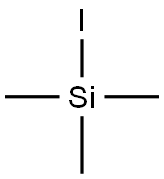Iodotrimethylsilane: properties and applications in organic synthesis
Sep 8,2023
General Description
Iodotrimethylsilane (ITMS) is a versatile organosilicon compound used in organic synthesis. It serves as a source of iodine, allowing for the introduction of iodine atoms into organic molecules. ITMS acts as a strong electrophile and is stable due to its silicon atom. It is used as a coupling partner in cross-coupling reactions, enabling the formation of carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds. ITMS plays a crucial role in the reductive cleavage of heteroaryl C-halogen bonds, allowing for the synthesis of complex organic molecules. It is also used in the dealkylation of ethers and esters to form alcohols or carboxylic acids. In nucleosidation, ITMS introduces iodine atoms into nucleosides, creating modified nucleosides for biomedical research and drug development.

Figure 1. Iodotrimethylsilane
Properties
Iodotrimethylsilane is a versatile organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiI. It is a colorless or pale yellow liquid with a pungent odor. This compound is widely used in organic synthesis due to its unique properties. It serves as an important source of iodine, allowing for the introduction of iodine atoms into organic molecules. Additionally, it acts as a strong electrophile, making it valuable in various reactions. The presence of three methyl groups and a silicon atom in iodotrimethylsilane provides stability and enhances its reactivity. The silicon atom stabilizes the molecule, making it easier to handle and store compared to other iodine sources. Furthermore, the silicon atom contributes to the compound's reactivity by influencing the electron distribution within the molecule. In organic synthesis, iodotrimethylsilane is utilized as a coupling partner in cross-coupling reactions, enabling the formation of carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds. This property makes it essential in the synthesis of complex organic molecules. 1
Applications in organic synthesis
Reductive cleavage of heteroaryl c-halogen bonds
Iodotrimethylsilane plays a crucial role in the reductive cleavage of heteroaryl C-halogen bonds, a significant reaction in organic synthesis. Heteroaryl C-halogen bonds refer to the connection between a halogen atom (such as chlorine, bromine, or iodine) and a heteroaryl group, which contains one or more heteroatoms, such as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur, within an aromatic ring. ITMS acts as a powerful reducing agent in this reaction, facilitating the cleavage of the C-halogen bond and providing various synthetic advantages. When ITMS is used in the presence of a suitable catalyst or base, it can selectively reduce the C-halogen bond in heteroaryl compounds while leaving other functional groups intact. This method allows for the synthesis of valuable building blocks for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. The reductive cleavage of heteroaryl C-halogen bonds using ITMS enables the preparation of heteroaryl organometallics, which can serve as versatile intermediates for further synthetic transformations. These organometallics can be employed in cross-coupling reactions, carbon-carbon bond formation, and other processes, leading to the creation of complex molecules with diverse structures and properties. 2
Dealkylation of ethers and esters
Iodotrimethylsilane is a vital component in the dealkylation process of ethers and esters. Ethers and esters commonly contain alkyl or aryl groups bonded to oxygen, and dealkylation involves eliminating these alkyl or aryl groups to form corresponding alcohols or carboxylic acids. ITMS serves as a potent reagent in this reaction, effectively breaking the carbon-oxygen bond and offering numerous synthetic benefits. When combined with an appropriate catalyst or base, ITMS can efficiently remove alkyl or aryl groups from ethers and esters while preserving other functional groups. This technique facilitates the synthesis of valuable intermediates in organic chemistry. Utilizing ITMS for the dealkylation of ethers and esters allows for the creation of alcohols or carboxylic acids, which are crucial building blocks for pharmaceuticals, natural products, and various organic compounds. Additionally, this reaction can be employed for modifying complex molecules by removing protective groups or preparing key fragments. 3
Nucleosidation
Iodotrimethylsilane acts as an iodinating agent to introduce iodine atoms into the nucleoside molecule. One important application of ITMS in nucleosidation is the synthesis of modified nucleosides for biomedical research and drug development. By selectively replacing hydrogen atoms with iodine atoms, ITMS enables the creation of novel nucleosides with enhanced properties or altered biological activities. These modified nucleosides can serve as valuable tools for studying nucleic acid structure and function, as well as potential candidates for therapeutic interventions. The reaction involving ITMS typically proceeds under mild conditions and shows high chemoselectivity, meaning that it selectively adds iodine to specific positions in the nucleoside molecule without affecting other functional groups. This selectivity allows for precise manipulation of the nucleoside structure while minimizing unwanted side reactions. Furthermore, ITMS is known for its efficiency and compatibility with various nucleoside substrates. It exhibits good reactivity even with hindered nucleosides and can be easily handled in the laboratory. 4
Reference
1. George AO, Subhash CN. Iodotrimethylsilane-a versatile synthetic reagent. Tetrahedron, 1982, 38, 15:2225-2277.
2. Sako M, Kihara T, Okada K, Ohtani Y, Kawamoto H. Reductive cleavage of heteroaryl c-halogen bonds by iodotrimethylsilane. Facile and regioselective dechlorination of antibiotic pyrrolnitrin. J Org Chem, 2001, 66(10):3610-3612.
3. Zhu Q, Tremblay MS. Allyl and benzyl iodides by the anomalous action of iodotrimethylsilane. Bioorg Med Chem Lett, 2006, 16(24):6170-6172.
4. Tocik Z, Earl RA, Beránek J. The use of iodotrimethylsilane in nucleosidation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res, 1980, 8(20):4755-4761.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Iodotrimethylsilane: Applications as Reactive Ligand and its Preparation Method Dec 2, 2024
Iodotrimethylsilane is a colorless to pale red flammable liquid with a boiling point of approximately 106°C and a density of 1.406 g/cm3. Its primary usage lies as a significant synthetic reagent and silylating agent
- Iodotrimethylsilane:an important silanization reagent Dec 22, 2023
Iodotrimethylsilane is an important silanization reagent with a wide range of applications in the chemical and pharmaceutical fields.
- Iodotrimethylsilane : A Mild and Efficient Reagent for the Reduction of Azides to Amines Nov 20, 2019
In the last two decades an explosive growth has been witnessed in the use of organo-silicon reagents in organic synthesis. Iodotrimethylsilane with remarkable reactivity as a hard-soft reagent has been known for a wide spectrum of synthetic
Cesium carbonate is a basic carbonate used in organic synthesis as a mild inorganic base.....
Sep 8,2023Inorganic chemistryIodotrimethylsilane
16029-98-4You may like
Iodotrimethylsilane manufacturers
- Iodotrimethylsilane
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2024-12-06
- CAS:16029-98-4
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5tons
- Trimethylsilyl Iodide
-
- $1450.00 / 1Kg
- 2024-11-18
- CAS:16029-98-4
- Min. Order: 0.100Kg
- Purity: 98
- Supply Ability: 500 Kg
- Iodotrimethylsilane
-

- $100.00 / 1KG
- 2024-10-11
- CAS:16029-98-4
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000kg