Alternatived Products of [ 92-81-9 ]
Product Details of [ 92-81-9 ]
| CAS No. : | 92-81-9 |
MDL No. : | MFCD00022256 |
| Formula : |
C13H11N
|
Boiling Point : |
No data available |
| Linear Structure Formula : | - |
InChI Key : | HJCUTNIGJHJGCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| M.W : |
181.23
|
Pubchem ID : | 7106 |
| Synonyms : |
|
Application In Synthesis of [ 92-81-9 ]
* All experimental methods are cited from the reference, please refer to the original source for details. We do not guarantee the accuracy of the content in the reference.
- Downstream synthetic route of [ 92-81-9 ]
- 1
-
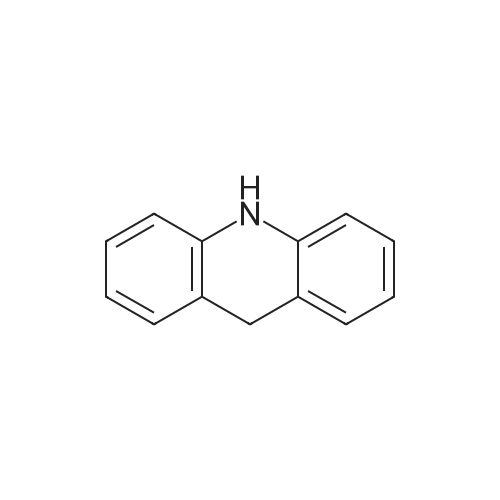 [ 92-81-9 ]
[ 92-81-9 ]

-
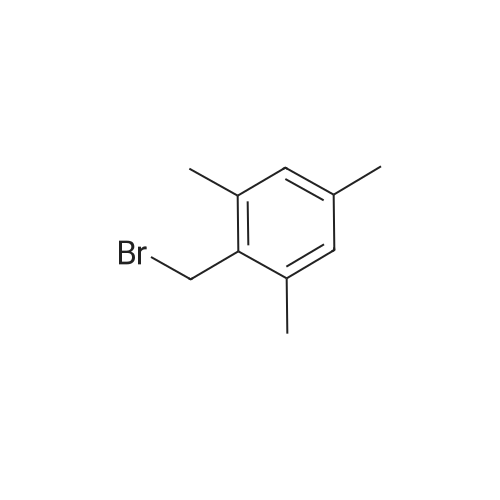 [ 4761-00-6 ]
[ 4761-00-6 ]

-
 [ 87742-37-8 ]
[ 87742-37-8 ]
- 2
-
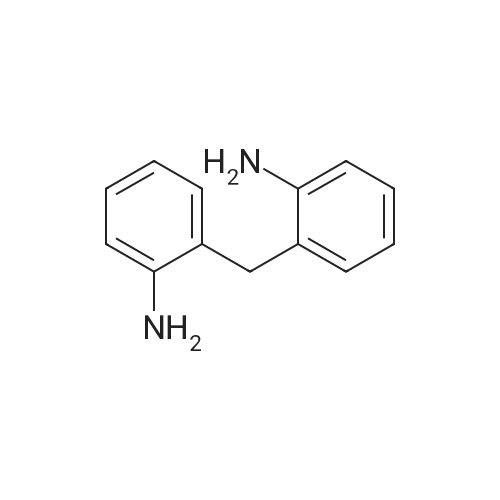 [ 6582-52-1 ]
[ 6582-52-1 ]

-
 [ 260-94-6 ]
[ 260-94-6 ]

-
 [ 92-81-9 ]
[ 92-81-9 ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
|
With hydrogenchloride; aniline; In water; at 160 - 180℃; |
In a series of experiments, the amount of aqueous 30% hydrochloric acid required in each case to achieve the desired protonation level (see table 3 below) was added to a 2,2?-MDA solution in aniline preheated to 100.0 C. The 2,2?-MDA concentration in each of the individual experiments was 1.0% by mass; in addition, the solutions contained octadecane as an internal standard for gas chromatography (GC) analysis. The resulting mixture was transferred as quickly as possible by means of a peristaltic pump to a Buechi glass autoclave preheated to 120.0 C. and heated to the reaction temperature envisaged (see table 3). On attainment of the desired reaction temperature, the first sample was taken (time=zero). In order to monitor the progress of the reaction, further samples were taken after 30, 60, 120 and 240 minutes and analyzed by means of GC analysis. Reaction conditions and experimental results are collated in table 3 below. It is found that, with rising temperature and rising hydrochloric acid concentration, the formation of the acridine and acridane secondary components from 2,2?-MDA occurs to an increased degree. |
|
With hydrogenchloride; In water; at 100 - 170℃; for 4h;Autoclave; |
General procedure: In a series of experiments, the amount of aqueous 30% hydrochloric acid required in each case to achieve the desired protonation level (see table 3 below) was added to a 2,2?-MDA solution in aniline preheated to 100.0 C. The 2,2?-MDA concentration in each of the individual experiments was 1.0% by mass; in addition, the solutions contained octadecane as an internal standard for gas chromatography (GC) analysis. The resulting mixture was transferred as quickly as possible by means of a peristaltic pump to a Blichi glass autoclave preheated to 120.0 C. and heated to the reaction temperature envisaged (see table 3). On attainment of the desired reaction temperature, the first sample was taken (time=zero). In order to monitor the progress of the reaction, further samples were taken after 30, 60, 120 and 240 minutes and analyzed by means of GC analysis. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science















 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping








