Identification of a targetable JAK-STAT enriched androgen receptor and androgen receptor splice variant positive triple-negative breast cancer subtype
Asemota, Sarah
;
Effah, Wendy
;
Young, Kirsten L.
, et al.
Cell Rep.,2023,42(12):113461.
DOI:
10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113461
PubMed ID:
37979170
More
Abstract: Triple-neg. breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive subtype with no targeted therapeutics. The luminal androgen receptor (LAR) subtype constitutes 15% of TNBC and is enriched for androgen receptor (AR) and AR target genes. Here, we show that a cohort of TNBC not only expresses AR at a much higher rate (~80%) but also expresses AR splice variants (AR-SVs) (~20%), further subclassifying LAR-TNBC. Higher AR and AR-SV expression and corresponding aggressive phenotypes are observed predominantly in specimens obtained from African American women. LAR TNBC specimens are enriched for interferon, Janus kinase (JAK)-signal activator and transducer (STAT), and androgen signaling pathways, which are exclusive to AR-expressing epithelial cancer cells. AR- and AR-SV-expressing TNBC cell proliferation and xenograft and patient-tumor explant growth are inhibited by AR N-terminal domain-binding selective AR degrader or by a JAK inhibitor. Biochem. anal. suggests that STAT1 is an AR coactivator. Collectively, our work identifies pharmacol. targetable TNBC subtypes and identifies growth-promoting interaction between AR and JAK-STAT signaling.
Purchased from AmBeed:
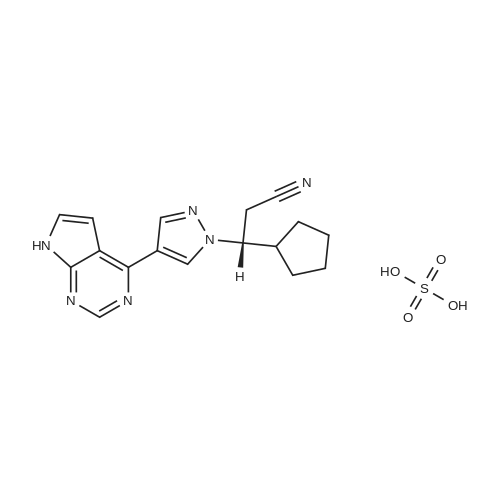
941678-49-5

JAK and mTOR inhibitors prevent cytokine release while retaining T cell bispecific antibody in vivo efficacy
Leclercq, Gabrielle
;
Haegel, Hélène
;
Toso, Alberto
, et al.
J. ImmunoTher. Cancer,2022,10,e003766.
DOI:
10.1136/jitc-2021-003766
PubMed ID:
35064010
More
Abstract: Background: T cell engaging therapies, like chimeric antigen receptor T cells and T cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs), efficiently redirect T cells towards tumor cells, facilitating the formation of a cytotoxic synapse and resulting in subsequent tumor cell killing, a process that is accompanied by the release of cytokines. Despite their promising efficacy in the clinic, treatment with TCBs is associated with a risk of cytokine release syndrome (CRS). The aim of this study was to identify small molecules able to mitigate cytokine release while retaining T cell-mediated tumor killing.
Methods: By screening a library of 52 Food and Drug Administration approved kinase inhibitors for their impact on T cell proliferation and cytokine release after CD3 stimulation, we identified mTOR, JAK and Src kinases inhibitors as potential candidates to modulate TCB-mediated cytokine release at pharmacologically active doses. Using an in vitro model of target cell killing by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells, we assessed the effects of mTOR, JAK and Src kinase inhibitors combined with 2+1 T cell bispecific antibodies (TCBs) including CEA-TCB and CD19-TCB on T cell activation, proliferation and target cell killing measured by flow cytometry and cytokine release measured by Luminex. The combination of mTOR, JAK and Src kinase inhibitors together with CD19-TCB was evaluated in vivo in non-tumor bearing stem cell humanized NSG mice in terms of B cell depletion and in a lymphoma patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model in humanized NSG mice in terms of antitumor efficacy.
Results: The effect of Src inhibitors differed from those of mTOR and JAK inhibitors with the suppression of CD19-TCB-induced tumor cell lysis in vitro, whereas mTOR and JAK inhibitors primarily affected TCB-mediated cytokine release. Importantly, we confirmed in vivo that Src, JAK and mTOR inhibitors strongly reduced CD19-TCB-induced cytokine release. In humanized NSG mice, continuous treatment with a Src inhibitor prevented CD19-TCB-mediated B cell depletion in contrast to mTOR and JAK inhibitors, which retained CD19-TCB efficacy. Ultimately, transient treatment with Src, mTOR and JAK inhibitors minimally interfered with antitumor efficacy in a lymphoma PDX model.
Conclusions: Taken together, these data support further evaluation of the use of Src, JAK and mTOR inhibitors as prophylactic treatment to prevent occurrence of CRS.
Purchased from AmBeed:
159351-69-6 ;
941678-49-5 ;
302962-49-8 ;
162635-04-3 ;
53123-88-9

Liver-expressed Cd302 and Cr1l limit hepatitis C virus cross-species transmission to mice
Brown, Richard J. P.
;
Tegtmeyer, Birthe
;
Sheldon, Julie
, et al.
Sci. Adv.,2020,6(45):eabd3233.
DOI:
10.1126/sciadv.abd3233
PubMed ID:
33148654
More
Abstract: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) has no animal reservoir, infecting only humans. To investigate species barrier determinants limiting infection of rodents, murine liver complementary DNA library screening was performed, identifying transmembrane proteins Cd302 and Cr1l as potent restrictors of HCV propagation. Combined ectopic expression in human hepatoma cells impeded HCV uptake and cooperatively mediated transcriptional dysregulation of a noncanonical program of immunity genes. Murine hepatocyte expression of both factors was constitutive and not interferon inducible, while differences in liver expression and the ability to restrict HCV were observed between the murine orthologs and their human counterparts. Genetic ablation of endogenous Cd302 expression in human HCV entry factor transgenic mice increased hepatocyte permissiveness for an adapted HCV strain and dysregulated expression of metabolic process and host defense genes. These findings highlight human-mouse differences in liver-intrinsic antiviral immunity and facilitate the development of next-generation murine models for preclin. testing of HCV vaccine candidates.
Purchased from AmBeed:
941678-49-5


 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping