506525 | [InChIKey]
OJVAMHKKJGICOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [LogP]
-0.270 | [CAS DataBase Reference]
110-13-4(CAS DataBase Reference) | [NIST Chemistry Reference]
CH3COCH2CH2COCH3(110-13-4) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
110-13-4(EPA Substance) |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Synthesis]
2,5-Hexanedione has been prepared in several ways. A common method involves hydrolysis of 2,5-dimethylfuran, a glucose derived heterocycle.
| [Mechanism of Toxicity]
Identification of 2,5-hexanedione as the major neurotoxic metabolite of n-hexane proceeded rapidly after its discovery as a urinary metabolite. 2,5-Hexanedione has been found to produce a polyneuropathy indistinguishable from n-hexane. 2,5-Hexanedione is many times more potent than n-hexane, the parent compound, in causing neurotoxicity in experimental animals. It appears that the neurotoxicity of 2,5-hexanedione resides in its γ-diketone structure since 2,3-, 2,4-hexanedione and 2,6-heptanedione are not neurotoxic, while 2,5-heptanedione and 3,6-octanedione and other γ-diketones are neurotoxic.
|
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
Xn,Xi | [Risk Statements ]
R36/38:Irritating to eyes and skin .
R48/20/21/22:Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation, and in contact with skin and if swallowed .
R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . | [Safety Statements ]
S23:Do not breathe gas/fumes/vapor/spray (appropriate wording to be specified by the manufacturer) .
S26:In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice .
S36/37:Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves .
S37/39:Wear suitable gloves and eye/face protection . | [WGK Germany ]
2 | [RTECS ]
MO3150000 | [F ]
8 | [Autoignition Temperature]
400 °C | [TSCA ]
Yes | [HS Code ]
29141990 | [Toxicity]
LD50 orally in rats: 2.7 g/kg (Smyth, Carpenter) |
| Raw materials And Preparation Products | Back Directory | [Raw materials]
Potassium carbonate-->2,3-Butanedione-->2,5-Dimethylfuran-->ETHYL ACETOACETATE SODIUM SALT-->IODINE PURE-->3-HEXENE-2,5-DIONE-->(2R,3S,4S,5R)-2,5-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-oxolane-2,3,4-triol-->5-Chloromethylfurfural-->5-Methyl furfural-->2,5-Hexanediol | [Preparation Products]
Ascorbic Acid-->Methyl 3-methyl-2-butenoate-->2,5-Dimethyl-1H-pyrrole-->1-[2,6-DICHLORO-4-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PHENYL]-2,5-DIMETHYL-1H-PYRROLE-3-CARBALDEHYDE-->2,5-Dimethylthiophene-->5-Methylisoxazole-3-carboxylic acid-->Tetrahydropyran-->2,5-DIMETHYL-1-PHENYLPYRROLE-->1-(4-CYANOPHENYL)-2,5-DIMETHYLPYRROLE |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [General Description]
Clear colorless to amber liquid with a sweet aromatic odor. | [Reactivity Profile]
2,5-HEXANEDIONE(110-13-4) is incompatible with oxidizing agents. 2,5-HEXANEDIONE(110-13-4) is also incompatible with strong bases and strong reducing agents. | [Air & Water Reactions]
Highly flammable. Water soluble. | [Fire Hazard]
This chemical is combustible. | [Description]
2, 5-hexadione (2,5HD,110-13-4) is a flammable, transparent colorless to amber water-soluble liquid that is a multifunctional platform chemical, a major metabolite of n-hexane, and a key intermediate for the production of high energy density aviation fuels from biomass resources. It has a sweet aromatic smell and neurotoxic effects. It can be used as a high energy density fuel additive of platform chemicals, and can induce ovarian granulosa cell cycle arrest to establish ovarian injury model. It can also be used for biological monitoring of 2, 5-hexanedione exposure to n-hexane[1-2].
| [Chemical Properties]
colourless to pale yellow liquid | [Uses]
It is the metabolite implicated in n-hexane neurotoxicity. | [Application]
2,5-Hexanedione is a neurotoxic metabolite of n-hexanes and methyl n-butyl ketone. It is also used as the starting material for diels-alder cycloaddition reactions, such as a reactions with amines to form 2,5-dimethylpyrroles. | [Preparation]
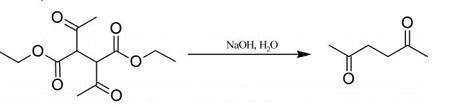
20 g of diethyl 2,3-diacetylbutanedioate are mechanically shaken for several days with 250 ml (excess) of 5% aqueous sodium hydroxide, and until no diethyl 2,3-diacetylbutanedioate
separates on acidification of a sample with dilute hydrochloric acid.
The solution is then saturated with potassium carbonate and extracted
with ether,
the extract is washed with brine to remove alcohol, dried over calcium
chloride, and distilled, the fraction 192-198° C being retained. You can get 2,5-Hexanedione with a yield of 70%. Colourless liquid; agreeable odour; miscible with water, alcohol
and ether; m.p. 9° C; b.p. 194° C; d=0.973 g/ml at 20° C. | [Definition]
ChEBI: A diketone that is hexane substituted by oxo groups at positions 2 and 5. It is a toxic metabolite of hexane and of 2-hexanone
| [Synthesis Reference(s)]
Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 59, p. 945, 1981 DOI: 10.1139/v81-137
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 105, p. 7200, 1983 DOI: 10.1021/ja00362a047
Tetrahedron Letters, 15, p. 4149, 1974 | [Purification Methods]
Purify it by dissolving in Et2O, stiring with K2CO3 (a quarter of the weight of dione), filtering, drying over anhydrous Na2SO4 (not CaCl2), filtering again, evaporating the filtrate and distilling it in a vacuum. It is then redistilled through a 30cm Vigreux column (p 11, oil bath temperature 150o). It is miscible with H2O and EtOH. The dioxime has m 137o (plates from *C6H6), the mono-oxime has b 130o/11mm, and the 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone has m 210-212o (red needles from EtOH). It forms complexes with many metals. [Werner et al. Chem Ber 22 2100 1989, for enol content see Gero J Org Chem 19 1960 1954, Beilstein 1 IV 3688.] | [References]
[1] KAIXUAN ZHOU, Xin L, Chenggong Sun. Directed glycerol conversion to 2,5-hexanedione and more advanced poly-oxygenates as platform chemicals and high energy–density fuel additives[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: Article 132981. DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2021.132981.
[2] XUEMING XU. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is involved in 2,5-hexanedione-induced ovarian granulosa cell cycle arrest[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2023, 268: Article 115720. DOI:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115720. |
|
|