Indole:Chemical Properties and Production
Apr 22,2022
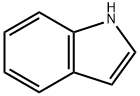
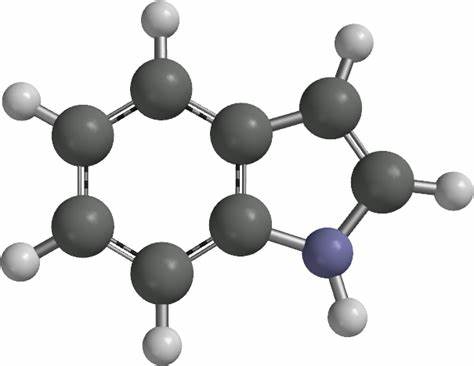
Indole [120-72-9], 1-benzo[b]pyrrole, C8H7N, was discovered by A. v. BAEYER and C. A. KNOP in 1866 as the basic structure of the natural dye, indigo, from which it was obtained. In 1910, R. WEISSGERBER found indole in coal tar.
Physical Properties
Indole, Mr 117.15, mp 52.5 ℃, bp 254.7 ℃ (101.3 kPa), d 1.22 g/cm3 (18 ℃), forms colorless, shiny flakes with a slight jasmine aroma. It is readily soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, and benzene, soluble in hot water, slightly soluble in cold water, and volatile in steam. The heat of combustion is 3.650 kJ/kg (25 ℃), the enthalpy of vaporization 597.5 kJ/ kg (10.3 – 27.4 ℃), and the dipole moment 2.11 D (benzene).
Chemical Properties
As a secondary amine, indole has a hydrogen atom which can be substituted by alkali metals. Oxidation leads to indigo, mild hydrogenation to 2,3-dihydroindole (indoline). Diindole, triindole, and resinification products are obtained upon treatment with acids.
Production
High-temperature coal tar contains on average just under 0.2 % indole. In coal tar distillation, the indole is concentrated in a biphenyl – indole fraction which boils between 245 and 255 ℃. Following extraction of phenols and bases, the indole is isolated from this fraction and separated from the other major component biphenyl, whose boiling point is only 0.3 ℃ higher. This is achieved by melting with potassium hydroxide to give the potassium salt of indole, by azeotropic distillation with diethylene glycol, or by extraction with selective solvents (e.g., glycols, aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide, or monoethanolamine). The crude indole can then be purified by crystallization from aliphatic hydrocarbon solvents.
In addition to its recovery from coal tar, indole is also synthesized in technical quantities. Methods used include Madelung synthesis of formyltoluidine (from o-toluidine and formic acid), followed by cyclization, dehydrogenating cyclization of 2-ethylaniline, cyclocondensation of aniline and ethylene glycol in the liquid or gas phase, and cyclization of 2- (2-nitrophenyl)ethanol.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Indole Synthesis: Methods and Mechanisms Aug 2, 2024
Indole is a benzo[b]pyrrole, a heterocyclic compound formed by the fusion of a benzene ring to the 2,3 positions of a pyrrole nucleus.
- Biologically active and Synthesis of indole Jan 21, 2022
The name indole is derived from the Indian word indigo, the blue dye that was first exported to Europe from India in the 16th century. It is constituted by fusion of the benzene ring with 2,3-positions of pyrrole and has properties of bot
- What is Indole? Feb 13, 2020
Indole, also called benzopyrrole, an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound occurring in some flower oils, such as jasmine and orange blossom, in coal tar, and in fecal matter, is a colorless solid having a pleasant fragrance.