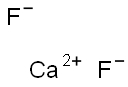Calcium fluoride: formation, toxicology and applications
Jul 20,2023
General Description
Calcium fluoride is formed through the interaction of calcium-rich solutions with fluoride-containing compounds in the Earth's crust. It occurs predominantly as fluorite and can be found in mineral deposits worldwide. Calcium fluoride has various applications, including optics and lens manufacturing, dental care, industrial processes, and construction materials. However, high consumption of calcium fluoride through drinking water can have toxic effects on the body, particularly in calcium-deficient individuals. Implementing public health measures to control fluoride levels and improve calcium nutrition is crucial in preventing the toxic effects of fluoride.
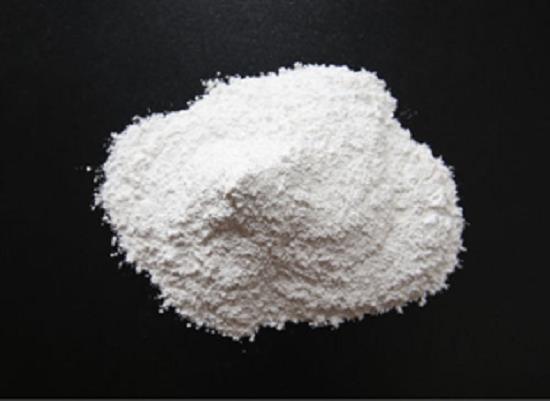

Figure 1. Calcium fluoride
Formation
The formation of calcium fluoride involves the interaction of calcium-rich solutions with fluoride-containing compounds in the Earth's crust. This chemical reaction takes place over extended periods, resulting in the creation of calcium fluoride crystals. Calcium fluoride is commonly found in mineral deposits, predominantly in the form of fluorite. Fluorite deposits can occur in various geological environments, including hydrothermal veins, limestone caves, and pegmatites. These deposits are often associated with igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, or hydrothermal activity. In its natural form, calcium fluoride forms crystals with a cubic or octahedral morphology. These crystals exhibit excellent symmetry due to the arrangement of calcium and fluoride ions within the crystal lattice structure. The presence of impurities during crystal growth accounts for the different colors often seen in fluorite specimens. Fluorite deposits can be found in numerous locations worldwide. Significant deposits have been discovered in countries like China, Mexico, Russia, South Africa, and the United States. The exact distribution and abundance of calcium fluoride deposits depend on regional geological characteristics and historical geological processes. 1
Toxicology
Calcium fluoride, when consumed in high amounts through drinking water, can have severe and complex toxic effects on the body. Children with inadequate calcium nutrition and similar fluoride intake are more likely to experience metabolic bone diseases and bony leg deformities compared to those with sufficient calcium intake. The syndrome associated with skeletal fluorosis and related metabolic bone diseases and deformities is classified as a variant of the osteosclerotic form of skeletal fluorosis. The presence of excess fluoride, coupled with low calcium levels, elevated parathyroid hormone (PTH), and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, contributes to the development of these conditions by affecting bone structure and metabolism. Children, especially during periods of active growth, are more susceptible to the rapid and significant impact of fluoride accumulation in their metabolically active and vascular bones. Even slightly higher exposures to fluoride (2.5 mg/d) can result in toxic effects, particularly in calcium-deficient children, further exacerbating the metabolic repercussions of calcium deficiency on bone health. For cases of calcium-deficient rickets in children, it is recommended to investigate potential interactions with fluoride. Implementing public health measures such as maintaining drinking water fluoride levels below 0.5 ppm and improving calcium nutrition are cost-effective and practical strategies for preventing and controlling endemic fluorosis, providing comprehensive protection against the toxic effects of fluoride. 2
Applications
Calcium fluoride finds a variety of applications due to its unique properties. One of the key uses of calcium fluoride is in optics and lens manufacturing. It has excellent optical clarity and low dispersion, making it ideal for producing lenses, prisms, and windows used in cameras, telescopes, microscopes, and other optical instruments. Another application of calcium fluoride is as a component in dental products. It is commonly added to toothpaste, mouthwashes, and dental treatments to strengthen tooth enamel and prevent tooth decay. Calcium fluoride remineralizes and protects teeth by forming a protective layer that resists acid attacks from bacteria and food. In the industrial sector, calcium fluoride serves as a raw material for the production of hydrogen fluoride and other fluorine compounds. Hydrogen fluoride is crucial in various industrial processes, including the production of refrigerants, plastics, detergents, and pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, calcium fluoride is employed in the manufacturing of cement, ceramics, and glass. Its high melting point and chemical resistance make it suitable for use in these applications, providing strength, durability, and heat resistance to the final products. 3, 4
Reference
1. Fuge R. Sources of halogens in the
environment, influences on human and animal health. Environ Geochem
Health, 1988, 10(2):51-61.
2. Teotia M, Teotia SP, Singh KP. Endemic chronic fluoride toxicity and dietary calcium deficiency interaction syndromes of metabolic bone disease and deformities in India: year 2000. Indian J Pediatr, 1998, 65(3):371-381.
3. Schiffner U. Verwendung von Fluoriden zur Kariespr?vention [Use of fluorides for caries prevention]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz, 2021, 64(7):830-837.
4. David LL, Shearer TR. Calcium-activated proteolysis in the lens nucleus during selenite cataractogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 1984, 25(11):1275-1283.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What is the Lewis structure of Calcium fluoride? Aug 15, 2024
The Lewis structure of Calcium fluoride (CaF2) consists of a central atom, calcium atom (Ca), and 2 non-metallic fluorine atoms (F).
- Luminescent Calcium Fluoride Nanoparticles as Theranostic Platforms Jan 10, 2024
Calcium fluoride is an advantageous optical matrix with transparency, low aberration, and fluorescence. Synthesized luminescent nanoparticles offer theranostic potential for nanomedicine.
- Physical Properties and Uses of Fluorite Dec 3, 2019
Fluorite is an important industrial mineral composed of calcium and fluorine (CaF2). It is used in a wide variety of chemical, metallurgical, and ceramic processes.
Calcium fluoride
7789-75-5You may like
Calcium fluoride manufacturers
- Calcium Fluoride
-

- $99.00/ kg
- 2025-01-08
- CAS:7789-75-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20ton
- Calcium Fluoride
-

- $0.00 / 1BAG
- 2024-11-19
- CAS:7789-75-5
- Min. Order: 1BAG
- Purity: ≥99%
- Supply Ability: 1000 Tons
- Calcium Fluoride
-

- $0.00 / 1BAG
- 2024-11-19
- CAS:7789-75-5
- Min. Order: 1BAG
- Purity: ≥99%
- Supply Ability: 1000 Tons