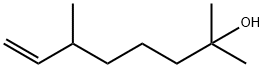
Dihydromyrcenol synthesis
- Product Name:Dihydromyrcenol
- CAS Number:18479-58-8
- Molecular formula:C10H20O
- Molecular Weight:156.27
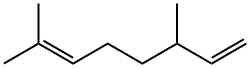
2436-90-0
124 suppliers
$46.70/1 mL

18479-58-8
234 suppliers
$45.00/10 g
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
with waterConversion of starting material;Heating;
Steps:
To produce dihydromyrcenol, a raw material for high-quality fragrance, through hydration of dihydromyrcene with catalysis of the acidic catalyst. The catalytic reaction-rectification integrated column (T-01) is 1.2 m in diameter and 28 m in height, wherein the reaction section (6) is 2.5 m in height while the rectification section(4) 14.5 m and the stripping section(9) (including the column kettle) 11 m; heat-resistant, high-acidic ion exchange resin is used as the catalyst; the column (T-02) is 25 m in height, wherein the rectification section is 10 m while the stripping section (including the column kettle) 15 m; the column (T-03) is 36 m in height, wherein the rectification section is 16 m while the stripping section (including the column kettle) 20 m; the whole manufacturing process goes as follows:Dihydromyrcene solution (purity 88%) and water, with mol ratio 1:1.2?, are fed into the reaction section (6) after being heated by the preheaters (1 and 2); meanwhile the catalyst is mixed with the reactants and flushed into the reaction section as well; during reaction process, the reactant fluid is pumped out through the filtering pipette by the pump (21); after being heated by the preheater (15), the fluid flows back to the reaction section (6) through the subsonic liquid jet agitator (34); the forced jet agitation occurs therein. The linear speed of the liquid in the jet agitator (34) can be adjusted between 150 m/s and 360 m/s, and the general practice is around 330 m/s so that oil and water can be completely mixed; thanks to its high vortical state, the fluid in the reaction section can obtain ideal contact with the catalyst; keep the average reaction time of the fluid in the reaction section around 25 minutes, the time the reaction approximately reaches its balance; in the reaction section exists a filtering overflow pipe (7) that allows the liquid to overflow out while keeps the solid components therein; the overflowed fluid goes into the liquid distributor (8) through the valve (13) and the pipe (6-9); after being evenly distributed therein, the fluid flows into the stripping section (9) and the components in the fluid will be separated therein.The gas emitting up from the stripping section goes through the pipe (9-4) into the rectification section (4); after being separated therein, the gas is condensed into liquid in the condenser (12) at the column top; the liquid then goes into the condensed liquid collector (11); the major components in the liquid are dihydromyrcenol, water and some light organics; part of the liquid flows back while the rest goes into the dehydration column (T-02) through the pipe (11-T-02) for further separation; the components obtained at the column top are water and some light organics (oil-phase); the gas collected therein is condensed in liquid at the condenser (22) and then flows into the oil-water separator (23) for phase-splitting; thereafter the water-phase components flow back while the oil-phase components are pumped out for storage. If the water-phase components are too much, they can also be channeled back to the reaction section (kettle).The fluid, the major components of which are dihydromyrcenol and some heavy organics, is channeled out from the stripping section (9) of the column (T-01) and flows through the pipe (9-T-03) into the rectification column (T-03) for separation; the major component of the gas gathering at the column top is dihydromyrcenol, its purity reaches 99.5%; after being condensed in liquid at the condenser (25), it is collected by the condensed liquid collector (26); part of the condensed liquid flows back while the rest is channeled into the product storage tank for storage; the major components gathering at the bottom of the rectification column (T-03) are heavy organics; they are pumped out by a pump secured at the bottom of the rectification column (T-03) and stored in the storage tank designed for storage of heavy organics.The system disclosed in this embodiment is able to increase the primary conversion rate of dihydromyrcene up to 88%, 18% higher than fixed-bed catalytic hydration-a currently existing method; in addition, the reaction time is shortened to one third of that of fixed-bed catalytic hydration; the reaction and separation procedures of this system is integrated as an organic whole so that the continuous operation is realized. The production capacity is therefore almost doubled, which in turn cuts down 56% on cost of dihydromyrcenol production.
References:
NANJING UNIVERSITY US2011/144378, 2011, A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 4-5