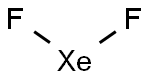Is XeF2 a polar or non-polar molecule?
Dec 20,2023
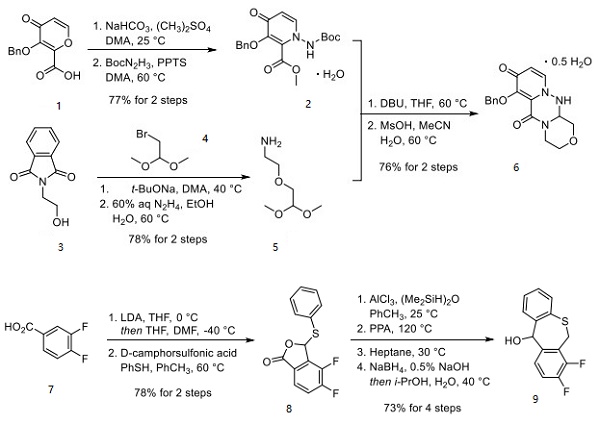
XeF2 is a non-polar molecule because the fluorine molecules on either side of the central atom do not have dipole moments and therefore have no polarity. XeF2 is nonpolar because of the symmetrical arrangement of electron bonding pairs.
Nature of XeF2
XeF2, or xenon difluoride, is a chemical compound composed of xenon (Xe) and fluorine (F) atoms. It is an interesting molecule to study because its nature, whether polar or nonpolar, can be determined by analyzing its molecular geometry and the polarity of its bonds.
Explanation of the linear-shaped geometry of XeF2
The molecular geometry of XeF2 is linear, meaning that the fluorine atoms are attached to the xenon atom in a straight line. This linear shape is a result of the arrangement of electron pairs around the central xenon atom. XeF2 has two lone pairs of electrons on the xenon atom, and the fluorine atoms are positioned on opposite sides of the central atom.
Symmetrical attachment of fluorine atoms on both sides of the xenon atom
In XeF2, the two fluorine atoms are symmetrically attached to the xenon atom. This symmetrical arrangement occurs because the xenon atom is larger than the fluorine atoms, and the lone pairs of electrons on the xenon atom repel the fluorine atoms equally. As a result, the fluorine atoms are positioned on opposite sides of the xenon atom, creating a linear molecule.
Electronegativity of xenon and fluorine
To determine the polarity of XeF2, we need to examine the polarity of the individual Xe-F bonds. The polarity of a bond is influenced by the difference in electronegativity between the atoms involved. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond.
In the case of XeF2, xenon has a lower electronegativity than fluorine. Fluorine is one of the most electronegative elements on the periodic table, while xenon is relatively less electronegative. The difference in electronegativity between xenon and fluorine results in a polar bond, with fluorine being slightly negative and xenon being slightly positive.
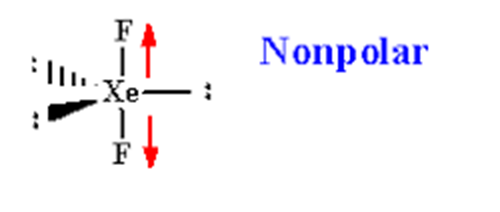
However, since XeF2 has a linear molecular geometry and the fluorine atoms are positioned symmetrically, the polarities of the individual Xe-F bonds cancel each other out. The bond dipoles of Xe-F bonds are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, resulting in a nonpolar molecule overall.
To summarize, XeF2 is a nonpolar molecule due to its linear molecular geometry and the cancellation of polarity in the Xe-F bonds caused by the symmetrical attachment of fluorine atoms on both sides of the xenon atom.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- XeF2 Lewis structure: drawing, hybridisation, geometry Dec 6, 2023
The XeF2 Lewis structure consists of a central xenon atom (Xe) and two external fluorine atoms (F). There are two single bonds between the xenon atom (Xe) and each fluorine atom (F).
XENON DIFLUORIDE
13709-36-9You may like
XENON DIFLUORIDE manufacturers
- XENON DIFLUORIDE
-

- $7.00 / 1KG
- 2020-01-14
- CAS:13709-36-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg