What Is Bisphenol A and Why Is It Bad for You?
Feb 18,2022
General description
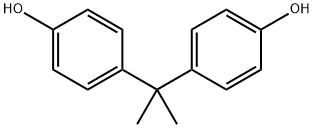
Bisphenol A is a diphenylmethane derivative with two hydroxyphenyl groups. Bisphenol A (BISPHENOL A) is a colorless solid that is used in the synthesis of commercial plastics, including polycarbonates and epoxy resins, which are incorporated into a wide variety of consumer goods. Bisphenol A is a bisphenol that is 4,4'-methanediyldiphenol in which the methylene hydrogens are replaced by two methyl groups. It has a role as a xenoestrogen, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic and an endocrine disruptor. 4,4'-isopropylidenediphenol appears as white to light brown flakes or powder. Has a weak medicine odor. Sinks in water. (USCG, 1999). Bisphenol A is a very versatile chemical raw material, but our bisphenol A plant is currently controlled by foreign countries both in capital and technology. Studying and improving the production process of bisphenol A is very meaningful for breaking foreign monopoly and reducing the cost and risk ofChina's economic development.[1]
Application
Bisphenol A is a chemical added to many commodities, including food containers and sanitary products. It was first discovered in the 1890s, but in the 1950s, chemists realized that it could be mixed with other compounds to produce strong and elastic plastics. Today, BISPHENOL A containing plastics are commonly used in food containers, baby bottles and other items (the EU and China have banned the production of polycarbonate baby bottles and other BISPHENOL A containing baby bottles). Bisphenol A is also used to make epoxy resin, which is coated on the lining of canned food containers to prevent metal corrosion and fracture.
Synthesis
In order to study the problem that the bisphenol A crystal clogging the catalyst bed caused the device to stop during the production of bisphenol A, a mathematical model of the reactor was established to calculate the temperature and composition distribution inside the bisphenol A synthesis reactor. The calculation results show that the bisphenol A in the reactor is at the precipitation edge, and the bisphenol A is most likely to precipitate on the top of the catalyst bed, and the problem will become more serious as the catalyst activity decreases. To solve this problem, we designed a heat pipe fixed bed reactor. The calculation results show that the addition of the heat pipe is equivalent to a constant wall temperature heat exchanger of 73.121°C, which improves the temperature distribution in the reactor and significantly reduces the possibility of blockage, without changing the final reaction temperature and conversion rate.
Figure 1 Bisphenol A(BPA) synthesis reaction mechanism
The reaction is carried out in two different stages: in the first stage, the positive carbon ion of acetone (I) combines with phenol to form protonated tertiary methanol (II), II is unstable, a molecule of water is immediately removed under the action of acidic medium and transformed into p-isopropenylphenol positive carbon ion (in); in the second stage, p-isopropenylphenol carbon ion (m) combines with the second phenol molecule to form an unstable intermediate product (IV), which further removes protons and becomes stable bisphenol A. if the reaction is carried out on resin catalyst, acetone needs to be adsorbed on the catalyst in advance before the reaction. Compared with propanone and water, the polarity of phenol is very weak, so its adsorption is not considered. [2]
Storage and Safety
Ingested Bisphenol A may exhibit estrogenic effects. Exposure to Bisphenol A may increase the risk of certain cancers. In view of the above information, many people doubt whether bisphenol A should be banned. The use of BISPHENOL A has been restricted in the European Union, Canada, China and Malaysia, especially in infant products. Some states in the United States have followed suit, but have not yet formulated federal regulations. In 2014, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) released the latest report, confirming that the initial daily exposure limit in the 1980s was 23 micrograms per pound of body weight (50 micrograms per kilogram), and concluded that exposure to bisphenol A was safe at the current allowable level[3]. However, studies in rodents have shown that the daily exposure limit to avoid the negative effects of bisphenol A is much lower-only 4.5 micrograms per pound of body weight (10 micrograms per kilogram per day). More importantly, studies on monkeys have shown that levels comparable to those currently measured in humans have a negative impact on monkey reproduction[4] Based on this evidence, the best approach is to take measures to limit exposure to bisphenol A and other potential food toxins. Especially pregnant women, avoiding BISPHENOL A is good for themselves-especially in early pregnancy. For others, occasionally drinking water or eating canned food in "PC" plastic bottles is not a big deal, so there is no need to panic. In other words, replacing plastic containers with BISPHENOL A Free Plastic containers requires little effort, but can have potentially huge health effects. If your goal is to eat fresh, all natural foods, you will limit your exposure to BISPHENOL A.[1]
Reference
1.Geens T., Aerts D. & Berthot C. et al., "A review of dietary and non-dietary exposure to bisphenol-A," Food and Chemical Toxicology, Vol.50, No.10(2012), pp.3725-3740.
2.Han Zhengguo: process research and engineering design of bisphenol a synthesis by resin method: Beijing University of chemical technology, 2019.
3.Alonso-Magdalena P., Morimoto S. & Ripoll C. et al., "The estrogenic effect of bisphenol A disrupts pancreatic beta-cell function in vivo and induces insulin resistance," Environ Health Perspect, Vol.114, No.1(2006), pp.106-112.
4.Hunt P. A., Lawson C. & Gieske M. et al., "Bisphenol A alters early oogenesis and follicle formation in the fetal ovary of the rhesus monkey," Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol.109, No.43(2012), pp.17525-17530.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What are the effects of Bisphenol A and its alternatives on human health? Dec 16, 2024
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a synthetic oestrogen that is used in large quantities in the global plastics industry in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins.
- Biological implications of Bisphenol A Jun 23, 2022
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical produced in large quantities for use primarily in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins.
- Uses of Bisphenol A Nov 26, 2021
Bisphenol A (BPA) was first synthesized in 1891, but it was not used widely until applications in the plastic industry were identified the 1950s. One method of production is by the condensation of 2 mol of phenol with 1 mol of acetone while
The classification of maleic anhydride antimicrobial polymers can be done by the reaction of anhydride groups with amines forming polyamides and polymaleimides.....
Feb 18,2022APIThis article is about the physical and chemical properties of oleic acid and the description of its preparation and use....
Feb 18,2022Organic ChemistryBisphenol A
80-05-7You may like
- Bisphenol A
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2025-01-09
- CAS:80-05-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month
- Bisphenol A
-

- $999.00/ ton
- 2025-01-09
- CAS:80-05-7
- Min. Order: 1ton
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000
- Bisphenol A BPA
-

- $200.00 / 1kg
- 2025-01-09
- CAS:80-05-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20ton