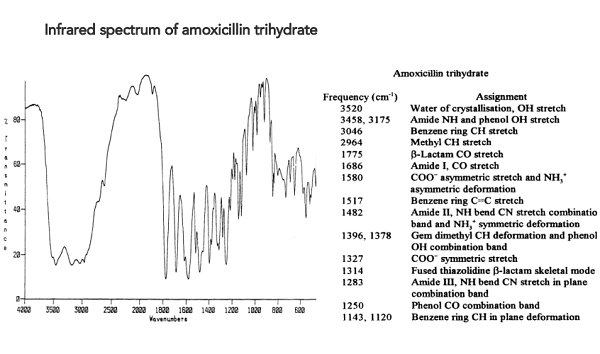
What does adenosine do for your body?
Aug 27,2024
Introduction
Adenosine, a naturally occurring endogenous metabolite formed by the degradation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), not only terminates but also helps define the mechanism of several arrhythmias discovered in 1929. ATP gets metabolized into adenosine after intravenous administration and is used to treat cardiac arrhythmias. Both have similar efficacy and clinical effects; however, adenosine is more stable at room temperature and is preferred over ATP.
Do for body
In the body, adenosine helps in cellular energy transfer by forming molecules like adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). Adenosine also plays a role in signalling various pathways and functions in the body by forming signal molecules like cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP).
In the brain, adenosine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter. This means adenosine can act as a central nervous system depressant. In normal conditions, it promotes sleep and suppresses arousal. When awake, the levels of adenosine in the brain rise each hour. In the heart, adenosine causes dilation of the coronary blood vessels, which improves blood circulation to the heart. Adenosine also increases the diameter of blood vessels in the peripheral organs. In the heart, adenosine decreases heart rate, and in blood, it has an anti-platelet action. Antiplatelet action prevents platelet aggregation and coagulation.
Effects for sleep
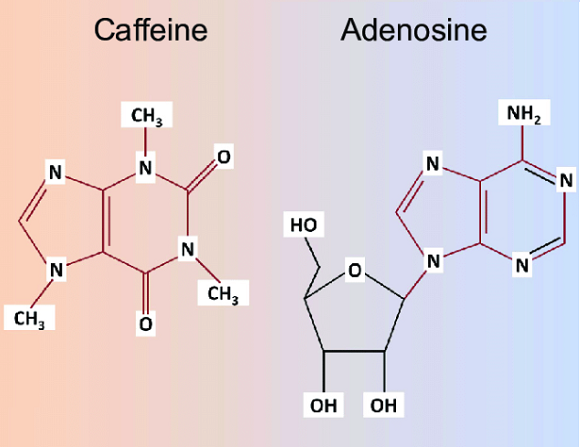
Sleep results from 2 physiologic processes -- process S (homeostatic process) and process C (circadian process). Process S is the process by which a growing sleep debt or pressure occurs the longer one is awake. The currency by which the brain measures time awake is adenosine accumulation. Adenosine is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, so the more active and alert we are during the day, the more adenosine builds up in the brain. Exercise, for example, can increase brain adenosine levels and promote sleep through stimulation of adenosine receptors. During sleep, adenosine is recycled, and levels are reduced in the brain; less adenosine receptor stimulation leads to more alertness. In essence, the longer you're awake, the more adenosine you accumulate, the more sleep pressure you acquire, and the more likely you are to fall asleep at bedtime. Likewise, the less adenosine receptor stimulation, the more alert you feel. Caffeine is an adenosine-receptor blocker and promotes alertness. However, with habitual caffeine use, the brain may upregulate adenosine receptors over time, leading to decreased effects of caffeine or the need for escalating doses. Therefore, to sustain the wake-promoting effect of caffeine, it may help to take breaks from caffeine to downregulate brain adenosine receptors.
Benefits
It terminates AV nodal-dependent arrhythmias like atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) and atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT). Due to triggered activity, it also terminates many focal atrial tachycardias and ventricular arrhythmias. Since it induces conduction block in the AV node, adenosine has diagnostic utility in patients with narrow QRS complex tachycardia. Similarly, adenosine could be of the most value in hemodynamically stable wide QRS tachycardia (WQRST) with 1:1 VA conduction when there is difficulty in differentiating supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy from ventricular tachycardia (VT). In the electrophysiology laboratory, adenosine plays a critical role in unmasking the accessory pathway conduction, both before and after ablation, and it also has a role in pulmonary vein isolation.
In specific, Likely Effective for
A heart condition marked by episodes of rapid heart rate (paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia). Adenosine is a prescription-only IV medicine approved to treat certain kinds of irregular heartbeat. This product can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Diagnosing heart disease. Adenosine is a prescription-only IV medicine approved to diagnose coronary artery disease. This product can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Possibly Effective for
Involuntary weight loss in people who are very ill (cachexia or wasting syndrome). Giving ATP by IV seems to improve appetite, food intake, and quality of life in people with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and other tumours. IV products can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Possibly Ineffective for
Heart attack. Giving adenosine by IV or injection directly into the heart vessels during procedures for a heart attack doesn't seem to reduce death or serious complications. IV products can only be given by a healthcare provider.
Pain after surgery. Giving adenosine by IV after surgery doesn't seem to reduce pain or the use of pain medication. IV products can only be given by a healthcare provider.
[1] MD, Anunay Gupta et al. “Adenosine—A drug with myriad utility in the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias.” Journal of Arrhythmia 37 1 (2020): 103–112.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The Biological activity, Drug Interactions, and Contraindications of Adenosine. Nov 17, 2023
Adenosine is a ubiquitous extracellular signaling molecule and plays a fundamental role in the regulation of coronary microcirculation through activation of adenosine receptors (ARs).
- Adenosine: Physiology, Clinical Applications and Safety Jul 13, 2023
Adenosine is a nucleoside involved in cellular function. It has antiarrhythmic effects, potential cardioprotective properties, and can cause side effects when administered.
- Application and Pharmacology of Adenosine Jun 20, 2022
Adenosine is a ribonucleoside comprised of adenine bound to ribose, with vasodilatory, antiarrhythmic and analgesic activities. Phosphorylated forms of adenosine play roles in cellular energy transfer
Adenosine
58-61-7You may like
- What is the function of 2′-Deoxycytidine?
Dec 17, 2024
- The introduction of 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin
Dec 17, 2024
- D-ribose and L-ribose
Dec 17, 2024