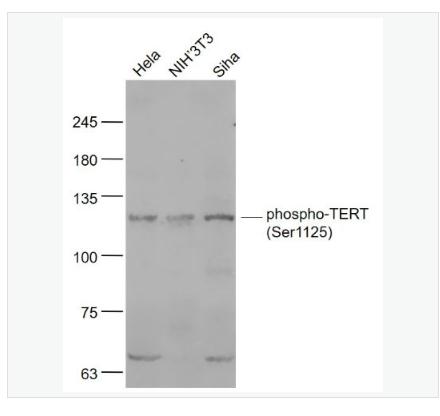
Host:Rabbit
Target Protein:phospho-TERT (Ser1125)
IR:Immunogen Range:LP(p-S)DF
Clonality:Polyclonal
Isotype:IgG
Entrez Gene:7015
Swiss Prot:O14746
Source:KLH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human TERT around the phosphorylation site of Ser1125:LP(p-S)DF
Purification:affinity purified by Protein A
Storage:0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Background:Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme essential for the replication of chromosome termini in most eukaryotes. It elongates telomeres. It is a reverse transcriptase that adds simple sequence repeats to chromosome ends by copying a template sequence within the RNA component of the enzyme. Telomerase are large DNA-protein complexes with telomerase expression being the subject of recent research due to its link to cell immortalization. Recent evidence has shown that MYC upregulates the catalytic subunit of telomerase, TERT, and that TERT cooperates with HPV E7 in cell immortalization. Ever since the discovery that telomeres are short in cancer cells and telomerase is activated in immortal cells, telomerase has been associated with oncogenes. During the past year, major advances have been made in understanding the link between telomerase expression and cell immortality. Studies of yeast telomeres have revealed an unexpected role for the non-homologous end-joining machinery in telomere maintenance and have provided the first definitive evidence that telomeres play a critical role in meiosis. Identification of new telomere proteins has led to a better understanding of vertebrate telomere structure and function.
Size:50ul
Concentration:1mg/ml
Applications:WB(1:500-2000)
ELISA(1:5000-10000)
Flow-Cyt(0.2μg/Test)
ICC(1:100)
Cross Reactive Species:Human
Mouse
Rat
.