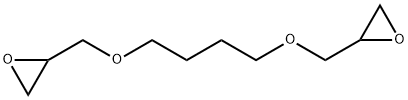
1,4-Butanediol Diglycidyl Ether–Crosslinked Dermal Fillers
Mar 11,2025
Degradation of 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER
1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether is the crosslinking agent used to stabilize the majority of the HA-based dermal fillers currently available on the market. Its ability to crosslink is attributed to the reactivity of the epoxide groups present at the two ends of the molecule. Under basic (pH > 7) conditions, these epoxide groups preferentially react with the most accessible primary alcohol in the HA backbone, forming an ether bond connection. The superior stability of the ether bond (relative to the ester or amide bond) is one of the reasons that 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER-crosslinked HA fillers have a clinical duration that can reach or exceed 1 year. In addition, 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER has a significantly lower toxicity than other ether-bond crosslinking chemistry based agents (e.g., divinyl sulfone), is biodegradable, and has been well studied. All these factors have contributed to 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER becoming the industry-standard crosslinker.[1]

Although unreacted 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER has been found to be mutagenic in the Drosophila model organism, a definitive carcinogenic effect has not been observed in mice. Despite this, and because of its mutagenic potential (thought to be the result of the reactive nature of the epoxide groups), the amount of unreacted 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER in dermal fillers is maintained at trace amounts. For Allergan’s range of HA dermal fillers, this is achieved through a complex purification process, which results in a residual level of unreacted 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER of <2 parts per million (ppm). This would equate to <0.002 mg of 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER in 1 mL of HA gel. This trace level, which historically was the limit of detection, has been determined to be safe after a Food and Drug Administration (FDA) safety risk assessment. Over time, unreacted 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER undergoes degradation through hydrolysis. The most favorable cleavage sites are the ether bonds in the epoxide groups and in the backbone of the molecule. Degradation of 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER can produce a number of nonreactive by-products
Hydrolyzed 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER
Hydrolyzed 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER is a diol-ether resulting from the hydrolysis of the epoxide groups in 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER or the hydrolytic cleavage of crosslinked 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER. Hydrolyzed 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER has been shown to be nontoxic and nongenotoxic, even at molar concentrations significantly higher than the concentrations used in commercial fillers (J.X. Roca-Martinez, unpublished data). (These concentrations are defined later in this section.) Although the metabolism of hydrolyzed 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER is not described in the literature, it is understood to proceed through ether bond cleavage by a family of enzymes called cytochromes P450. These enzymes are involved in the oxidative degradation of organic molecules and can catalyze the cleavage of ether bonds into alcohols. After degradation, two main products can emerge: glycerol and butanediol. Similar to all diol-ethers, hydrolyzed 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER is also known to be eliminated in urine.[2]
Biocompatibility of 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER-Crosslinked HA fillers
In addition to clinical safety data spanning longer than 15 years, a substantial body of biocompatibility data exists for 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER-crosslinked HA fillers. As early as the 1980s, reports on acute and chronic biocompatibility of crosslinked HA were published after testing in the vitreous cavity of the eye and viscosupplementation of the osteoarthritic synovial fluid. Furthermore, animal studies have successfully provided information on topics such as length of tissue reaction (acute, subchronic, or chronic), type of reaction (systemic vs local tissue toxicity), hypersensitivity, and genotoxicity. For the majority of the commercially available fillers, much of these data were generated in compliance with regulatory agencies to gain market approval. Based on these results, no evidence of acute, subchronic, or chronic inflammation; sensitivity; irritation; intracutaneous reactivity; systemic toxicity; hypersensitivity; or genotoxicity were observed for these products.[3]
1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER is the crosslinker used in the majority of the market-leading HA fillers. After reaction with HA, the epoxide groups of 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER are neutralized, and only trace amounts of unreacted 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER remain in the product (<2 ppm). These trace amounts, which the FDA has determined to be below the level that is safe after a safety risk assessment, are prone to hydrolysis that ultimately yields CO2 and water. Crosslinked HA is expected to follow a degradation pathway that is similar to that of uncrosslinked HA and unreacted 1,4-BUTANEDIOL DIGLYCIDYL ETHER, because the crosslinking reaction does not affect the backbone chemistry of these molecules.
References
[1] Smith L, Cockerham K. Hyaluronic acid dermal fillers: can adjunctive lidocaine improve patient satisfaction without decreasing efficacy or duration? Patient Prefer Adherence. 2011;5:133–9. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S11251.
[2] Kontis TC, Rivkin A. The history of injectable facial fillers. Facial Plast Surg. 2009;25:67–72. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1220645.
[3] Stern R. Hyaluronan catabolism: a new metabolic pathway. Eur J Cell Biol. 2004;83:317–25. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00392
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Hydrocortisone acetate, a synthetic derivative of the natural steroid hormone hydrocortisone, is widely used in the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries.....
Apr 10,2025Chemical ReagentsTris(2-Carboxyethyl)Phosphine Hydrochloride is a strong reducing agent,it is synthesized by the acid hydrolysis of tris(2-cyanoethyl)phosphine in refluxing aqueous HCl.....
Mar 11,2025Organic reagents1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether
2425-79-8You may like
1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether manufacturers
- 1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether
-

- 2025-07-06
- CAS:2425-79-8
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- 1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether
-

- $0.00 / 1G/KG
- 2025-07-04
- CAS:2425-79-8
- Min. Order: 1G/KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100MT
- 1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2025-06-27
- CAS:2425-79-8
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg