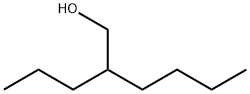
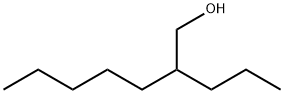
2-propylhexan-1-ol synthesis
- Product Name:2-propylhexan-1-ol
- CAS Number:817-46-9
- Molecular formula:C9H20O
- Molecular Weight:144.25
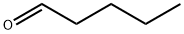
110-62-3
250 suppliers
$13.44/25ML
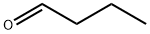
123-72-8
422 suppliers
$12.32/25ML
10042-59-8
126 suppliers
$9.00/1g
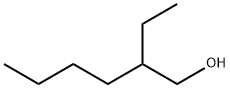
104-76-7
666 suppliers
$5.00/10g

817-46-9
10 suppliers
inquiry
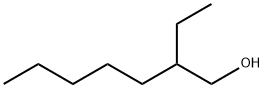
817-60-7
3 suppliers
inquiry
Yield:-
Reaction Conditions:
Stage #1: pentanal;butyraldehydewith sodium hydroxide in water at 20 - 130; for 3.25 h;
Stage #2: with hydrogen in water;
Steps:
2 Preparation 1: Preparation of Mixed C8-C10 Enals Via a Cross Aldol Condensation
The procedure is conducted in a mechanically stirred 10 gallon stainless steel reactor rated for high pressure service. Heating is supplied by circulating hot oil through an outer jacket; and the reactor temperature is monitored by a thermocouple in contact with the stirred reaction mixture. A 2 wt. % aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (7723 g) is charged to the reactor and agitation is initiated at ambient temperature. A premixed solution of butyraldehyde (N:I ratio 10:1; 5273 g; 73 moles) and valeraldehyde (N:I ratio 45:1; 6284 g; 73 moles) is pumped into the reactor slowly over 15 minutes. The aldol condensation reaction is exothermic; thus, the temperature of the reaction mixture rises during this time from 20° C. to 44° C. Once the aldehyde addition is complete, heating is initiated, and the temperature of the reaction mixture is increased to 130° C. over the course of one hour and then is maintained at that temperature for an additional two hours. Then, the reactor is cooled and the biphasic reaction mixture is decanted. The organic (top) layer is analyzed on an Agilent 6890 GC using the conditions described in the following table: The analysis indicates four major products, namely a mixture of 2-ethylhexenal, 2-ethylhept-2-enal, 2-propyhex-2-enal and 2-propylheptenal at a molar ratio of 1.2:1.0:1.2:1.3. Two minor enal products attributed to condensation reactions of isobutyraldehyde with butyraldehyde and valeraldehyde respectively are also detected; the combined concentration of these two minor enal products is approximately 5 wt. %. The total concentration of unreacted butyraldehyde and valeraldehyde is approximately 2 wt. %, indicating nearly complete conversion. Preparation 2: Hydrogenation of Mixed C8-C10 Enals Initial catalyst loading: Twenty five grams of water wet Raney Ni 5887-200 is transferred into a Robinson-Mahoney basket and placed into a 1 liter reactor. Three “pressurization to 500 psia and venting” cycles of the reactor are conducted then 3 similar cycles with nitrogen, another three times with hydrogen, and the reactor is then purged with nitrogen to remove any water from the catalyst. Approximately 350 g of n-butanol is loaded to the reactor, is mixed at 300 rpm, and is drained to remove any fines. Catalyst washing with n-butanol is completed three times. An additional three pressurization to 500 psia and venting cycles are completed using hydrogen. The reactor is then left at 500 psia under hydrogen with a jacket temperature of 100° C. for 48-72 hours prior to the hydrogenation process. The C8-C10 enals from the cross aldol reaction are loaded into a 500 mL shot tube in approximately 250 g increments at ambient temperature. Five nitrogen pressurization-venting-vacuum cycles are completed prior to addition of the enals to the reactor. The reaction is controlled at approximately 25° C. and 1000 rpm during the addition of the enals. Hydrogen pressure control is established and time zero is established at the time the temperature is ramped to the desired set point. The end of the reaction is defined by zero hydrogen being consumed from the 1 gallon hydrogen supply cylinder. At the conclusion of the run, the product is drained and filtered to remove Raney Nickel catalyst fines. The resulting mixture of C8-C10 alcohols is characterized by gas chromatography using a flame ionization detector (GC-FID) to obtain the alcohol compositions and ratios. GC-FID is used to further characterize the isomeric composition of the C8-C10 alcohols. Four major alcohol isomers are identified in the GC-FID spectra, which includes four major components: 2-ethylhexanol (2-EH, a C8 alcohol, 21.6 area %), 2-ethylheptanol (C9-1, a C9 alcohol, 22.0 area %), 2-propylhexanol (C9-2, a C9 alcohol, 21.0 area %) and 2-propylheptanol (2-PH, a C10 alcohol, 28.9 area %). Less than 4 area % of two other isomers are from a branched C8 alcohol (2.7 area %) and a branched C9 alcohol (3.8 area %). The C9 alcohol isomers (C9-1 and C9-2), which are difficult to obtain using tedious prior art synthetic approaches, constitute 43 area % of the product mixture. Calculated product ratios using GC-FID data are found to correspond to a nominal C8:C9:C10 molar ratio of 1:2:1. The analytical data is summarized in Table 1.
References:
US2021/139400,2021,A1 Location in patent:Paragraph 0040-0043

111-66-0
158 suppliers
$10.00/10ml
201230-82-2
1 suppliers
inquiry

817-46-9
10 suppliers
inquiry
818-81-5
48 suppliers
$45.00/10mg

817-60-7
3 suppliers
inquiry

143-08-8
301 suppliers
$6.00/5g
111-67-1
33 suppliers
$26.25/5g
201230-82-2
1 suppliers
inquiry

817-46-9
10 suppliers
inquiry

818-81-5
48 suppliers
$45.00/10mg

817-60-7
3 suppliers
inquiry

143-08-8
301 suppliers
$6.00/5g
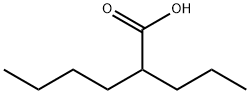
3274-28-0
45 suppliers
$320.00/100mg

817-46-9
10 suppliers
inquiry