| Identification | More | [Name]
COBALT CARBONYL | [CAS]
10210-68-1 | [Synonyms]
COBALT CARBONYL
COBALT TETRACARBONYL
DICOBALT OCTACARBONYL
OCTACARBONYLDICOBALT
carbonyl,tetra-cobal
Co2(CO)8
Cobalt carbonyl (Co2(CO)8)
Cobalt tetracarbonyl dimer
Cobalt, di-mu-carbonylhexacarbonyldi-
Cobalt, di-mu-carbonylhexacarbonyldi-, (Co-Co)
Cobalt,di-μ-carbonylhexacarbonyldi-,(Co-Co)
cobaltcarbonyl(asco)
cobaltcarbonyl(co2(co)8)
cobaltcarbonyle
cobaltoctacarbonyl
cobalttetracarbonyldimer
Dicobalt carbonyl (Co2(CO)8)
dicobaltcarbonyl
di-mu-carbonylhexacarbonyldi-cobal
di-mu-carbonylhexacarbonyldi-cobal(co-co) | [EINECS(EC#)]
233-514-0 | [Molecular Formula]
C8Co2O8+4 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00016024 | [Molecular Weight]
341.95 | [MOL File]
10210-68-1.mol |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
Cobalt carbonyl is a pyrophoric (spontaneously flammable in air), red-orange (when pure) to dark-brown crystalline solid. | [Melting point ]
51-52 °C
| [Boiling point ]
52°C | [density ]
1.81
| [vapor pressure ]
9.333-200Pa at 15-25℃ | [Fp ]
-13 °C
| [storage temp. ]
2-8°C
| [solubility ]
Dichloromethane (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | [form ]
crystal | [color ]
dark orange | [Specific Gravity]
1.73 | [Water Solubility ]
Insoluble in water. Soluble in alcohol, ether and carbon disulfideSoluble in ether, naphtha and carbon disulfide. Slightly soluble in alcohol. Insoluble in water. | [Hydrolytic Sensitivity]
7: reacts slowly with moisture/water | [Sensitive ]
Air Sensitive | [Merck ]
13,3112 | [Exposure limits]
TLV-TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 as Co (ACGIH)
PEL-TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 as Co (OSHA). | [Stability:]
Air sensitive | [CAS DataBase Reference]
10210-68-1(CAS DataBase Reference) | [EPA Substance Registry System]
Cobalt carbonyl (10210-68-1) |
| Safety Data | Back Directory | [Hazard Codes ]
F,Xn | [Risk Statements ]
R11:Highly Flammable.
R22:Harmful if swallowed.
R40:Limited evidence of a carcinogenic effect.
R43:May cause sensitization by skin contact.
R48/20:Harmful: danger of serious damage to health by prolonged exposure through inhalation .
R52/53:Harmful to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment .
R62:Possible risk of impaired fertility. | [Safety Statements ]
S36/37:Wear suitable protective clothing and gloves .
S61:Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions safety data sheet . | [OEB]
D | [OEL]
TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 | [RIDADR ]
UN 3190 4.2/PG 2
| [WGK Germany ]
3
| [RTECS ]
GG0300000
| [F ]
23-25 | [TSCA ]
No | [HazardClass ]
4.1 | [PackingGroup ]
II | [HS Code ]
29319090 | [Safety Profile]
Poison by inhalation
and intraperitoneal routes. Questionable
carcinogen. Decomposes in air to form a
product that ignites spontaneously in air.
"hen heated to decomposition it emits
acrid smoke and fumes. See also
CARBONYLS and COBALT
COMPOUNDS. | [Hazardous Substances Data]
10210-68-1(Hazardous Substances Data) | [Toxicity]
LD50 in mice, rats (mg/kg): 377.7, 753.8 by gavage (Spiridonova, Shabalina) |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Hazard]
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. | [Potential Exposure]
This material is used as a catalyst for a number of reactions. It is also used in antiknock gasoline and for high-purity cobalt salts. | [First aid]
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek Medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a Medical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Medical observation is recommended for 24 to 48 hours after breathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may be delayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor or authorized paramedic may consider administering a drug or other inhalation therapy | [Shipping]
UN3124 Toxic solids, self-heating, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; 6.1-Poisonous materials, 4.2-Spontaneously combustible material. Technical Name Required. UN3190 Self-heating solid, inorganic, Hazard Class: 4.2; Labels: 4.2-Spontaneously combustible material, Technical Name Required. UN1325 Flammable solid, organic, n.o.s. Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid | [Incompatibilities]
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Decomposes on exposure to air or heat (@ ~52°C) producing toxic fumes of cobalt and oxides of carbon | [Chemical Properties]
Cobalt carbonyl is a pyrophoric (spontaneously flammable in air), red-orange (when pure) to dark-brown crystalline solid. | [Chemical Properties]
red-orange to dark red crystals or flakes | [Physical properties]
Orange crystals; density 1.78 g/cm3; melts at 5l°C; decomposes above this temperature; insoluble in water; soluble in most organic solvents including alcohol, ether, carbon disulfide. | [Uses]
Cobalt octacarbonyl is used as a catalyst in the Oxo process. It also is used as a catalyst for hydrogenation, isomerization, hydrosilation and polymerization reactions. The compound is also a source of producing pure cobalt metal and its purified salts.
| [Uses]
It is used as a catalyst in many organicconversion reactions, which include hydrogenation,isomerization, hydroformylation,polymerization, and carbonylation. | [Uses]
The use of dicobalt octacarbonyl as a catalyst in a variety of organic syntheses has led to the study of an extensive and important organometallic chemistry of cobalt. | [Preparation]
Cobalt octacarbonyl is prepared by the reaction of finely divided cobalt with carbon monoxide under pressure:
2Co + 8CO → Co2(CO)8
The compound may be prepared in a similar way from cobalt(II) iodide. Also, it may be prepared by thermal decomposition of cobalt carbonyl hydride:
2HCo(CO)4 → Co2(CO)8 + H2
| [Health Hazard]
Dicobalt octacarbonyl exhibits moderate toxicityby inhalation route and somewhatlower toxicity by intraperitoneal and oralroutes. However, it is much less toxicthan nickel tetracarbonyl or iron pentacarbonyl.A 2-hour LC50 value in mice isreported as 27 mg/m3 (Lewis 1996). Anoral LD50 value in rats is within the rangeof 750–800 mg/kg. It decomposes, evolvingtoxic carbon monoxide. | [reaction suitability]
core: cobalt
reagent type: catalyst | [storage]
Color Code—Red Stripe: Flammability Hazard:Store separately from all other flammable materials. Priorto working with this chemical you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. Decomposes on exposure toair or heat; stable in atmosphere of hydrogen and carbonmonoxide. Store in airtight, unbreakable containers in acool, well-ventilated area away from strong oxidizers andacids. | [Purification Methods]
It forms orange-brown crystals on recrystallisation from n-hexane under a carbon monoxide atmosphere [Ojima et al. J Am Chem Soc 109 7714 1987; see also Hileman in Preparative Inorganic Reactions, Ed. Jolly, Vol 1 p 101 1987]. |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Description]
Cobalt carbonyl (known as dicobalt octocarbonyl) is a versatile reagent and catalyst in organometallic chemistry and organic synthesis. It has catalytic applications in various chemical reactions such as hydroformylation of unsaturated compound, homogeneous hydrogenation of aromatic hydrocarbons, hydrosilation of alkenes, reactions of disulfides such as carbonylation to thio-esters and desulfurization to sulfides, hydroformylation as well as the conversion of alkenes into aldehydes. It can also promote both the Pauson-Khand reactions and Nicholas reaction.
 | [Reaction]
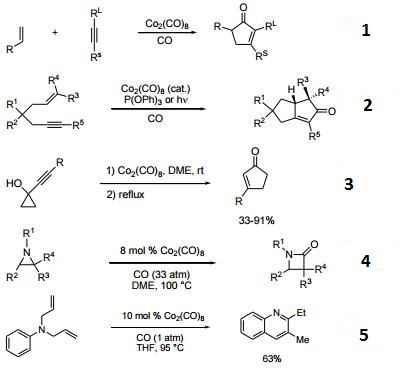
- Reagent for the Pauson-Khand conversion of an olefin, an alkyne and carbon monoxide into a cyclopentenone.
- Precatalyst in combination with triphenylphosphite for the cataytic Pauson-Khand reaction.
- Catalyzes the rearrangement of 1-alkynylcyclopropanols to cyclopentenones.
- Catalyzes the conversion of aziridines to β-lactams.
- Catalyzes the conversion of diallylanilines and aryliminies to quinolines.
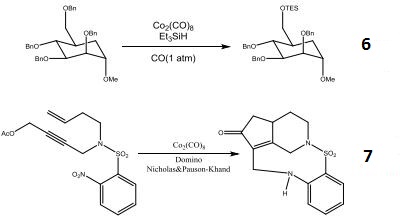
- Reagent for the selective cleavage of benzyl ethers.
- Domino Nicholas and Pauson-Khand process induced by nitroarene reduction.
| [Sources]
Adkins, Homer., and G. Krsek. JACS 71.9(1949):3051-3055.
Feder, Harold M., and J. Halpern. Cheminform 7.7(1976):no-no.
Seitz, Friedrich, and M. S. Wrighton. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 27.2(1988):289-291.
Antebi, Shlomo, and H. Alper. Tetrahedron Letters 16.38(1985):no-no.
Krafft, Marie E., L. V. R. Boñaga, and C. Hirosawa. Cheminform 32.37(2001):no-no.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dicobalt_octacarbonyl
|
|
|