Alternatived Products of [ 72040-63-2 ]
Product Details of [ 72040-63-2 ]
| CAS No. : | 72040-63-2 |
MDL No. : | MFCD00065502 |
| Formula : |
C20H30N4O6S
|
Boiling Point : |
No data available |
| Linear Structure Formula : | - |
InChI Key : | UVGHPGOONBRLCX-NJSLBKSFSA-N |
| M.W : |
454.54
|
Pubchem ID : | 83874 |
| Synonyms : |
|
Chemical Name : | 2,5-Dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl 6-(5-((3aS,4S,6aR)-2-oxohexahydro-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)pentanamido)hexanoate |
Application In Synthesis of [ 72040-63-2 ]
* All experimental methods are cited from the reference, please refer to the original source for details. We do not guarantee the accuracy of the content in the reference.
- Downstream synthetic route of [ 72040-63-2 ]
- 1
-
N-(4-azido-2-nitrobenzoyl)-1,7-diaminoheptane
[ No CAS ]

-
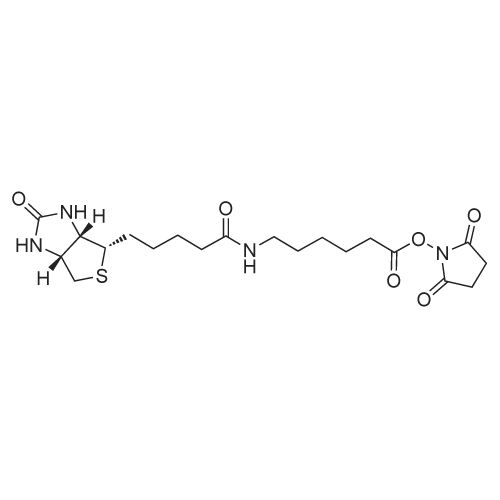 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
4-Azido-2-nitro-N-(7-{6-[5-(2-oxo-hexahydro-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-6-yl)-pentanoylamino]-hexanoylamino}-heptyl)-benzamide
[ No CAS ]
- 2
-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
5-(3-aminopropen-1-yl)-5'-O-(β,γ-diphosphoryl-α-phosphonomethyl)-2'-deoxyuridine
[ No CAS ]

-
5-[3-(N-biotinyl-6-aminohexanoylamino)propen-1-yl]-5'-O-(β,γ-diphosphoryl-α-phosphonomethyl)-2'-deoxyuridine
[ No CAS ]
- 3
-
 [ 34284-75-8 ]
[ 34284-75-8 ]

-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
4-(2-{6-[5-(2-oxo-hexahydro-thieno[3,4-<i>d</i>]imidazol-6-yl)-pentanoylamino]-hexanoylamino}-ethyl)-benzenesulfonyl fluoride
[ No CAS ]
- 4
-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
 [ 9050-30-0 ]
[ 9050-30-0 ]

-
biotinylated heparan sulfate
[ No CAS ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
|
With sodium hydrogencarbonate; In water; dimethyl sulfoxide; at 20.0℃; for 1h;pH 8.5; |
Heparan sulfate (HS) was biotinylated using biotin with extended spacer arms usingsuccinimidyl-6- (biotinamido) hexanoate(NHS-LC-Biotin) obtained from Pierce. About 0.5 ml HS solution (2 mg/ml in NaHC03, pH 8.5) was mixed with 0.05 ml of a freshly prepared solution of NHS-LC-Biotin in dimethyl sulfoxide. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 1 hour. Unconjugated biotin was removed by centrifugation (10,000 RPM) through Microcon-3 filter (Millipore) followed by dilution with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). This procedure was repeated five times to ensure complete removal of free biotin. Unwanted aldehydes in the reaction were then quenched by incubation with one milliliter of Tris-glycine <Desc/Clms Page number 357>buffer (25mM-183 mM, pH 8. 3) at room temperature for 20 minutes. The mixture was subjected to three rounds of microfiltration as described above. Biotinylated HS (5 mg/ml in PBS) was aliquoted and storedat-20 C. To obtain maximum biotinylation, a25-fold molar excess of biotin was used. Using HABA reagent, it was determined that the ratio of HS to biotin was 1: 2. The extent of biotinylation of HS was determined using Avidin-HABA (Pierce Chemical Co). The HABA assay can be used over a wide range of pH and salt concentrations. HABA (4-hydroxyazobenzene-2'-carboxylic acid) is a dye that binds to avidin and can serve as an indicator of unoccupied binding sites. Avidin combines stoichiometrically with biotin, making it possible to use any physiochemical differences between avidin and the avidin-biotin complex as the basis of a qualitative and quantitative assay method for either component. When HABA binds to avidin, there is a large spectral change in the HABA dye. A new absorption band appears at 500 nm, which is characteristic of the quinoid form of the dye. The avidin-biotin complex does not bind HABA and because the dissociation constant of the complex is so low, the dye is stoichiometrically displaced by biotin. Consequently, the HABA assay can be the basis of both colorimetric and titrimetric assays. The amount of avidin can be calculated directly from the increased absorbance at 500 nm, or the dye may be used as an indicator in a spectrophotometric titration with biotin. The absorption band that results from the avidin-HABA complex decreases proportionately when biotin is added. Since biotin has such a high affinity for avidin, it displaces the HABA dye. The unknown amount of biotin can be determined by preparing a standard curve using known amounts of biotin to displace the HABA which bound to avidin, and plotting against the absorbance at 500 mu. HABA solution was prepared by adding 24.2 mg of HABA (Pierce) to 9.9 ml H20, and then adding0. 1 ml1 M NaOH. Avidin-HABA reagent was prepared by adding 10 mg of avidin and 600 gl of HABA solution to 19.4 ml of phosphate buffered saline. To1 ml of Avidin-HABA reagent in a cuvette,100ul of biotinylated HS was added, and the optical density was measured at 500 nm in a spectrophotometer. A standard curve was determined using known amounts of HABA. The decrease in optical density of the HABA following the addition of biotinylated HS was determined. |
- 5
-
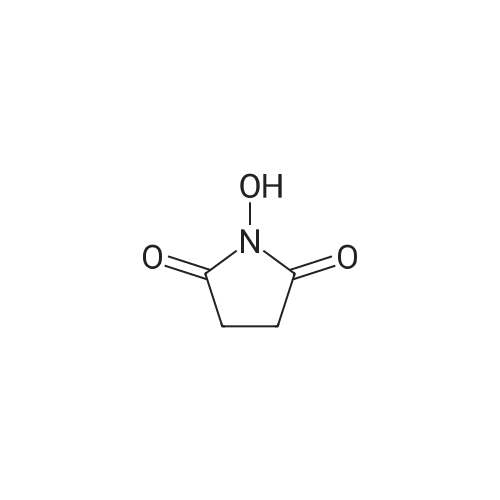 [ 6066-82-6 ]
[ 6066-82-6 ]

-
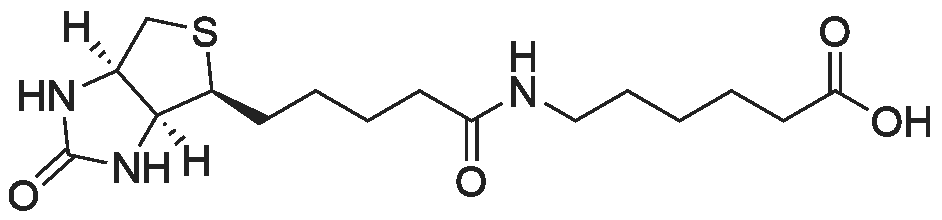 [ 72040-64-3 ]
[ 72040-64-3 ]

-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]
- 6
-
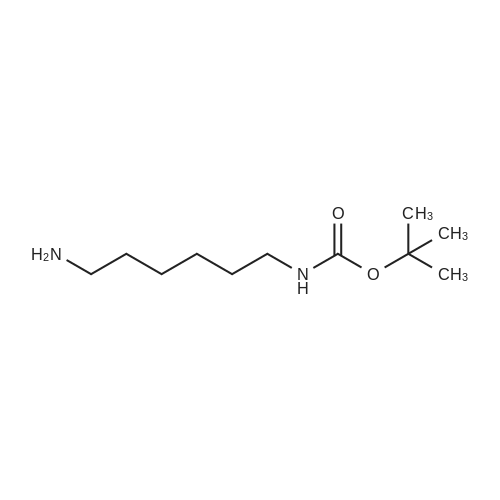 [ 51857-17-1 ]
[ 51857-17-1 ]

-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
(6-{6-[5-(2-oxo-hexahydro-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)-pentanoylamino]-hexanoylamino}-hexyl)-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[ No CAS ]
- 7
-
 [ 4443-68-9 ]
[ 4443-68-9 ]

-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]
- 8
-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
6-[5-(2-oxo-hexahydro-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)-pentanoylamino]-hexanoic acid (6-amino-hexyl)-amide trifluoroacetate
[ No CAS ]
- 9
-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
[(6-{6-[5-(2-oxo-hexahydro-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)-pentanoylamino]-hexanoylamino}-hexylcarbamoyl)-methyl]-carbamic acid tert-butyl ester
[ No CAS ]
- 10
-
 [ 72040-63-2 ]
[ 72040-63-2 ]

-
6-[5-(2-oxo-hexahydro-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl)-pentanoylamino]-hexanoic acid [6-(2-amino-acetylamino)-hexyl]-amide
[ No CAS ]

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science















 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping










